
British Association screw threads
Encyclopedia
British Association or BA screw threads are a largely obsolete set of small screw thread
s, the largest being 0BA at 6 mm diameter. They were, and to some extent still are, used for miniature instruments and modelling.
They are unusual in that they were probably the most "scientific" design of screw, with a basis in metric size (the 1 mm pitch and 6 mm diameter of 0BA) and with a mathematical relationship between the 'number' (e.g. 2BA with K=2) and the corresponding pitch, major diameter, and then spanner size. Though originally defined in terms of the imperial unit
s then in use in the United Kingdom, this was deliberately set to be exact multiples of the metric system
units, rounded to the nearest thousandth of an inch
. This anticipated worldwide metrication
by about a century. The design was first formulated in 1884, following a study of Swiss practice and was standardised in 1903.
The British Standards Institution recommended the use of BA sizes in place of the smaller BSW
and BSF
screws (those below 1/4"). Generally, the 0BA size was dropped in place of 7/32" BSF in assemblies that included larger fasteners, however, in smaller equipment that was primarily electronic/electrical the 0BA size would typically be used in place of the BSF or BSW screw where it was the largest size required.
BA threads are still used in some precision instruments, such as optics and moving-coil meters, relays etc. A 2BA thread is used to connect the head of a dart
to its shaft — as such, it is one of the few common uses of this thread in North America.
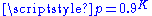 . The major diameter is given by
. The major diameter is given by 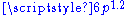 and the hex head size (across the flats) is 1.75 times the major diameter.
and the hex head size (across the flats) is 1.75 times the major diameter.
BA sizes are specified by the following British Standards
:
The shortening at the crest and root is given by 0.2681683p with a radius of 0.1808346p at both crest and root. The angle of the thread is 47.5 degrees which is different from that used by Whitworth (55 degrees) and ISO Metric (60 degrees) so BA fasteners are never interchangeable with Whitworth/Metric ones even when the pitch and diameter seem similar (e.g. 0BA which appears similar to M6x1mm). Standard BA sizes are defined between 0BA and 22BA. The very small sizes are not used very often and other standards tend to be used (e.g., NHS).
Screw thread
A screw thread, often shortened to thread, is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a straight thread and the latter called a tapered thread...
s, the largest being 0BA at 6 mm diameter. They were, and to some extent still are, used for miniature instruments and modelling.
They are unusual in that they were probably the most "scientific" design of screw, with a basis in metric size (the 1 mm pitch and 6 mm diameter of 0BA) and with a mathematical relationship between the 'number' (e.g. 2BA with K=2) and the corresponding pitch, major diameter, and then spanner size. Though originally defined in terms of the imperial unit
Imperial unit
The system of imperial units or the imperial system is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act of 1824, which was later refined and reduced. The system came into official use across the British Empire...
s then in use in the United Kingdom, this was deliberately set to be exact multiples of the metric system
Metric system
The metric system is an international decimalised system of measurement. France was first to adopt a metric system, in 1799, and a metric system is now the official system of measurement, used in almost every country in the world...
units, rounded to the nearest thousandth of an inch
Thou (unit of length)
A thou also known as a mil or point, is the verbalized abbreviation for "thousandth of an inch." It is a unit of length equal to 0.001 inch....
. This anticipated worldwide metrication
Metrication
Metrication refers to the introduction and use of the SI metric system, the international standard for physical measurements. This has involved a long process of independent and systematic conversions of countries from various local systems of weights and measures. Metrication began in France in...
by about a century. The design was first formulated in 1884, following a study of Swiss practice and was standardised in 1903.
The British Standards Institution recommended the use of BA sizes in place of the smaller BSW
British Standard Whitworth
British Standard Whitworth is one of a number of imperial unit based screw thread standards which use the same bolt heads and nut hexagonal sizes, the others being British Standard Fine thread and British Standard Cycle...
and BSF
British standard fine thread
British standard fine thread is a fine screw thread alternative to British Standard Whitworth thread.It is used for steel bolts and nuts on much British machinery, including automobiles, prior to adoption of the metric standards...
screws (those below 1/4"). Generally, the 0BA size was dropped in place of 7/32" BSF in assemblies that included larger fasteners, however, in smaller equipment that was primarily electronic/electrical the 0BA size would typically be used in place of the BSF or BSW screw where it was the largest size required.
BA threads are still used in some precision instruments, such as optics and moving-coil meters, relays etc. A 2BA thread is used to connect the head of a dart
Darts
Darts is a form of throwing game where darts are thrown at a circular target fixed to a wall. Though various boards and games have been used in the past, the term "darts" usually now refers to a standardised game involving a specific board design and set of rules...
to its shaft — as such, it is one of the few common uses of this thread in North America.
BA thread sizes
The pitch of 0BA is 1 mm and the pitch of each higher numbered thread is obtained by multiplying the pitch of the lower number by 0.9 so K-BA has a pitch of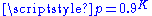 . The major diameter is given by
. The major diameter is given by 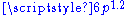 and the hex head size (across the flats) is 1.75 times the major diameter.
and the hex head size (across the flats) is 1.75 times the major diameter.BA sizes are specified by the following British Standards
British Standards
British Standards are the standards produced by BSI Group which is incorporated under a Royal Charter...
:
- BS 93:1951 — Specification for British Association (B.A.) screw threads with tolerances for sizes 0 B.A. to 16 B.A.
- BS 93:2008 — British Association (B.A.) screw threads. Requirements
The shortening at the crest and root is given by 0.2681683p with a radius of 0.1808346p at both crest and root. The angle of the thread is 47.5 degrees which is different from that used by Whitworth (55 degrees) and ISO Metric (60 degrees) so BA fasteners are never interchangeable with Whitworth/Metric ones even when the pitch and diameter seem similar (e.g. 0BA which appears similar to M6x1mm). Standard BA sizes are defined between 0BA and 22BA. The very small sizes are not used very often and other standards tend to be used (e.g., NHS).
| BA | Outer Diameter |
Threads per inch |
Threads per mm |
Tap drill |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.2362 in / 6 mm | 25.38 | 1 | 5.1 mm / 7 gauge |
| 1 | 0.2087 in / 5.3 mm | 28.25 | 1.112 | 4.5 mm / 16 gauge |
| 2 | 0.1850 in / 4.7 mm | 31.35 | 1.234 | 4.0 mm / 21 gauge |
| 3 | 0.1614 in / 4.1 mm | 34.84 | 1.372 | 3.4 mm |
| 4 | 0.1417 in / 3.6 mm | 38.46 | 1.514 | 3.0 mm |
| 5 | 0.1260 in / 3.2 mm | 43.10 | 1.697 | 2.65 mm / 37 gauge |
| 6 | 0.1102 in / 2.8 mm | 47.85 | 1.884 | 2.3 mm |
| 7 | 0.0984 in / 2.5 mm | 52.91 | 2.083 | 2.05 mm / 46 gauge |
| 8 | 0.0866 in / 2.2 mm | 59.17 | 2.330 | 1.8 mm |
| 9 | 0.0748 in / 1.9 mm | 64.94 | 2.557 | 1.55 mm |
| 10 | 0.0669 in / 1.7 mm | 72.46 | 2.853 | 1.4 mm / 54 gauge |
| 11 | 0.0591 in / 1.5 mm | 81.97 | 3.227 | 1.2 mm |
| 12 | 0.0511 in / 1.3 mm | 90.91 | 3.579 | 1.05 mm |
External links
- Bolt Science writeup.
- Early history of non-metric bolts including BA and Whitworth.
- Table of thread dimensions
- Recommended ISO substitutions
- Useful comparison of obsolete British threads

