Book of Gates
Encyclopedia
The Book of Gates is an Ancient Egyptian funerary text
dating from the New Kingdom
. It narrates the passage of a newly deceased soul into the next world, corresponding to the journey of the sun
though the underworld
during the hours of the night. The soul is required to pass though a series of 'gates' at different stages in the journey. Each gate is associated with a different goddess, and requires that the deceased recognise the particular character of that deity. The text implies that some people will pass through unharmed, but that others will suffer torment in a lake of fire
.
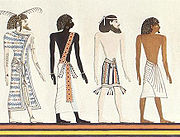
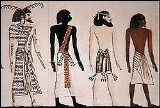
, dividing them up into four categories that are now conventionally labelled "Egyptians", "Asiatics", "Libyans
", and "Nubians
". These are depicted in procession entering the next world.
The text and images associated with the Book of Gates appear in many tombs of the New Kingdom, including all the pharaonic tombs between Horemheb
and Ramesses VII
. They also appear in the tomb
of Sennedjem
, a worker in the village of Deir el-Medina, the ancient village of artists and craftsmen who built pharaonic tombs in the New Kingdom
.
The goddesses listed in the Book of Gates each have different titles, and wear different coloured clothes, but are identical in all other respects, wearing a five pointed star above their heads. Most of the goddesses are specific to the Book of Gates, and do not appear elsewhere in Egyptian mythology
, and so it has been suggested that the Book of Gates originated merely as a system for determining the time at night, with the goddess at each gate being a representation of the main star appearing during the hour.
Ancient Egyptian Funerary Texts
The literature that make up the Ancient Egyptian Funerary Texts are a collection of religious documents that were used in Ancient Egypt, usually to help the spirit of the concerned person to be preserved in the afterlife....
dating from the New Kingdom
New Kingdom
The New Kingdom of Egypt, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the 16th century BC and the 11th century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth Dynasties of Egypt....
. It narrates the passage of a newly deceased soul into the next world, corresponding to the journey of the sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
though the underworld
Duat
In Egyptian mythology, Duat is the underworld. The Duat is a vast area under the Earth, connected with Nun, the waters of the primordial abyss. The Duat is the realm of the god Osiris and the residence of other gods and supernatural beings...
during the hours of the night. The soul is required to pass though a series of 'gates' at different stages in the journey. Each gate is associated with a different goddess, and requires that the deceased recognise the particular character of that deity. The text implies that some people will pass through unharmed, but that others will suffer torment in a lake of fire
Lake of Fire
A lake of fire appears, in both ancient Egyptian and Christian religion, as a place of after-death punishment of the wicked. The phrase is used in four verses of the Book of Revelation. The image was also used by the Early Christian Hippolytus of Rome in about the year 200 and has continued to be...
.

Categories
The most famous part of the Book of Gates today refers to the different races of humanity known to the EgyptiansEgyptians
Egyptians are nation an ethnic group made up of Mediterranean North Africans, the indigenous people of Egypt.Egyptian identity is closely tied to geography. The population of Egypt is concentrated in the lower Nile Valley, the small strip of cultivable land stretching from the First Cataract to...
, dividing them up into four categories that are now conventionally labelled "Egyptians", "Asiatics", "Libyans
Ancient Libya
The Latin name Libya referred to the region west of the Nile Valley, generally corresponding to modern Northwest Africa. Climate changes affected the locations of the settlements....
", and "Nubians
Nubians
The Nubians are an ethnic group originally from northern Sudan, and southern Egypt now inhabiting North Africa and some parts of East Africa....
". These are depicted in procession entering the next world.
The text and images associated with the Book of Gates appear in many tombs of the New Kingdom, including all the pharaonic tombs between Horemheb
Horemheb
Horemheb was the last Pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty from either 1319 BC to late 1292 BC, or 1306 to late 1292 BC although he was not related to the preceding royal family and is believed to have been of common birth.Before he became pharaoh, Horemheb was the commander in chief...
and Ramesses VII
Ramesses VII
Usermaatre Meryamun Setepenre Ramesses VII was the sixth pharaoh of the 20th dynasty of Ancient Egypt. He reigned from about 1136 to 1129 BC and was the son of Ramesses VI. Other dates for his reign are 1138-1131 BC...
. They also appear in the tomb
TT1
The Theban Tomb TT1 is located in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the Ancient Egyptian official, Sennedjem and his family....
of Sennedjem
Sennedjem
The Ancient Egyptian artisan Sennedjem lived in Deir el-Medina on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes, during the reigns of Seti I and Ramesses II. He was buried along with his wife, Iy-neferti, and family in a tomb in the village necropolis. His tomb was discovered January 31, 1886...
, a worker in the village of Deir el-Medina, the ancient village of artists and craftsmen who built pharaonic tombs in the New Kingdom
New Kingdom
The New Kingdom of Egypt, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the 16th century BC and the 11th century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth Dynasties of Egypt....
.
The goddesses listed in the Book of Gates each have different titles, and wear different coloured clothes, but are identical in all other respects, wearing a five pointed star above their heads. Most of the goddesses are specific to the Book of Gates, and do not appear elsewhere in Egyptian mythology
Egyptian mythology
Ancient Egyptian religion was a complex system of polytheistic beliefs and rituals which were an integral part of ancient Egyptian society. It centered on the Egyptians' interaction with a multitude of deities who were believed to be present in, and in control of, the forces and elements of nature...
, and so it has been suggested that the Book of Gates originated merely as a system for determining the time at night, with the goddess at each gate being a representation of the main star appearing during the hour.
The titles of the goddesses
| | Hour | | Title | | Explanation of the title | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Splitter of the heads of the enemies of Ra Ra Ra is the ancient Egyptian sun god. By the Fifth Dynasty he had become a major deity in ancient Egyptian religion, identified primarily with the mid-day sun... |
||
| 2 | Wise guard of the lord | ||
| 3 | The one who cuts through Ba Egyptian soul The ancient Egyptians believed that a human soul was made up of five parts: the Ren, the Ba, the Ka, the Sheut, and the Ib. In addition to these components of the soul there was the human body... |
||
| 4 | The one of great power | ||
| 5 | She who is on her boat | ||
| 6 | Successful leader | ||
| 7 | The one who repels the serpent | ||
| 8 | Lady of the night | ||
| 9 | She who is in adoration | ||
| 10 | The one who beheads rebels | ||
| 11 | The star who repels rebels | ||
| 12 | The witness to Ra's magnificence | Ra is the sun Sun The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields... , and this is the dawn Dawn Dawn is the time that marks the beginning of the twilight before sunrise. It is recognized by the presence of weak sunlight, while the sun itself is still below the horizon... |

