
Bottomley projection
Encyclopedia
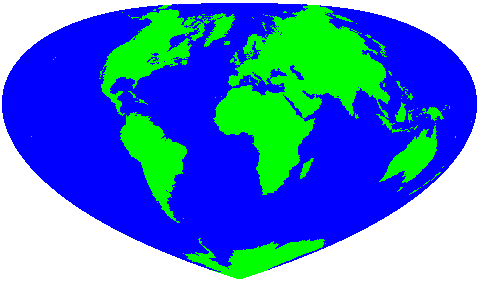
Map projection
A map projection is any method of representing the surface of a sphere or other three-dimensional body on a plane. Map projections are necessary for creating maps. All map projections distort the surface in some fashion...
.
The projection is:


where


and φ is the latitude, λ is the longitude from the central meridian, and φ1 is the given parallel of the projection which determines its shape, all in radians.
Parallels (i.e. lines of latitude) are concentric elliptical
Ellipse
In geometry, an ellipse is a plane curve that results from the intersection of a cone by a plane in a way that produces a closed curve. Circles are special cases of ellipses, obtained when the cutting plane is orthogonal to the cone's axis...
arcs of constant eccentricity
Eccentricity (mathematics)
In mathematics, the eccentricity, denoted e or \varepsilon, is a parameter associated with every conic section. It can be thought of as a measure of how much the conic section deviates from being circular.In particular,...
, centred on the north pole
North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface...
. On the central meridian
Meridian (geography)
A meridian is an imaginary line on the Earth's surface from the North Pole to the South Pole that connects all locations along it with a given longitude. The position of a point along the meridian is given by its latitude. Each meridian is perpendicular to all circles of latitude...
, shapes are not distorted, but elsewhere they are. Different projections can be produced by altering the eccentricity of the arcs, making it vary between the sinusoidal projection
Sinusoidal projection
The sinusoidal projection is a pseudocylindrical equal-area map projection, sometimes called the Sanson–Flamsteed or the Mercator equal-area projection. Jean Cossin of Dieppe was one of the first mapmakers to use the sinusoidal, appearing in a world map of 1570...
and the Werner projection
Werner projection
The Werner projection is a pseudoconic equal-area map projection sometimes called the Stab-Werner or Stabius-Werner projection. Like other heart-shaped projections, it is also categorized as cordiform...
.
It was introduced by Henry Bottomley as an alternative to the Bonne projection
Bonne projection
A Bonne projection is a pseudoconical equal-area map projection, sometimes called a dépôt de la guerre or a Sylvanus projection. Although named after Rigobert Bonne , the projection was in use prior to his birth, in 1511 by Sylvano, Honter in 1561, De l'Isle before 1700 and Coronelli in 1696.The...
to reduce the extent of extreme distortion at the edges and give a more satisfying overall shape.

