
Brodmann area 8
Encyclopedia
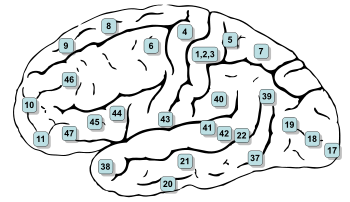
Brodmann
Brodmann may refer to:* Korbinian Brodmann, German neurologist* Brodmann area, a region in the brain cortex...
's cytologically defined regions of the brain. It is involved in planning complex movements.
Human
Brodmann area 8, or BA8, is part of the frontalFrontal lobe
The frontal lobe is an area in the brain of humans and other mammals, located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere and positioned anterior to the parietal lobe and superior and anterior to the temporal lobes...
cortex
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain. It plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. It is constituted of up to six horizontal layers, each of which has a different...
in the human brain
Human brain
The human brain has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times larger than the brain of a typical mammal with an equivalent body size. Estimates for the number of neurons in the human brain range from 80 to 120 billion...
. Situated just anterior to the premotor cortex (BA6
Brodmann area 6
- Human :Brodmann area 6 is part of the frontal cortex in the human brain. Situated just anterior to the primary motor cortex , it is composed of the premotor cortex and, medially, the supplementary motor area, or SMA...
), it includes the frontal eye fields
Frontal eye fields
The frontal eye fields is a region located in the premotor cortex, which is part of the frontal cortex of the primate brain.-Function:...
(so-named because they are believed to play an important role in the control of eye movements). Damage to this area, by stroke, trauma or infection, causes tonic deviation of the eyes towards the side of the injury. This finding occurs during the first few hours of an acute event such as cerebrovascular infarct (stroke) or hemorrhage (bleeding).
Guenon
The term Brodmann area 8 refers to a cytoarchitecturally defined portion of the frontal lobe of the guenonGuenon
The guenons are the genus Cercopithecus of Old World monkeys. Not all the members of this genus have the word "guenon" in their common names, and because of changes in scientific classification, some monkeys in other genera may have common names that do include the word "guenon"...
. Located rostral to the arcuate sulcus, it was not considered by Brodmann-1909 to be topographically homologous
Homology (biology)
Homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. In 1843, Richard Owen defined homology as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function". Organs as different as a bat's wing, a seal's flipper, a cat's paw and a human hand have a common underlying...
to the intermediate frontal area 8 of the human.
Distinctive features
Distinctive features (Brodmann-1905): compared to Brodmann area 6Brodmann area 6
- Human :Brodmann area 6 is part of the frontal cortex in the human brain. Situated just anterior to the primary motor cortex , it is composed of the premotor cortex and, medially, the supplementary motor area, or SMA...
-1909, area 8 has a diffuse but clearly present internal granular layer
Granular layer
The term granular layer may refer to:*the granular layer of Tomes, seen in dentin of the teeth. When dry section of the root dentin of teeth are visualized under transmitted light, a granular layer is seen adjacent to cementum.It is believed to be caused by coalescing & looping of terminal portion...
(IV); sublayer 3b of the external pyramidal layer (III) has densely distributed medium sized pyramidal cell
Pyramidal cell
Pyramidal neurons are a type of neuron found in areas of the brain including cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and in the amygdala. Pyramidal neurons are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cortex and the corticospinal tract. Pyramidal neurons were first discovered and...
s; the internal pyramidal layer (V) has larger ganglion cell
Ganglion cell
A retinal ganglion cell is a type of neuron located near the inner surface of the retina of the eye. It receives visual information from photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: bipolar cells and amacrine cells...
s densely distributed with some granule cell
Granule cell
In neuroscience, granule cells refer to tiny neurons that are around 10 micrometres in diameter. Granule cells are found within the granular layer of the cerebellum , the dentate gyrus of the...
s interspersed; the external granular layer (II) is denser and broader; cell layers are more distinct; the abundance of cells is somewhat greater.
Functions
The area is involved in the management of uncertainty. A functional magnetic resonance imaging study demonstrated that brodmann area 8 activation occurs when test subjects experience uncertainty, and that with increasing uncertainty there is increasing activation.An alternative interpretation is that this activation in frontal cortex encodes hope, a higher-order expectation positively correlated with uncertainty.
See also
- Brodmann areaBrodmann areaA Brodmann area is a region of the cerebral cortex defined based on its cytoarchitectonics, or structure and organization of cells.-History:...
- List of regions in the human brain

