Branchio-oto-renal syndrome
Encyclopedia
Branchio-oto-renal syndrome (BOR), also known as branciootorenal syndrome or BOR syndrome, is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder
involving the kidney
s, ears, and neck. It has also been described as Melnick-Fraser syndrome after Frank Clarke Fraser
and Michael Melnick.
kidneys with resultant renal insufficiency or renal failure
.
Ear anomalies include extra openings in front of the ears (preauricular pits), extra pieces of skin in front of the ears (preauricular tags
), or further malformation or absence of the outer ear (pinna). Malformation or absence of the middle ear
is also possible. Individuals can have mild to profound hearing loss, which can either be sensorineural, conductive, or mixed. People with BOR may also have cysts or fistula
e along the sides of their neck corresponding to
the location of the embryologic branchial cleft
s.
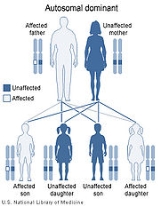
 BOR is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, and results from a mutation in the EYA1 gene. Autosomal dominant inheritance indicates that the defective gene responsible for a disorder is located on an autosome
BOR is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, and results from a mutation in the EYA1 gene. Autosomal dominant inheritance indicates that the defective gene responsible for a disorder is located on an autosome
, and only one copy of the gene is sufficient to cause the disorder, when inherited from a parent who has the disorder.
Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is an illness caused by abnormalities in genes or chromosomes, especially a condition that is present from before birth. Most genetic disorders are quite rare and affect one person in every several thousands or millions....
involving the kidney
Kidney
The kidneys, organs with several functions, serve essential regulatory roles in most animals, including vertebrates and some invertebrates. They are essential in the urinary system and also serve homeostatic functions such as the regulation of electrolytes, maintenance of acid–base balance, and...
s, ears, and neck. It has also been described as Melnick-Fraser syndrome after Frank Clarke Fraser
Clarke Fraser
Frank Clarke Fraser, OC, FRSC is a Canadian medical geneticist. Spanning the fields of science and medicine, he was Canada's first medical geneticist, one of the creators of the discipline of medical genetics in North America, and laid the foundations in the field of Genetic Counselling, which...
and Michael Melnick.
Presentation
Individiduals with BOR may have underdeveloped (hypoplastic) or absentRenal agenesis
Renal agenesis is a unilateral or bilateral medical condition in which one or both fetal kidneys fail to develop leading to oligohydramnios, resulting in a 40-fold increase in perinatal mortality.It can be associated with RET or UPK3A.-Bilateral:...
kidneys with resultant renal insufficiency or renal failure
Renal failure
Renal failure or kidney failure describes a medical condition in which the kidneys fail to adequately filter toxins and waste products from the blood...
.
Ear anomalies include extra openings in front of the ears (preauricular pits), extra pieces of skin in front of the ears (preauricular tags
Acrochordon
An acrochordon An acrochordon An acrochordon (plural acrochorda, and also known as a (cutaneous) skin tag, or fibroepithelial polyp, is a small benign tumour that forms primarily in areas where the skin forms creases, such as the neck, armpit, and groin. They may also occur on the face, usually on...
), or further malformation or absence of the outer ear (pinna). Malformation or absence of the middle ear
Middle ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear internal to the eardrum, and external to the oval window of the cochlea. The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles, which couple vibration of the eardrum into waves in the fluid and membranes of the inner ear. The hollow space of the middle ear has...
is also possible. Individuals can have mild to profound hearing loss, which can either be sensorineural, conductive, or mixed. People with BOR may also have cysts or fistula
Fistula
In medicine, a fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between two epithelium-lined organs or vessels that normally do not connect. It is generally a disease condition, but a fistula may be surgically created for therapeutic reasons.-Locations:Fistulas can develop in various parts of the...
e along the sides of their neck corresponding to
the location of the embryologic branchial cleft
Branchial arch
In the development of vertebrate animals, the pharyngeal arches are anlage for a multitude of structures. In humans, they develop during the fourth week in utero as a series of mesodermal outpouchings on the left and right sides of the developing pharynx...
s.
Genetics

Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and only one copy of the gene is sufficient to cause the disorder, when inherited from a parent who has the disorder.

