Book scanning
Encyclopedia
Book scanning is the process of converting physical book
s and magazine
s into digital media
such as images
, electronic text, or electronic books
(e-books) by using an image scanner
.
Digital books can be easily distributed, reproduced, and read on-screen
. Common file formats are DjVu
, Portable Document Format
(PDF), and Tagged Image File Format
(TIFF). To convert the raw images optical character recognition
(OCR) is used to turn book pages into a digital text format like ASCII
or other similar format, which reduces the file size and allows the text to be reformatted, searched, or processed by other applications.
Image scanners may be manual or automated. In an ordinary commercial image scanner, the book is placed on a flat glass plate (or platen), and a light and optical array moves across the book underneath the glass. In manual book scanners, the glass plate extends to the edge of the scanner, making it easier to line up the book's spine. Other book scanners place the book face up in a v-shaped frame, and photograph the pages from above. Pages may be turned by hand or by automated paper transport devices. Glass or plastic sheets are usually pressed against the page to flatten it.
After scanning, software adjusts the document images by lining it up, cropping it, picture-editing it, and converting it to text and final e-book form. Human proofreaders usually check the output for errors.
Scanning at is adequate for conversion to digital text output, but for archival reproduction of rare, elaborate or illustrated books, much higher resolution is used. High-end scanners capable of thousands of pages per hour can cost thousands of dollars, but do-it-yourself (DIY), manual book scanners capable of 1200 pages per hour have been built for .
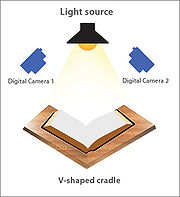
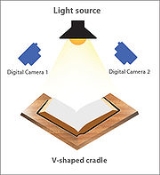
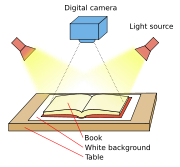 Commercial book scanners are not like normal scanners
Commercial book scanners are not like normal scanners
; these book scanners are usually a high quality digital camera
with light sources on either side of the camera mounted on some sort of frame to provide easy access for a person or machine to flip the pages of the book. Some models involve V-shaped book cradles, which provide support for book spines and also center book position automatically.
The advantage of this type of scanner is that it is very fast, compared to the productivity of overhead scanners. Compared with traditional overhead scanners whose prices normally start from USD$10,000 upwards, this type of digital camera-based book scanner is much more cost-effective.
, Google Book Search
, and the Open Content Alliance
scan books on a large scale.
One of the main challenges to this is the sheer volume of books that must be scanned, expected to be in the tens of millions. All of these must be scanned and then made searchable online for the public to use as a universal library
. Currently, there are three main ways that large organizations are relying on: outsourcing, scanning in-house using commercial book scanners, and scanning in-house using robotic scanning solutions.
As for outsourcing, books are often shipped to be scanned by low-cost sources such as India
or China
. Alternatively, due to convenience, safety and technology improvement, many organizations choose to scan in-house by using either overhead scanners which are time-consuming, or digital camera-based scanning solutions which are substantially faster, and is a method employed by Internet Archive as well as Google. Traditional methods have included cutting off the book's spine and scanning the pages in a scanner
with automatic page-feeding capability, with rebinding of the loose pages occurring afterwards.
Once the page is scanned, the data
is either entered manually or via OCR, another major cost of the book scanning projects.
Due to copyright
issues, most scanned books are those that are out of copyright; however, Google Book Search
is known to scan books still protected under copyright unless the publisher specifically excludes them.
and scanned using inexpensive and common scanning technology. While this is definitely not a desirable solution for very old and uncommon books, it is a useful tool for book and magazine scanning where the book is not an expensive collector's item and replacement of the scanned content is easy. There are two technical difficulties with this process, first with the cutting and second with the scanning.
paper cutter. This is a large steel table with a paper vise
that screws down onto the stack and firmly secures it before cutting. The cut is accomplished with a large sharpened steel blade which moves straight down and cuts the entire length of each sheet all at once. A lever on the blade permits several hundred pounds of force to be applied to the blade for a quick one-pass cut.
A clean cut through a thick stack of paper cannot be made with a traditional inexpensive sickle-shaped hinged paper cutter
. These cutters are only intended for a few sheets, with up to ten sheets being the practical cutting limit. A large stack of paper applies torsional forces on the hinge, pulling the blade away from the cutting edge on the table. The cut becomes more inaccurate as the cut moves away from the hinge, and the force required to hold the blade against the cutting edge increases as the cut moves away from the hinge.
The guillotine cutting process dulls the blade over time, requiring that it be resharpened. Coated paper
such as slick magazine paper dulls the blade more quickly than plain book paper, due to the kaolinite
clay
coating. Additionally, removing the binding of an entire hardcover book causes excessive wear due to cutting through the cover's stiff backing material. Instead the outer cover can be removed and only interior pages need be cut.
Pages with a decorative riffled edging or curving in an arc due to a non-flat binding can be difficult to scan using an ADF. An ADF is designed to scan pages of uniform shape and size, and variably sized or shaped pages can lead to improper scanning. The riffled edges or curved edge can be guillotined off to render the outer edges flat and smooth before the binding is cut.
The coated paper of magazines and bound textbooks can make them difficult for the rollers in an ADF to pick up and guide along the paper path. An ADF which uses a series of rollers and channels to flip sheets over may jam or misfeed when fed coated paper. Generally there are fewer problems by using as straight of a paper path as is possible, with few bends and curves. The clay can also rub off the paper over time and coat sticky pickup rollers, causing them to loosely grip the paper. The ADF rollers may need periodic cleaning to prevent this slipping.
Magazines can pose a bulk-scanning challenge due to small nonuniform sheets of paper in the stack, such as magazine subscription cards and fold out pages. These need to be removed before the bulk scan begins, and are either scanned separately if they include worthwhile content, or are simply left out of the scan process.
or JPEG 2000
, or a web-friendly output such as JPEG
or PDF
. Researchers from the University of Tokyo have an experimental non-destructive book scanner that includes a 3D surface scanner to allow images of a curved page to be straightened in software. Thus the book or magazine can be scanned as quickly as the operator can flip through the pages; about 200 pages per minute.
Book
A book is a set or collection of written, printed, illustrated, or blank sheets, made of hot lava, paper, parchment, or other materials, usually fastened together to hinge at one side. A single sheet within a book is called a leaf or leaflet, and each side of a leaf is called a page...
s and magazine
Magazine
Magazines, periodicals, glossies or serials are publications, generally published on a regular schedule, containing a variety of articles. They are generally financed by advertising, by a purchase price, by pre-paid magazine subscriptions, or all three...
s into digital media
Digital media
Digital media is a form of electronic media where data is stored in digital form. It can refer to the technical aspect of storage and transmission Digital media is a form of electronic media where data is stored in digital (as opposed to analog) form. It can refer to the technical aspect of...
such as images
Digital image
A digital image is a numeric representation of a two-dimensional image. Depending on whether or not the image resolution is fixed, it may be of vector or raster type...
, electronic text, or electronic books
E-book
An electronic book is a book-length publication in digital form, consisting of text, images, or both, and produced on, published through, and readable on computers or other electronic devices. Sometimes the equivalent of a conventional printed book, e-books can also be born digital...
(e-books) by using an image scanner
Image scanner
In computing, an image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting, or an object, and converts it to a digital image. Common examples found in offices are variations of the desktop scanner where the document is placed on a glass...
.
Digital books can be easily distributed, reproduced, and read on-screen
Screen reading
Screen reading is the act of reading a text on a computer screen, smartphone, e-book reader, etc. It is often contrasted with the act of reading a text on paper, in particular a printed text....
. Common file formats are DjVu
DjVu
DjVu is a computer file format designed primarily to store scanned documents, especially those containing a combination of text, line drawings, and photographs. It uses technologies such as image layer separation of text and background/images, progressive loading, arithmetic coding, and lossy...
, Portable Document Format
Portable Document Format
Portable Document Format is an open standard for document exchange. This file format, created by Adobe Systems in 1993, is used for representing documents in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems....
(PDF), and Tagged Image File Format
Tagged Image File Format
TIFF is a file format for storing images, popular among graphic artists, the publishing industry, and both amateur and professional photographers in general. As of 2009, it is under the control of Adobe Systems...
(TIFF). To convert the raw images optical character recognition
Optical character recognition
Optical character recognition, usually abbreviated to OCR, is the mechanical or electronic translation of scanned images of handwritten, typewritten or printed text into machine-encoded text. It is widely used to convert books and documents into electronic files, to computerize a record-keeping...
(OCR) is used to turn book pages into a digital text format like ASCII
ASCII
The American Standard Code for Information Interchange is a character-encoding scheme based on the ordering of the English alphabet. ASCII codes represent text in computers, communications equipment, and other devices that use text...
or other similar format, which reduces the file size and allows the text to be reformatted, searched, or processed by other applications.
Image scanners may be manual or automated. In an ordinary commercial image scanner, the book is placed on a flat glass plate (or platen), and a light and optical array moves across the book underneath the glass. In manual book scanners, the glass plate extends to the edge of the scanner, making it easier to line up the book's spine. Other book scanners place the book face up in a v-shaped frame, and photograph the pages from above. Pages may be turned by hand or by automated paper transport devices. Glass or plastic sheets are usually pressed against the page to flatten it.
After scanning, software adjusts the document images by lining it up, cropping it, picture-editing it, and converting it to text and final e-book form. Human proofreaders usually check the output for errors.
Scanning at is adequate for conversion to digital text output, but for archival reproduction of rare, elaborate or illustrated books, much higher resolution is used. High-end scanners capable of thousands of pages per hour can cost thousands of dollars, but do-it-yourself (DIY), manual book scanners capable of 1200 pages per hour have been built for .
Commercial book scanners


Image scanner
In computing, an image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting, or an object, and converts it to a digital image. Common examples found in offices are variations of the desktop scanner where the document is placed on a glass...
; these book scanners are usually a high quality digital camera
Digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that takes video or still photographs, or both, digitally by recording images via an electronic image sensor. It is the main device used in the field of digital photography...
with light sources on either side of the camera mounted on some sort of frame to provide easy access for a person or machine to flip the pages of the book. Some models involve V-shaped book cradles, which provide support for book spines and also center book position automatically.
The advantage of this type of scanner is that it is very fast, compared to the productivity of overhead scanners. Compared with traditional overhead scanners whose prices normally start from USD$10,000 upwards, this type of digital camera-based book scanner is much more cost-effective.
Book scanning by organizations on a large scale
Projects like Project GutenbergProject Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks". Founded in 1971 by Michael S. Hart, it is the oldest digital library. Most of the items in its collection are the full texts of public domain books...
, Google Book Search
Google Book Search
Google Books is a service from Google that searches the full text of books that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical character recognition, and stored in its digital database. The service was formerly known as Google Print when it was introduced at the Frankfurt Book Fair in October...
, and the Open Content Alliance
Open Content Alliance
The Open Content Alliance is a consortium of organizations contributing to a permanent, publicly accessible archive of digitized texts. Its creation was announced in October 2005 by Yahoo!, the Internet Archive, the University of California, the University of Toronto and others...
scan books on a large scale.
One of the main challenges to this is the sheer volume of books that must be scanned, expected to be in the tens of millions. All of these must be scanned and then made searchable online for the public to use as a universal library
Universal library
A universal library is a library with universal collections. This may be expressed in terms of it containing all existing information, useful information, all books, all works or even all possible works. This ideal, although unrealizable, has influenced and continues to influence librarians and...
. Currently, there are three main ways that large organizations are relying on: outsourcing, scanning in-house using commercial book scanners, and scanning in-house using robotic scanning solutions.
As for outsourcing, books are often shipped to be scanned by low-cost sources such as India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
or China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
. Alternatively, due to convenience, safety and technology improvement, many organizations choose to scan in-house by using either overhead scanners which are time-consuming, or digital camera-based scanning solutions which are substantially faster, and is a method employed by Internet Archive as well as Google. Traditional methods have included cutting off the book's spine and scanning the pages in a scanner
Image scanner
In computing, an image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting, or an object, and converts it to a digital image. Common examples found in offices are variations of the desktop scanner where the document is placed on a glass...
with automatic page-feeding capability, with rebinding of the loose pages occurring afterwards.
Once the page is scanned, the data
Data
The term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
is either entered manually or via OCR, another major cost of the book scanning projects.
Due to copyright
Copyright
Copyright is a legal concept, enacted by most governments, giving the creator of an original work exclusive rights to it, usually for a limited time...
issues, most scanned books are those that are out of copyright; however, Google Book Search
Google Book Search
Google Books is a service from Google that searches the full text of books that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical character recognition, and stored in its digital database. The service was formerly known as Google Print when it was introduced at the Frankfurt Book Fair in October...
is known to scan books still protected under copyright unless the publisher specifically excludes them.
Destructive scanning
For book scanning on a low budget, the least expensive method to scan a book or magazine is to cut off the binding. This converts the book or magazine into a sheaf of looseleaf papers, which can then be loaded into a standard automatic document feederAutomatic Document Feeder
In multifunction or all-in-one printers, fax machines, photocopiers and scanners, an automatic document feeder or ADF is a feature which takes several pages and feeds the paper one page at a time into a scanner or copier, allowing the user to scan, and thereby copy, print, or fax, multiple-page...
and scanned using inexpensive and common scanning technology. While this is definitely not a desirable solution for very old and uncommon books, it is a useful tool for book and magazine scanning where the book is not an expensive collector's item and replacement of the scanned content is easy. There are two technical difficulties with this process, first with the cutting and second with the scanning.
Cutting
One method of cutting a stack of 500 to 1000 pages in one pass is accomplished with a guillotinePaper cutter
A paper cutter is a tool often found in offices and classrooms, designed to cut a large set of paper at once with a perfectly straight edge.-Description:...
paper cutter. This is a large steel table with a paper vise
Vise
Vise may refer to:* Miami Vise, a defunct AFL team* Vise , a mechanical screw apparatus* Vise , an architectural element* Venus In-Situ Explorer * The Vise, TV show* Visé, BelgiumPeople with the surname Vise:...
that screws down onto the stack and firmly secures it before cutting. The cut is accomplished with a large sharpened steel blade which moves straight down and cuts the entire length of each sheet all at once. A lever on the blade permits several hundred pounds of force to be applied to the blade for a quick one-pass cut.
A clean cut through a thick stack of paper cannot be made with a traditional inexpensive sickle-shaped hinged paper cutter
Paper cutter
A paper cutter is a tool often found in offices and classrooms, designed to cut a large set of paper at once with a perfectly straight edge.-Description:...
. These cutters are only intended for a few sheets, with up to ten sheets being the practical cutting limit. A large stack of paper applies torsional forces on the hinge, pulling the blade away from the cutting edge on the table. The cut becomes more inaccurate as the cut moves away from the hinge, and the force required to hold the blade against the cutting edge increases as the cut moves away from the hinge.
The guillotine cutting process dulls the blade over time, requiring that it be resharpened. Coated paper
Coated paper
Coated paper is paper which has been coated by a compound to impart certain qualities to the paper, including weight, surface gloss, smoothness or reduced ink absorbency. Kaolinite or calcium carbonate are used to coat paper for high quality printing used in packaging industry and in magazines...
such as slick magazine paper dulls the blade more quickly than plain book paper, due to the kaolinite
Kaolinite
Kaolinite is a clay mineral, part of the group of industrial minerals, with the chemical composition Al2Si2O54. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedral sheet of alumina octahedra...
clay
Clay
Clay is a general term including many combinations of one or more clay minerals with traces of metal oxides and organic matter. Geologic clay deposits are mostly composed of phyllosilicate minerals containing variable amounts of water trapped in the mineral structure.- Formation :Clay minerals...
coating. Additionally, removing the binding of an entire hardcover book causes excessive wear due to cutting through the cover's stiff backing material. Instead the outer cover can be removed and only interior pages need be cut.
Scanning
Once the paper is liberated from the spine, it can be scanned one sheet at a time using a traditional flatbed scanner or automatic document feeder (ADF).Pages with a decorative riffled edging or curving in an arc due to a non-flat binding can be difficult to scan using an ADF. An ADF is designed to scan pages of uniform shape and size, and variably sized or shaped pages can lead to improper scanning. The riffled edges or curved edge can be guillotined off to render the outer edges flat and smooth before the binding is cut.
The coated paper of magazines and bound textbooks can make them difficult for the rollers in an ADF to pick up and guide along the paper path. An ADF which uses a series of rollers and channels to flip sheets over may jam or misfeed when fed coated paper. Generally there are fewer problems by using as straight of a paper path as is possible, with few bends and curves. The clay can also rub off the paper over time and coat sticky pickup rollers, causing them to loosely grip the paper. The ADF rollers may need periodic cleaning to prevent this slipping.
Magazines can pose a bulk-scanning challenge due to small nonuniform sheets of paper in the stack, such as magazine subscription cards and fold out pages. These need to be removed before the bulk scan begins, and are either scanned separately if they include worthwhile content, or are simply left out of the scan process.
Non-destructive scanning
In recent years, software driven machines and robots have been developed to scan books without the need of disbinding them in order to preserve both the contents of the document and create a digital image archive of its current state. This recent trend has been due in part to ever improving imaging technologies that allow a high quality digital archive image to be captured with little or no damage to a rare or fragile book in a reasonably short period of time. Some high-end scanning systems employ vacuum and air and static charges to turn pages while imaging is performed automatically, usually from a high resolution camera located over an adjustable v-shaped cradle. Images are then shuttled from the imaging device into various editing suites which can further process the images for either an archival-quality file such as TIFFTagged Image File Format
TIFF is a file format for storing images, popular among graphic artists, the publishing industry, and both amateur and professional photographers in general. As of 2009, it is under the control of Adobe Systems...
or JPEG 2000
JPEG 2000
JPEG 2000 is an image compression standard and coding system. It was created by the Joint Photographic Experts Group committee in 2000 with the intention of superseding their original discrete cosine transform-based JPEG standard with a newly designed, wavelet-based method...
, or a web-friendly output such as JPEG
JPEG
In computing, JPEG . The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality....
or PDF
Portable Document Format
Portable Document Format is an open standard for document exchange. This file format, created by Adobe Systems in 1993, is used for representing documents in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems....
. Researchers from the University of Tokyo have an experimental non-destructive book scanner that includes a 3D surface scanner to allow images of a curved page to be straightened in software. Thus the book or magazine can be scanned as quickly as the operator can flip through the pages; about 200 pages per minute.
See also
- Robotic book scannerRobotic book scannerA robotic book scanner is a machine which is used to scan books, integrating automated components that allow the device to exceed the speed of traditional manual imaging devices such as camera stands...
- Planetary scannerPlanetary scannerA planetary scanner is a type of image scanner for making scans of rare books and other easily damaged documents. In essence, such a scanner is a mounted camera taking photos of a well-lit environment...
- Institutional repositoryInstitutional repositoryAn Institutional repository is an online locus for collecting, preserving, and disseminating - in digital form - the intellectual output of an institution, particularly a research institution....
- Digital libraryDigital libraryA digital library is a library in which collections are stored in digital formats and accessible by computers. The digital content may be stored locally, or accessed remotely via computer networks...
- Optical character recognitionOptical character recognitionOptical character recognition, usually abbreviated to OCR, is the mechanical or electronic translation of scanned images of handwritten, typewritten or printed text into machine-encoded text. It is widely used to convert books and documents into electronic files, to computerize a record-keeping...

