
Bone remodeling period
Encyclopedia
In bone physiology
, the bone remodeling period describes the temporal duration (i.e. lifespan) of the basic multicellular unit (BMU) that is responsible for bone turnover. Historically, this was referred to as the sigma (σ) or sigma period, but the terminology is now outdated.
throughout the life of the vertebrate organism. This occurs with the synchronized action of osteoclast
s and osteoblast
s, cells that resorb and deposit bone, respectively. Bone remodeling also occurs in response to trauma, such as that following accidental bone fracture or the placement of dental implant
s into the jaw bones.
, the osteoclastic reversal (the phase marked by shifting of resorption processes into formative processes) and the formation periods of bone growth and development. This period refers to the average total duration of a single cycle of bone remodeling
at any point on a bone surface.
In bone physiology
, the bone remodeling period describes the temporal duration (i.e. lifespan) of the basic multicellular unit (BMU) that is responsible for bone turnover. Historically, this was referred to as the sigma (σ) or sigma period, but the terminology is now outdated.
throughout the life of the vertebrate organism. This occurs with the synchronized action of osteoclast
s and osteoblast
s, cells that resorb and deposit bone, respectively. Bone remodeling also occurs in response to trauma, such as that following accidental bone fracture or the placement of dental implant
s into the jaw bones.
, the osteoclastic reversal (the phase marked by shifting of resorption processes into formative processes) and the formation periods of bone growth and development. This period refers to the average total duration of a single cycle of bone remodeling
at any point on a bone surface.
In bone physiology
, the bone remodeling period describes the temporal duration (i.e. lifespan) of the basic multicellular unit (BMU) that is responsible for bone turnover. Historically, this was referred to as the sigma (σ) or sigma period, but the terminology is now outdated.
throughout the life of the vertebrate organism. This occurs with the synchronized action of osteoclast
s and osteoblast
s, cells that resorb and deposit bone, respectively. Bone remodeling also occurs in response to trauma, such as that following accidental bone fracture or the placement of dental implant
s into the jaw bones.
, the osteoclastic reversal (the phase marked by shifting of resorption processes into formative processes) and the formation periods of bone growth and development. This period refers to the average total duration of a single cycle of bone remodeling
at any point on a bone surface.
For the remodeling to occur, appropriate cell signaling occurs to trigger osteoclasts to resorb the surface of the bone, followed by deposition of bone by osteoblasts. Together, the cells in any given particular region of the bone surface that are responsible for bone remodeling are known as the basic multicellular unit (BMU), and it is the average lifespan of the BMU that is referred to as the remodeling period. The size of a BMU is roughly 200μm in diameter, defined by the 100μm diffusion capability in bone.
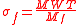
in which MWT refers to the mean wall thickness of the completed bone unit and Mf refers to the prevailing mean effective bone appositional rate. In other words, what this formula means is that the bone remodeling period is equivalent to the thickness of the microscopic segment of bone being formed divided by the rate at which it forms. If the mean linear rate of bone resorption is known, the bone resorption portion (σr) can be similarly calculated:
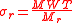
Consequently, the entire bone remodeling period (σr + f, equivalent to σ) can be represented by the following formula:
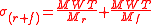
The linear bone resorption rate (Mr) cannot be measured directly, but it approximates a third of σf.
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
, the bone remodeling period describes the temporal duration (i.e. lifespan) of the basic multicellular unit (BMU) that is responsible for bone turnover. Historically, this was referred to as the sigma (σ) or sigma period, but the terminology is now outdated.
Bone remodeling
Although bone may appear superficially as a static tissue, it is actually very dynamic, undergoing constant remodelingBone remodeling
Bone remodeling is a lifelong process where mature bone tissue is removed from the skeleton and new bone tissue is formed...
throughout the life of the vertebrate organism. This occurs with the synchronized action of osteoclast
Osteoclast
An osteoclast is a type of bone cell that removes bone tissue by removing its mineralized matrix and breaking up the organic bone . This process is known as bone resorption. Osteoclasts were discovered by Kolliker in 1873...
s and osteoblast
Osteoblast
Osteoblasts are mononucleate cells that are responsible for bone formation; in essence, osteoblasts are specialized fibroblasts that in addition to fibroblastic products, express bone sialoprotein and osteocalcin.Osteoblasts produce a matrix of osteoid, which is composed mainly of Type I collagen...
s, cells that resorb and deposit bone, respectively. Bone remodeling also occurs in response to trauma, such as that following accidental bone fracture or the placement of dental implant
Dental implant
A dental implant is a "root" device, usually made of titanium, used in dentistry to support restorations that resemble a tooth or group of teeth to replace missing teeth....
s into the jaw bones.
The remodeling period
The remodeling period consists of the combined duration of the resorptionBone resorption
Bone resorption is the process by which osteoclasts break down bone and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone fluid to the blood....
, the osteoclastic reversal (the phase marked by shifting of resorption processes into formative processes) and the formation periods of bone growth and development. This period refers to the average total duration of a single cycle of bone remodeling
Bone remodeling
Bone remodeling is a lifelong process where mature bone tissue is removed from the skeleton and new bone tissue is formed...
at any point on a bone surface.
In bone physiology
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
, the bone remodeling period describes the temporal duration (i.e. lifespan) of the basic multicellular unit (BMU) that is responsible for bone turnover. Historically, this was referred to as the sigma (σ) or sigma period, but the terminology is now outdated.
Bone remodeling
Although bone may appear superficially as a static tissue, it is actually very dynamic, undergoing constant remodelingBone remodeling
Bone remodeling is a lifelong process where mature bone tissue is removed from the skeleton and new bone tissue is formed...
throughout the life of the vertebrate organism. This occurs with the synchronized action of osteoclast
Osteoclast
An osteoclast is a type of bone cell that removes bone tissue by removing its mineralized matrix and breaking up the organic bone . This process is known as bone resorption. Osteoclasts were discovered by Kolliker in 1873...
s and osteoblast
Osteoblast
Osteoblasts are mononucleate cells that are responsible for bone formation; in essence, osteoblasts are specialized fibroblasts that in addition to fibroblastic products, express bone sialoprotein and osteocalcin.Osteoblasts produce a matrix of osteoid, which is composed mainly of Type I collagen...
s, cells that resorb and deposit bone, respectively. Bone remodeling also occurs in response to trauma, such as that following accidental bone fracture or the placement of dental implant
Dental implant
A dental implant is a "root" device, usually made of titanium, used in dentistry to support restorations that resemble a tooth or group of teeth to replace missing teeth....
s into the jaw bones.
The remodeling period
The remodeling period consists of the combined duration of the resorptionBone resorption
Bone resorption is the process by which osteoclasts break down bone and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone fluid to the blood....
, the osteoclastic reversal (the phase marked by shifting of resorption processes into formative processes) and the formation periods of bone growth and development. This period refers to the average total duration of a single cycle of bone remodeling
Bone remodeling
Bone remodeling is a lifelong process where mature bone tissue is removed from the skeleton and new bone tissue is formed...
at any point on a bone surface.
In bone physiology
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
, the bone remodeling period describes the temporal duration (i.e. lifespan) of the basic multicellular unit (BMU) that is responsible for bone turnover. Historically, this was referred to as the sigma (σ) or sigma period, but the terminology is now outdated.
Bone remodeling
Although bone may appear superficially as a static tissue, it is actually very dynamic, undergoing constant remodelingBone remodeling
Bone remodeling is a lifelong process where mature bone tissue is removed from the skeleton and new bone tissue is formed...
throughout the life of the vertebrate organism. This occurs with the synchronized action of osteoclast
Osteoclast
An osteoclast is a type of bone cell that removes bone tissue by removing its mineralized matrix and breaking up the organic bone . This process is known as bone resorption. Osteoclasts were discovered by Kolliker in 1873...
s and osteoblast
Osteoblast
Osteoblasts are mononucleate cells that are responsible for bone formation; in essence, osteoblasts are specialized fibroblasts that in addition to fibroblastic products, express bone sialoprotein and osteocalcin.Osteoblasts produce a matrix of osteoid, which is composed mainly of Type I collagen...
s, cells that resorb and deposit bone, respectively. Bone remodeling also occurs in response to trauma, such as that following accidental bone fracture or the placement of dental implant
Dental implant
A dental implant is a "root" device, usually made of titanium, used in dentistry to support restorations that resemble a tooth or group of teeth to replace missing teeth....
s into the jaw bones.
The remodeling period
The remodeling period consists of the combined duration of the resorptionBone resorption
Bone resorption is the process by which osteoclasts break down bone and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone fluid to the blood....
, the osteoclastic reversal (the phase marked by shifting of resorption processes into formative processes) and the formation periods of bone growth and development. This period refers to the average total duration of a single cycle of bone remodeling
Bone remodeling
Bone remodeling is a lifelong process where mature bone tissue is removed from the skeleton and new bone tissue is formed...
at any point on a bone surface.
| Resorption | Reversal | Formation | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rabbits | 1 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 6 |
| Dogs | 1.5 | 0.5 | 10 | 12 |
| Humans | 2 | 2 | 13 | 17 |
For the remodeling to occur, appropriate cell signaling occurs to trigger osteoclasts to resorb the surface of the bone, followed by deposition of bone by osteoblasts. Together, the cells in any given particular region of the bone surface that are responsible for bone remodeling are known as the basic multicellular unit (BMU), and it is the average lifespan of the BMU that is referred to as the remodeling period. The size of a BMU is roughly 200μm in diameter, defined by the 100μm diffusion capability in bone.
Determining the bone remodeling period
In calculating the bone remodeling period, a two-dimensional model is examined, referring to the time it takes for the area in question to be eroded and then filled in with new bone (sigma will be used here for simplicity's sake). The bone formation portion (σf) of the bone remodeling period is calculated as follows: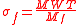
in which MWT refers to the mean wall thickness of the completed bone unit and Mf refers to the prevailing mean effective bone appositional rate. In other words, what this formula means is that the bone remodeling period is equivalent to the thickness of the microscopic segment of bone being formed divided by the rate at which it forms. If the mean linear rate of bone resorption is known, the bone resorption portion (σr) can be similarly calculated:
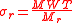
Consequently, the entire bone remodeling period (σr + f, equivalent to σ) can be represented by the following formula:
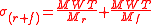
The linear bone resorption rate (Mr) cannot be measured directly, but it approximates a third of σf.
Interspecies differences
Each vertebrate species exhibits a distinct duration of bone regeneration and remodeling, and it appears as though there is an inversely proportional relationship between the rate of bone regeneration and the phylogenetic evolution of the animal. Each remodeling period lasts 3–6 months in humans, 3 months in dogs, and 6 weeks in rabbits.
