Bouri Field
Encyclopedia
The Bouri Offshore Field is part of Block NC-41, which is located 120 kilometres (74.6 mi) north of the Libyan coast in the Mediterranean Sea
. It was first discovered in 1976 at a depth of 8700 feet (2,651.8 m) and is estimated to contain 2 Goilbbl in proven recoverable crude oil reserves and 2.5 Tcuft of associated natural gas
with an annual production potential of 6 billion m³. Bouri is considered the largest producing oilfield in the Mediterranean.
oil company Eni
S.p.A signed a Production sharing agreement
(PSA) awarded by the state-owned National Oil Corporation (NOC) of Libya for onshore and offshore exploration in areas near Tripoli. This is where the Bouri field was discovered offshore at a depth of 8700 feet (2,651.8 m) in the Gulf of Gabes by Eni's subsidiary company Agip
Oil in 1976. The Bouri field is jointly operated by Agip and NOC, with production initiating from two oil platforms (DP4 and DP3) in August 1988. By the end of 1989 it was producing an average of 60 Moilbbl/d. The first phase of development, costing nearly $2 billion, was completed in 1990. This was immediately followed by commencement of a second development phase which entailed the drilling of 55 new wells and construction of three additional platforms.
In 1995, the Bouri field was producing nearly 150000 oilbbl/d, followed by a sharp decline to 60000 oilbbl/d in 1998. This decline was largely a result of the country's inability to import enhanced oil recovery
(EOR) equipment under United Nations
sanctions, specifically Security Council Resolution 883
of November 11, 1993, which banned Libya from importing refinery equipment. The situation has improved since the UN Security Council officially lifted sanctions against Libya during September 2003 and foreign investment is expected in the future. In 2006, Eni reported that the Bouri field was producing about 55 kbboe
per day.
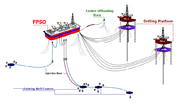 Block NC-41 contains three known petroleum reservoirs; one oil reservoir and two gas reservoirs. NC-41 has two production platforms: DP4 and DP3. The latter is tied back to the DP4 platform located 6.5 km northeast. The DP4 platform is permanently moored at a single point to a Floating Production Storage and Offloading
Block NC-41 contains three known petroleum reservoirs; one oil reservoir and two gas reservoirs. NC-41 has two production platforms: DP4 and DP3. The latter is tied back to the DP4 platform located 6.5 km northeast. The DP4 platform is permanently moored at a single point to a Floating Production Storage and Offloading
(FPSO) tanker with a storage capacity of approximately 1.5 Moilbbl. Bouri has three subsea
wells independently tied to the DP3 platform by underwater safety valves (USV) mounted on a subsea-deployed skid located 150 meters from the DP3 jacket. The three wells were initially drilled in 1994-1995 and temporarily abandoned until completion in 1998. The subsea trees are an integral protection structure for deflection and protection, preventing the release of oil or gas from wells into the environment and controlling formation fluids. The wells, notable for Hydrogen sulfide, are controlled by chokes on subsea trees. Hydrocarbons are produced by their respective underwater safety valves to the DP3 platform through flexible 4" nominal-diameter flowlines. Topside controls were installed by FMC Technology on the DP3 platform and use a multiplex electro-hydraulic control system with independent production umbilical
at each well.
 In 2004, Agip Oil commissioned Saipem
In 2004, Agip Oil commissioned Saipem
S.p.A. for additional development projects related to the Bouri Field. The project carried out through a joint venture
between Saipem and Korea’s Hyundai Corporation
, which fabricated process and utility modules. Apart from drilling modules, designed and with fabrication follow up by Saipem, the contract covered installation of two drilling and production platforms in 160 meter water depths. Overall, twenty-seven modules, ranging in weight from 500 to 1700 tons, and totalling 26,000 tons, were installed. Work conducted on the Bouri Field DP-4 Rig, included; a Removal project: decommissioning and removal of one of the two drilling rig
s and associated modules from the DP-4 platform. These operations were carried out utilising the Saipem 7000
, which is the world's second largest crane vessel.
is a 50-50 joint venture between Eni and NOC which came online in October 2004. This project transports natural gas from Bouri and other Eni fields through the $6.6 billion, 32 inch (0.8128 m), 520 km Greenstream underwater pipeline. Currently, 280 Gcuft per year of natural gas is exported from a processing facility at Melitah, on the Libyan coast, via Greenstream to southeastern Sicily. From Sicily, the natural gas flows to the Italian mainland, and then onwards to the rest of Europe. Throughput on the Greenstream line reportedly can be boosted to 385 Gcuft per year.
and northern Libya (northwest of the Sirte Basin
), and extending slightly into Italian and Maltese
territorial waters. The Pelagian Province contains over 2.3 Goilbbl of known (estimated total recoverable, including cumulative production plus remaining reserves) petroleum liquids; consisting of about 1 Goilbbl of recoverable oil reserves and approximately 17 Tcuft of known natural gas. It is speculated that Tertiary
carbonates might contain indigenous hydrocarbon sources, particularly in Eocene
rocks (Gir Formation), that could have contributed to the large reserves in Djefarra-Pelagian. In addition to Bouris, other major fields located in the province are the Ashtart and Sidi el Itayem fields.
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
. It was first discovered in 1976 at a depth of 8700 feet (2,651.8 m) and is estimated to contain 2 Goilbbl in proven recoverable crude oil reserves and 2.5 Tcuft of associated natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
with an annual production potential of 6 billion m³. Bouri is considered the largest producing oilfield in the Mediterranean.
Overview
In 1974, the ItalianItaly
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
oil company Eni
Eni
Eni S.p.A. is an Italian multinational oil and gas company, present in 70 countries, and currently Italy's largest industrial company with a market capitalization of 87.7 billion euros , as of July 24, 2008...
S.p.A signed a Production sharing agreement
Production sharing agreement
Production sharing agreements are a common type of contract signed between a government and a resource extraction company concerning how much of the resource extracted from the country each will receive....
(PSA) awarded by the state-owned National Oil Corporation (NOC) of Libya for onshore and offshore exploration in areas near Tripoli. This is where the Bouri field was discovered offshore at a depth of 8700 feet (2,651.8 m) in the Gulf of Gabes by Eni's subsidiary company Agip
Agip
Agip is an Italian automotive gasoline and diesel retailer established in 1926. It is a subsidiary of the multinational petroleum company Eni.In 2003, Eni S.p.A...
Oil in 1976. The Bouri field is jointly operated by Agip and NOC, with production initiating from two oil platforms (DP4 and DP3) in August 1988. By the end of 1989 it was producing an average of 60 Moilbbl/d. The first phase of development, costing nearly $2 billion, was completed in 1990. This was immediately followed by commencement of a second development phase which entailed the drilling of 55 new wells and construction of three additional platforms.
In 1995, the Bouri field was producing nearly 150000 oilbbl/d, followed by a sharp decline to 60000 oilbbl/d in 1998. This decline was largely a result of the country's inability to import enhanced oil recovery
Enhanced oil recovery
Enhanced Oil Recovery is a generic term for techniques for increasing the amount of crude oil that can be extracted from an oil field...
(EOR) equipment under United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
sanctions, specifically Security Council Resolution 883
United Nations Security Council Resolution 883
UN Security Council Resolution 883, adopted on 11 November 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 731 and 748 , the Council noted that, twenty months later, Libya had not complied with previous Security Council resolutions and as a consequence imposed further international sanctions on the...
of November 11, 1993, which banned Libya from importing refinery equipment. The situation has improved since the UN Security Council officially lifted sanctions against Libya during September 2003 and foreign investment is expected in the future. In 2006, Eni reported that the Bouri field was producing about 55 kbboe
Barrel of oil equivalent
The barrel of oil equivalent is a unit of energy based on the approximate energy released by burning one barrel of crude oil. The US Internal Revenue Service defines it as equal to 5.8 × 106 BTU...
per day.
Block NC-41 Facilities

Floating Production Storage and Offloading
A floating production, storage and offloading unit is a floating vessel used by the offshore industry for the processing of hydrocarbons and for storage of oil. A FPSO vessel is designed to receive hydrocarbons produced from nearby platforms or subsea template, process them, and store oil until it...
(FPSO) tanker with a storage capacity of approximately 1.5 Moilbbl. Bouri has three subsea
Subsea
Subsea is a general term frequently used to refer to equipment, technology, and methods employed in marine biology, undersea geology, offshore oil and gas developments, underwater mining, and offshore wind power industries.- Oil and gas :...
wells independently tied to the DP3 platform by underwater safety valves (USV) mounted on a subsea-deployed skid located 150 meters from the DP3 jacket. The three wells were initially drilled in 1994-1995 and temporarily abandoned until completion in 1998. The subsea trees are an integral protection structure for deflection and protection, preventing the release of oil or gas from wells into the environment and controlling formation fluids. The wells, notable for Hydrogen sulfide, are controlled by chokes on subsea trees. Hydrocarbons are produced by their respective underwater safety valves to the DP3 platform through flexible 4" nominal-diameter flowlines. Topside controls were installed by FMC Technology on the DP3 platform and use a multiplex electro-hydraulic control system with independent production umbilical
Umbilical cable
An umbilical cable or umbilical is a cable which supplies required consumables to an apparatus. It is named by analogy with an umbilical cord...
at each well.
Field Development Since 2004

Saipem
Saipem S.p.A. is an Italian oil and gas industry contractor. It is a subsidiary of Italian energy company Eni, which owns approximately 43% of Saipem's shares. Saipem has contracted for designing and constructing several pipelines, including Blue Stream, Greenstream, Nord Stream and South...
S.p.A. for additional development projects related to the Bouri Field. The project carried out through a joint venture
Joint venture
A joint venture is a business agreement in which parties agree to develop, for a finite time, a new entity and new assets by contributing equity. They exercise control over the enterprise and consequently share revenues, expenses and assets...
between Saipem and Korea’s Hyundai Corporation
Hyundai Corporation
Hyundai Corporation is a South Korean company founded in 1976 as part of the Hyundai Group. It is composed of five divisions: Automobile and Electrical Equipment, Ship and Machinery, Steel, Brand Licensing and Commodities, and Natural Resources...
, which fabricated process and utility modules. Apart from drilling modules, designed and with fabrication follow up by Saipem, the contract covered installation of two drilling and production platforms in 160 meter water depths. Overall, twenty-seven modules, ranging in weight from 500 to 1700 tons, and totalling 26,000 tons, were installed. Work conducted on the Bouri Field DP-4 Rig, included; a Removal project: decommissioning and removal of one of the two drilling rig
Drilling rig
A drilling rig is a machine which creates holes or shafts in the ground. Drilling rigs can be massive structures housing equipment used to drill water wells, oil wells, or natural gas extraction wells, or they can be small enough to be moved manually by one person...
s and associated modules from the DP-4 platform. These operations were carried out utilising the Saipem 7000
Saipem 7000
Saipem 7000 is the world's second largest crane vessel, after the Thialf. The crane radius of the Saipem 7000 grants a lifting capability of 14,000 tonnes at 42 meters while the Thialf can lift 14,200 tonnes at 31.2 meters...
, which is the world's second largest crane vessel.
Export Development
The Western Libyan Gas ProjectWestern Libyan Gas Project
The Western Libyan Gas Project is a 50-50 joint venture between the Libyan National Oil Corporation and the Italian company Eni which came online in October 2004. By July 2007, per year of natural gas was being exported from a processing facility at Melitah, on the Libyan coast, through the...
is a 50-50 joint venture between Eni and NOC which came online in October 2004. This project transports natural gas from Bouri and other Eni fields through the $6.6 billion, 32 inch (0.8128 m), 520 km Greenstream underwater pipeline. Currently, 280 Gcuft per year of natural gas is exported from a processing facility at Melitah, on the Libyan coast, via Greenstream to southeastern Sicily. From Sicily, the natural gas flows to the Italian mainland, and then onwards to the rest of Europe. Throughput on the Greenstream line reportedly can be boosted to 385 Gcuft per year.
Djeffara-Pelagian Basin Province: Formation
The Bouri field is situated in the Djeffara-Pelagian Basin Province (also known as the “Pelagian Basin”), and produces from the Bou Dabbous-Tertiary TPS. The Province is primarily an offshore region of the Mediterranean, located off eastern TunisiaTunisia
Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area...
and northern Libya (northwest of the Sirte Basin
Sirte Basin
The Sirte Basin is a late Mesozoic and Tertiary triple junction continental rift along northern Africa that was initiated during the late Jurassic Period. It borders a relatively stable Paleozoic craton and cratonic sag basins along its southern margins...
), and extending slightly into Italian and Maltese
Malta
Malta , officially known as the Republic of Malta , is a Southern European country consisting of an archipelago situated in the centre of the Mediterranean, south of Sicily, east of Tunisia and north of Libya, with Gibraltar to the west and Alexandria to the east.Malta covers just over in...
territorial waters. The Pelagian Province contains over 2.3 Goilbbl of known (estimated total recoverable, including cumulative production plus remaining reserves) petroleum liquids; consisting of about 1 Goilbbl of recoverable oil reserves and approximately 17 Tcuft of known natural gas. It is speculated that Tertiary
Tertiary
The Tertiary is a deprecated term for a geologic period 65 million to 2.6 million years ago. The Tertiary covered the time span between the superseded Secondary period and the Quaternary...
carbonates might contain indigenous hydrocarbon sources, particularly in Eocene
Eocene
The Eocene Epoch, lasting from about 56 to 34 million years ago , is a major division of the geologic timescale and the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Palaeocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the...
rocks (Gir Formation), that could have contributed to the large reserves in Djefarra-Pelagian. In addition to Bouris, other major fields located in the province are the Ashtart and Sidi el Itayem fields.

