
Capture of Fort Rocher
Encyclopedia
The Capture of Fort Rocher took place on 9 February 1654, during the Anglo-Spanish War
. Equipped with one siege battery, a Spanish expedition of 700 troops attacked the buccaneer stronghold of Tortuga, capturing the fort and 500 prisoners including 330 buccaneers and goods valued at approximately 160,000 pieces-of-eight. The Spanish burned the colony to the ground and slaughtered its inhabitants, leaving behind a fort manned by 150 soldiers. They possessed the island for about eighteen months, but on the approach of the expedition under Penn and Venerables
were ordered by the Conde de Peñalva, Governor of Santo Domingo, to demolish the fortifications, bury the artillery and other arms, and retire to his aid
in Hispaniola
.
counterattack had been prompted by the buccaneers’ sack of Santiago de los Caballeros, in 1650, and that of the Cuban port of San Juan de los Remedios on August 1652. Consequently, a punitive expedition had slipped out of the capital of Santo Domingo on 4 December 1653, bearing 200 soldiers and 500 volunteers under Captain Gabriel de Rojas y Figueroa, seconded by the former Irish renegade John Murphy (promoted to maestre de campo and invested with a knighthood in the Order of Santiago
. This Spanish squadron had captured a trio of buccaneer craft off Monte Cristi before sighting Tortuga.
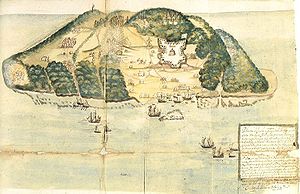 The buccaneer fort was built by a skilled French engineer on a rocky hill which dominated the island harbour of Cayenne. By 18 February the French and English requested terms and two days later the Chavalier de Fontenay decided to surrender. More than 500 captives were captured, among them 330 boucaniers. All were allowed to sail to France aboard a pair of ships under de Fontenay and Tibaut and Martin, respectively—with the exception of two leaders who were kept as hostages; the Spanish seized 70 cannons in the fortress and shore batteries, three ships, a frigate, and eight lesser craft as booty. These attackers also decided to hold their hard-won conquest by leaving behind a garrison of one hundred men under the Irish-born Murphy.
The buccaneer fort was built by a skilled French engineer on a rocky hill which dominated the island harbour of Cayenne. By 18 February the French and English requested terms and two days later the Chavalier de Fontenay decided to surrender. More than 500 captives were captured, among them 330 boucaniers. All were allowed to sail to France aboard a pair of ships under de Fontenay and Tibaut and Martin, respectively—with the exception of two leaders who were kept as hostages; the Spanish seized 70 cannons in the fortress and shore batteries, three ships, a frigate, and eight lesser craft as booty. These attackers also decided to hold their hard-won conquest by leaving behind a garrison of one hundred men under the Irish-born Murphy.
Hoping that the Spanish had abandoned the island, three buccaneer ships returned in August, but found that the Spaniards had already installed a garrison. However, coinciding with the English invasion of Hispaniola, on 13 September 1654 Spanish governor issued a real cédula ordering the withdrawal from Tortuga after first throwing down its fortifications. Tortuga was reoccupied the next year by English and French interlopers under Elias Watts, who secured a commission from Col. William Brayne, acting as military Governor on Jamaica, to serve as "Governor" of Tortuga.
Anglo-Spanish War (1654)
The Anglo-Spanish War was a conflict between the English Protectorate of Oliver Cromwell and Spain, between 1654 and 1660. It was caused by commercial rivalry. Each side attacked the other's commercial and colonial interests in various ways such as privateering and naval expeditions. In 1655, an...
. Equipped with one siege battery, a Spanish expedition of 700 troops attacked the buccaneer stronghold of Tortuga, capturing the fort and 500 prisoners including 330 buccaneers and goods valued at approximately 160,000 pieces-of-eight. The Spanish burned the colony to the ground and slaughtered its inhabitants, leaving behind a fort manned by 150 soldiers. They possessed the island for about eighteen months, but on the approach of the expedition under Penn and Venerables
Robert Venables
Robert Venables , was a soldier during the English Civil War and noted angler.Venables was lieutenant-colonel in the parliamentary army. He was wounded at Chester in 1645. He was appointed governor of Liverpool in 1648. He served with success in Ireland from 1649 until 1654...
were ordered by the Conde de Peñalva, Governor of Santo Domingo, to demolish the fortifications, bury the artillery and other arms, and retire to his aid
Siege of Santo Domingo (1655)
The Siege of Santo Domingo of 1655, was fought between April 23, 1655 to April 30, 1655 at the Spanish Colony of Santo Domingo. A force of 2,400 Spanish troops led by Governor Don Bernardino Meneses y Bracamonte, Count of Peñalba, successfully resisted a force of 13,120 troops and 34 ships of the...
in Hispaniola
Hispaniola
Hispaniola is a major island in the Caribbean, containing the two sovereign states of the Dominican Republic and Haiti. The island is located between the islands of Cuba to the west and Puerto Rico to the east, within the hurricane belt...
.
Background
At midday, the French and English inhabitants of Tortuga sighted four Spanish vessels bearing down. Thiscounterattack had been prompted by the buccaneers’ sack of Santiago de los Caballeros, in 1650, and that of the Cuban port of San Juan de los Remedios on August 1652. Consequently, a punitive expedition had slipped out of the capital of Santo Domingo on 4 December 1653, bearing 200 soldiers and 500 volunteers under Captain Gabriel de Rojas y Figueroa, seconded by the former Irish renegade John Murphy (promoted to maestre de campo and invested with a knighthood in the Order of Santiago
Order of Santiago
The Order of Santiago was founded in the 12th century, and owes its name to the national patron of Galicia and Spain, Santiago , under whose banner the Christians of Galicia and Asturias began in the 9th century to combat and drive back the Muslims of the Iberian Peninsula.-History:Santiago de...
. This Spanish squadron had captured a trio of buccaneer craft off Monte Cristi before sighting Tortuga.
Capture
Gliding past its harbor, the Spaniards bombarded the vessels in the roads, then continued two or three miles farther down the coast and disembarked several hundred troops at the hamlet of Cayonne, marching back to besiege the island’s principal fortress. On the night of 12 February, Rojas sent a company with grappling lines to scale the heights behind the keep and install siege artillery.
Aftermath
The prisoners were shipped to Santo Domingo and would become slaves on Spanish plantations.Hoping that the Spanish had abandoned the island, three buccaneer ships returned in August, but found that the Spaniards had already installed a garrison. However, coinciding with the English invasion of Hispaniola, on 13 September 1654 Spanish governor issued a real cédula ordering the withdrawal from Tortuga after first throwing down its fortifications. Tortuga was reoccupied the next year by English and French interlopers under Elias Watts, who secured a commission from Col. William Brayne, acting as military Governor on Jamaica, to serve as "Governor" of Tortuga.

