Bollard pull
Encyclopedia
Bollard pull is a value that allows the comparison of the pulling force of watercraft, particularly tugboat
s. A mooring bollard
may be used as a point of attachment for measuring the force
, or pull of the craft.
is not sufficient to understand how strong a tug is - this is because other factors, like transmission losses, propulsion type, propulsion system efficiency, have an influence as well.
Bollard pull values are stated in tons. They are an indication of the maximum pulling force that a ship can exert on another ship or an object.
s. It is limited in precision - a number of boundary conditions need to be observed to obtain reliable results. Summarizing the below requirements, practical bollard pull trials need to be conducted in a deep water seaport, ideally not at the mouth of a river, on a calm day with hardly any traffic.
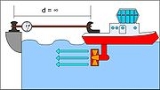
See Figure 2 for an illustration of error influences in a practical bollard pull trial. Note the difference in elevation of the ends of the line (the port bollard is higher than the ship's towing hook). Furthermore, there is the partial short circuit in propeller discharge current, the uneven trim of the ship and the short length of the tow line. All of these factors contribute to measurement error.
Both methods can be combined. Practical trials can be used to validate the result of numerical simulation.
Tugboat
A tugboat is a boat that maneuvers vessels by pushing or towing them. Tugs move vessels that either should not move themselves, such as ships in a crowded harbor or a narrow canal,or those that cannot move by themselves, such as barges, disabled ships, or oil platforms. Tugboats are powerful for...
s. A mooring bollard
Bollard
A bollard is a short vertical post. Originally it meant a post used on a ship or a quay, principally for mooring. The word now also describes a variety of structures to control or direct road traffic, such as posts arranged in a line to obstruct the passage of motor vehicles...
may be used as a point of attachment for measuring the force
Force
In physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, a change in direction, or a change in shape. In other words, a force is that which can cause an object with mass to change its velocity , i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform...
, or pull of the craft.
Background
Unlike in ground vehicles, the statement of installed horsepowerHorsepower
Horsepower is the name of several units of measurement of power. The most common definitions equal between 735.5 and 750 watts.Horsepower was originally defined to compare the output of steam engines with the power of draft horses in continuous operation. The unit was widely adopted to measure the...
is not sufficient to understand how strong a tug is - this is because other factors, like transmission losses, propulsion type, propulsion system efficiency, have an influence as well.
Bollard pull values are stated in tons. They are an indication of the maximum pulling force that a ship can exert on another ship or an object.
Practical trial
This method is useful for one-off ship designs and smaller shipyardShipyard
Shipyards and dockyards are places which repair and build ships. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Dockyards are sometimes more associated with maintenance and basing activities than shipyards, which are sometimes associated more with initial...
s. It is limited in precision - a number of boundary conditions need to be observed to obtain reliable results. Summarizing the below requirements, practical bollard pull trials need to be conducted in a deep water seaport, ideally not at the mouth of a river, on a calm day with hardly any traffic.
- The ship needs to be in undisturbed water. CurrentsOcean currentAn ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, cabbeling, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun...
or strong windWindWind is the flow of gases on a large scale. On Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of air. In outer space, solar wind is the movement of gases or charged particles from the sun through space, while planetary wind is the outgassing of light chemical elements from a planet's atmosphere into space...
s would falsify the measurement. - The static forceForceIn physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, a change in direction, or a change in shape. In other words, a force is that which can cause an object with mass to change its velocity , i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform...
that intends to move the ship forward must only be generated by the frictionFrictionFriction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and/or material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:...
between the propellerPropellerA propeller is a type of fan that transmits power by converting rotational motion into thrust. A pressure difference is produced between the forward and rear surfaces of the airfoil-shaped blade, and a fluid is accelerated behind the blade. Propeller dynamics can be modeled by both Bernoulli's...
discharge race and the surrounding water. If the ship were too close to a wall, the measurement would be falsified. - The ship must be in deep water. If there were any ground effect, the measurement would be falsified. The same holds true for propeller walkPropeller walkPropeller walk is the term for a propeller's tendency to rotate a boat as well as accelerating it forwards or backwards.A right-handed propeller will tend to push the stern of the boat to starboard.When in reverse gear, the effect will be much greater and opposite...
. - Water salinitySalinitySalinity is the saltiness or dissolved salt content of a body of water. It is a general term used to describe the levels of different salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium and calcium sulfates, and bicarbonates...
must have a well-defined value, as it influences the specific weight of the water and thereby the massMassMass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
moved by the propeller per unit of time. - The geometry of the towing line must have a well-defined value. Ideally, one would expect it to be exactly horizontal and straight. This is impossible in reality, because
- the line falls into a catenaryCatenaryIn physics and geometry, the catenary is the curve that an idealised hanging chain or cable assumes when supported at its ends and acted on only by its own weight. The curve is the graph of the hyperbolic cosine function, and has a U-like shape, superficially similar in appearance to a parabola...
due to its weight; - the two fixed points of the line, being the bollard on shore and the ship's towing hook or cleat, may not have the same height above water.
- the line falls into a catenary
- Conditions must be static. The engine power, the headingCourse (navigation)In navigation, a vehicle's course is the angle that the intended path of the vehicle makes with a fixed reference object . Typically course is measured in degrees from 0° clockwise to 360° in compass convention . Course is customarily expressed in three digits, using preliminary zeros if needed,...
of the ship, the conditions of the propeller discharge race and the tension in the towing line must have settled to a constant or near-constant value for a reliable measurement. - One condition to watch out for is the formation of a short circuitShort circuitA short circuit in an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path, often where essentially no electrical impedance is encountered....
in propeller discharge race. If part of the discharge race is sucked back into the propeller, efficiency decreases sharply. This could occur due to a trial that is performed in too shallow water or too close to a wall.
See Figure 2 for an illustration of error influences in a practical bollard pull trial. Note the difference in elevation of the ends of the line (the port bollard is higher than the ship's towing hook). Furthermore, there is the partial short circuit in propeller discharge current, the uneven trim of the ship and the short length of the tow line. All of these factors contribute to measurement error.
Simulation
This method eliminates much of the uncertainties of the practical trial. However, any numerical simulation also has an error margin. Furthermore, simulation tools and computer systems capable of determining bollard pull for a ship design are costly. Hence, this method makes sense for larger shipyards and for the design of a series of ships.Both methods can be combined. Practical trials can be used to validate the result of numerical simulation.

