
Brinkman number
Encyclopedia
The Brinkman number is a dimensionless number related to heat conduction from a wall to a flowing viscous fluid
, commonly used in polymer
processing. There are several definitions; one is
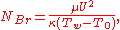
where
In, for example, a screw extruder, the energy supplied to the polymer melt comes primarily from two sources:
The former is supplied by the motor turning the screw, the latter by heaters. The Brinkman number is a measure of the ratio of the two.
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
, commonly used in polymer
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
processing. There are several definitions; one is
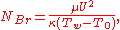
where
- NBr is the Brinkman number;
- μ is the fluid's dynamic viscosity;
- U is the fluid's velocity;
- κ is the thermal conductivityThermal conductivityIn physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
of the fluid; - T0 is the bulk fluid temperature;
- Tw is the wall temperature.
In, for example, a screw extruder, the energy supplied to the polymer melt comes primarily from two sources:
- viscous heat generated by shear between parts of the flow moving at different velocities;
- direct heat conduction from the wall of the extruder.
The former is supplied by the motor turning the screw, the latter by heaters. The Brinkman number is a measure of the ratio of the two.

