
Cardiac index
Encyclopedia
Cardiac index is a vasodynamic parameter that relates the cardiac output
(CO) to body surface area (BSA), thus relating heart performance to the size of the individual. The unit of measurement is litre
s per minute
per square metre (l/min/m2).
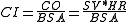
where
If the CI falls below 1.8 L/min/m², the patient may be in cardiogenic shock
.
Cardiac output
Cardiac output is the volume of blood being pumped by the heart, in particular by a left or right ventricle in the time interval of one minute. CO may be measured in many ways, for example dm3/min...
(CO) to body surface area (BSA), thus relating heart performance to the size of the individual. The unit of measurement is litre
Litre
pic|200px|right|thumb|One litre is equivalent to this cubeEach side is 10 cm1 litre water = 1 kilogram water The litre is a metric system unit of volume equal to 1 cubic decimetre , to 1,000 cubic centimetres , and to 1/1,000 cubic metre...
s per minute
Minute
A minute is a unit of measurement of time or of angle. The minute is a unit of time equal to 1/60th of an hour or 60 seconds. In the UTC time scale, a minute on rare occasions has 59 or 61 seconds; see leap second. The minute is not an SI unit; however, it is accepted for use with SI units...
per square metre (l/min/m2).
Calculation
The index is usually calculated using the following formula: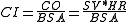
where
- CI=Cardiac index
- BSA=Body surface areaBody surface areaIn physiology and medicine, the body surface area is the measured or calculated surface of a human body. For many clinical purposes BSA is a better indicator of metabolic mass than body weight because it is less affected by abnormal adipose mass...
- SV=Stroke volumeStroke volumeIn cardiovascular physiology, stroke volume is the volume of blood pumped from one ventricle of the heart with each beat. SV is calculated using measurements of ventricle volumes from an echocardiogram and subtracting the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of a beat from the volume...
- HR=Heart rateHeart rateHeart rate is the number of heartbeats per unit of time, typically expressed as beats per minute . Heart rate can vary as the body's need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide changes, such as during exercise or sleep....
- CO=Cardiac outputCardiac outputCardiac output is the volume of blood being pumped by the heart, in particular by a left or right ventricle in the time interval of one minute. CO may be measured in many ways, for example dm3/min...
Clinical significance
The normal range of cardiac index is 2.6 - 4.2 L/min per square meter.If the CI falls below 1.8 L/min/m², the patient may be in cardiogenic shock
Cardiogenic shock
Cardiogenic shock is based upon an inadequate circulation of blood due to primary failure of the ventricles of the heart to function effectively....
.

