Bouveault aldehyde synthesis
Encyclopedia
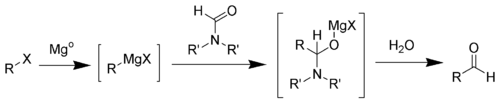
The Bouveault aldehyde synthesis is a one-pot chemical reaction
that converts a primary alkyl halide to an aldehyde
one carbon longer.
(such as DMF
) a hemiaminal
is formed, which can easily be hydrolyzed into the desired aldehyde .
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
that converts a primary alkyl halide to an aldehyde
Aldehyde
An aldehyde is an organic compound containing a formyl group. This functional group, with the structure R-CHO, consists of a carbonyl center bonded to hydrogen and an R group....
one carbon longer.
Reaction mechanism
The first step of the Bouveault aldehyde synthesis is the formation of the Grignard reagent. Upon addition of a N,N-disubstituted formamideFormamide
Formamide, also known as methanamide, is an amide derived from formic acid. It is a clear liquid which is miscible with water and has an ammonia-like odor. It is used primarily for manufacturing sulfa drugs and synthesizing vitamins and as a softener for paper and fiber...
(such as DMF
Dimethylformamide
Dimethylformamide is an organic compound with the formula 2NCH. Commonly abbreviated as DMF , this colourless liquid is miscible with water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions...
) a hemiaminal
Hemiaminal
A hemiaminal is a functional group or type of chemical compound that has a hydroxyl group and an amine attached to the same carbon atom: -C-. R can be hydrogen or an alkyl group...
is formed, which can easily be hydrolyzed into the desired aldehyde .