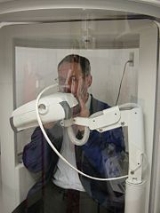
Body plethysmography
Encyclopedia
Body plethysmography or "Body Box" for short, is a very sensitive lung measurement used to detect lung pathology that might be missed with conventional pulmonary function tests. This method of obtaining the absolute volume
of air within one's lungs may also be used in situations where several repeated trials are required or where the patient is unable to perform the multibreath tests. The technique requires moderately complex coaching and instruction for the subject. In the USA, such tests are usually performed by Certified or Registered Pulmonary Function Technologists (CPFT or RPFT) who are credentialed by the National Board for Respiratory Care NBRC http://www.nbrc.org.
More specifically, the test is done by enclosing the subject in an airtight chamber often referred to as a body box; a pneumotachometer is used to measure airflow while a mouth pressure transducer with a shutter measures the alveolar pressure. The most common measurements made using body plethysmographs are thoracic gas volume (VTG) and airway resistance
(RAW). This test is used mainly in the Pulmonary Function Testing laboratories.
Using body plethysmography, doctors can examine the lungs' resistance to airflow, distinguish between restrictive and obstructive lung diseases, determine the response to bronchodilator
s, and determine bronchial hyperreactivity in response to methacholinehttp://www.thoracic.org/sections/publications/statements/pages/pfet/methacholine1-21.html, histamine
, or isocapnic hyperventilation.
Pressure plethysmographs are usually measured at the end-expiratory level and are then equal to FRC. The patient sits in the box, which has the pressure transducer in the wall of the device, and breathes through a mouthpiece connected to a device that contains an electronic shutter and a differential pressure pneumotachometer. The mouth pressure and box pressure changes that are measured during tidal breathing and panting maneuvers which are performed during the test by the patient at the end of expiration are sent to a microprocessor unit that calculates thoracic gas volume.
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
of air within one's lungs may also be used in situations where several repeated trials are required or where the patient is unable to perform the multibreath tests. The technique requires moderately complex coaching and instruction for the subject. In the USA, such tests are usually performed by Certified or Registered Pulmonary Function Technologists (CPFT or RPFT) who are credentialed by the National Board for Respiratory Care NBRC http://www.nbrc.org.
More specifically, the test is done by enclosing the subject in an airtight chamber often referred to as a body box; a pneumotachometer is used to measure airflow while a mouth pressure transducer with a shutter measures the alveolar pressure. The most common measurements made using body plethysmographs are thoracic gas volume (VTG) and airway resistance
Airway resistance
Airway resistance is a concept used in respiratory physiology to describe mechanical factors which limit the access of inspired air to the pulmonary alveoli, and thus determine airflow....
(RAW). This test is used mainly in the Pulmonary Function Testing laboratories.
Using body plethysmography, doctors can examine the lungs' resistance to airflow, distinguish between restrictive and obstructive lung diseases, determine the response to bronchodilator
Bronchodilator
A bronchodilator is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lungs. Bronchodilators may be endogenous , or they may be medications administered for the treatment of breathing difficulties...
s, and determine bronchial hyperreactivity in response to methacholinehttp://www.thoracic.org/sections/publications/statements/pages/pfet/methacholine1-21.html, histamine
Histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogen compound involved in local immune responses as well as regulating physiological function in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter. Histamine triggers the inflammatory response. As part of an immune response to foreign pathogens, histamine is produced by...
, or isocapnic hyperventilation.
Flow and Pressure Plethysmographs
There are two types of plethysmographs: flow and pressure. In flow plethysmography, airway resistance is measured by two maneuvers. The patient first pants while the mouth shutter is open to allow flow changes to be measured. Then, the mouth shutter closes at the patient's end expiratory or FRC level and the patient continues panting while maintaining an open glottis. This provides a measure of the driving pressure used to move air into the lungs.Pressure plethysmographs are usually measured at the end-expiratory level and are then equal to FRC. The patient sits in the box, which has the pressure transducer in the wall of the device, and breathes through a mouthpiece connected to a device that contains an electronic shutter and a differential pressure pneumotachometer. The mouth pressure and box pressure changes that are measured during tidal breathing and panting maneuvers which are performed during the test by the patient at the end of expiration are sent to a microprocessor unit that calculates thoracic gas volume.

