
Branchiostoma lanceolatum
Encyclopedia
Branchiostoma lanceolatum or amphioxus is a lancelet
in the subphylum
Cephalochordata
. It is a marine invertebrate
found in soft substrates in shallow seas. It is used as a model organism
to study the development of vertebrate
s. The mitochondrial genome
has been sequenced
.
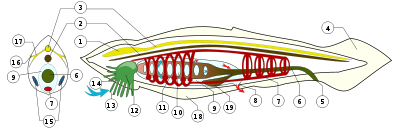 Branchiostoma lanceolatum has an elongated body, flattened laterally and pointed at both ends. A stiffening rod of tightly packed cells, the notochord
Branchiostoma lanceolatum has an elongated body, flattened laterally and pointed at both ends. A stiffening rod of tightly packed cells, the notochord
, extends the whole length of the body. Above it is a nerve cord with a single frontal eye. The mouth is on the underside of the body and is surrounded by a tuft of 20 or 30 cirri or slender sensory appendages. The gut runs just below the notochord from the mouth to the anus, in front of the tail. There is a flap-like, vertical fin surrounding the pointed tail. Gas exchange takes place as water passes through gill slits in the mid region, and segmented gonad
s lie just behind these. The animal is pearly white and semi-transparent which enables the internal organs to be seen from outside. Its appearance is similar to a "primitive fish". It can grow up to 6 cm (2.5 in) long.
, from Norway
south to the Mediterranean Sea
and the Black Sea
. Its range has expanded through the Suez Canal
to the northerly parts of the Indian Ocean
and the coasts of East Africa
. It burrows in soft substrates such as sand, gravel and shell fragments and is quite particular as to the size of the particles. It occurs from the low tide mark down to about 40 metres (130 ft).
, breeding takes place in June and July. The mature adult Branchiostoma lanceolatum, aged 2 to 3 years, congregate in masses on the sea floor. Individuals are either male or female and spawn once a year. The eggs are laid and fertilisation takes place externally. The early larval stages take place in the substrate but a little later, the larvae become pelagic. They are elongated and flattened laterally and have a swollen region around the gill
slits. These slits number 6 to 19, the number increasing as the larva passes through its various stages. The larvae have a vertical daily migration. Each evening they rise to near the surface of the sea and in the morning they sink through the water column, feeding on phytoplankton
, copepod
s and detritus
as they descend. While in these surface waters they drift with the current. The larval stage lasts for up to 200 days.
for studying the development of vertebrate
s. The way the coding genes and the two rRNA genes are organised is the same as the organisational method used by the sea lamprey
(Petromyzon marinus). These data, among others, suggest a close relationship between amphioxus and the vertebrates.
For use as a model organism, breeding can now be done in the laboratory. Adults can be induced to spawn by experiencing a thermal shock and can be encouraged to spawn several times a year. Metamorphosis
in the lab took place in 1 to 3 months.
Lancelet
The lancelets , also known as amphioxus, are the modern representatives of the subphylum Cephalochordata, formerly thought to be the sister group of the craniates. They are usually found buried in sand in shallow parts of temperate or tropical seas. In Asia, they are harvested commercially as food...
in the subphylum
Phylum
In biology, a phylum The term was coined by Georges Cuvier from Greek φῦλον phylon, "race, stock," related to φυλή phyle, "tribe, clan." is a taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. "Phylum" is equivalent to the botanical term division....
Cephalochordata
Cephalochordata
Cephalochordata is a chordate subphylum defined by the presence of a notochord that persists throughout life. It is represented in the modern oceans by the lancelets...
. It is a marine invertebrate
Invertebrate
An invertebrate is an animal without a backbone. The group includes 97% of all animal species – all animals except those in the chordate subphylum Vertebrata .Invertebrates form a paraphyletic group...
found in soft substrates in shallow seas. It is used as a model organism
Model organism
A model organism is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the organism model will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are in vivo models and are widely used to...
to study the development of vertebrate
Vertebrate
Vertebrates are animals that are members of the subphylum Vertebrata . Vertebrates are the largest group of chordates, with currently about 58,000 species described. Vertebrates include the jawless fishes, bony fishes, sharks and rays, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds...
s. The mitochondrial genome
Genome
In modern molecular biology and genetics, the genome is the entirety of an organism's hereditary information. It is encoded either in DNA or, for many types of virus, in RNA. The genome includes both the genes and the non-coding sequences of the DNA/RNA....
has been sequenced
Sequencing
In genetics and biochemistry, sequencing means to determine the primary structure of an unbranched biopolymer...
.
Description

Notochord
The notochord is a flexible, rod-shaped body found in embryos of all chordates. It is composed of cells derived from the mesoderm and defines the primitive axis of the embryo. In some chordates, it persists throughout life as the main axial support of the body, while in most vertebrates it becomes...
, extends the whole length of the body. Above it is a nerve cord with a single frontal eye. The mouth is on the underside of the body and is surrounded by a tuft of 20 or 30 cirri or slender sensory appendages. The gut runs just below the notochord from the mouth to the anus, in front of the tail. There is a flap-like, vertical fin surrounding the pointed tail. Gas exchange takes place as water passes through gill slits in the mid region, and segmented gonad
Gonad
The gonad is the organ that makes gametes. The gonads in males are the testes and the gonads in females are the ovaries. The product, gametes, are haploid germ cells. For example, spermatozoon and egg cells are gametes...
s lie just behind these. The animal is pearly white and semi-transparent which enables the internal organs to be seen from outside. Its appearance is similar to a "primitive fish". It can grow up to 6 cm (2.5 in) long.
Distribution and habitat
Branchiostoma lanceolatum is found in shallow seas in the north-east Atlantic OceanAtlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
, from Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
south to the Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
and the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
. Its range has expanded through the Suez Canal
Suez Canal
The Suez Canal , also known by the nickname "The Highway to India", is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea. Opened in November 1869 after 10 years of construction work, it allows water transportation between Europe and Asia without navigation...
to the northerly parts of the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
and the coasts of East Africa
East Africa
East Africa or Eastern Africa is the easterly region of the African continent, variably defined by geography or geopolitics. In the UN scheme of geographic regions, 19 territories constitute Eastern Africa:...
. It burrows in soft substrates such as sand, gravel and shell fragments and is quite particular as to the size of the particles. It occurs from the low tide mark down to about 40 metres (130 ft).
Biology
In the North SeaNorth Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
, breeding takes place in June and July. The mature adult Branchiostoma lanceolatum, aged 2 to 3 years, congregate in masses on the sea floor. Individuals are either male or female and spawn once a year. The eggs are laid and fertilisation takes place externally. The early larval stages take place in the substrate but a little later, the larvae become pelagic. They are elongated and flattened laterally and have a swollen region around the gill
Gill
A gill is a respiratory organ found in many aquatic organisms that extracts dissolved oxygen from water, afterward excreting carbon dioxide. The gills of some species such as hermit crabs have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist...
slits. These slits number 6 to 19, the number increasing as the larva passes through its various stages. The larvae have a vertical daily migration. Each evening they rise to near the surface of the sea and in the morning they sink through the water column, feeding on phytoplankton
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton are the autotrophic component of the plankton community. The name comes from the Greek words φυτόν , meaning "plant", and πλαγκτός , meaning "wanderer" or "drifter". Most phytoplankton are too small to be individually seen with the unaided eye...
, copepod
Copepod
Copepods are a group of small crustaceans found in the sea and nearly every freshwater habitat. Some species are planktonic , some are benthic , and some continental species may live in limno-terrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests,...
s and detritus
Detritus
Detritus is a biological term used to describe dead or waste organic material.Detritus may also refer to:* Detritus , a geological term used to describe the particles of rock produced by weathering...
as they descend. While in these surface waters they drift with the current. The larval stage lasts for up to 200 days.
Research
The mitochondrial genome of Branchiostoma lanceolatum has been sequenced, and the species serves as a model organismModel organism
A model organism is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the organism model will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are in vivo models and are widely used to...
for studying the development of vertebrate
Vertebrate
Vertebrates are animals that are members of the subphylum Vertebrata . Vertebrates are the largest group of chordates, with currently about 58,000 species described. Vertebrates include the jawless fishes, bony fishes, sharks and rays, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds...
s. The way the coding genes and the two rRNA genes are organised is the same as the organisational method used by the sea lamprey
Sea lamprey
The sea lamprey is a parasitic lamprey found on the Atlantic coasts of Europe and North America, in the western Mediterranean Sea, and in the Great Lakes. It is brown, gray, or black on its back and white or gray on the underside and can grow up to 90 cm long. Sea lampreys prey on a wide...
(Petromyzon marinus). These data, among others, suggest a close relationship between amphioxus and the vertebrates.
For use as a model organism, breeding can now be done in the laboratory. Adults can be induced to spawn by experiencing a thermal shock and can be encouraged to spawn several times a year. Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops after birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation...
in the lab took place in 1 to 3 months.

