Cardiothoracic anesthesiology
Encyclopedia
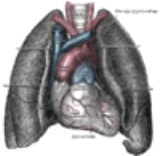
Cardiothoracic anesthesiology is a subspeciality of the medical practice of anesthesiology
devoted to the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care of adult patients undergoing cardiothoracic surgery and related invasive procedures. It is the most intellectually challenging and demanding subspecialty in anesthesiology.
It deals with the anesthesia
aspects of care related to surgical
cases such as, but not limited to, open heart surgery
, lung
surgery, and other operations of the human chest
.
Most cardiac procedures require a machine that takes over the functions of the heart and lungs while the heart is repaired. The responsibility of a cardiovascular and thoracic (CVT) anesthesiologist is to supervise the "bypass" (or heart-lung) machine and to control the patient's physiology (blood pressure, pulse, respiration, fluid status, temperature, coagulation, etc.) and manage any problems that may arise through use of invasive monitors and pharmacology during the pre- and post- bypass portions of the case, as well as in the cardiothoracic intensive care unit.
 After satisfactory completion of Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) accredited residency
After satisfactory completion of Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) accredited residency
program in anesthesiology formal advanced training in cardiac, vascular, and thoracic anesthesia is available via a one-year fellowship
.http://anesthesiology.med.miami.edu/x161.xmlhttp://www.scahq.org/sca3/fellowships/.The Adult Cardiothoracic Anesthesiology fellowship program has been Governed by Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesioloist http://www.scahq.org/ which is an international organization of over 6000 cardiac, vascular and thoracic anesthesiologists. Adult Cardiothoracic Anesthesiology became an ACGME approved fellowship in 2006 and there are 44 ACGME accredited programs for current academic year(2008–2009).
This fellowship consists of at least eight months of adult cardiothoracic anesthesiology, one month dedicated to transesophageal echocardiography, one month in surgical intensive care unit and two months of elective rotation which includes inpatient or outpatient cardiology or pulmonary medicine, invasive cardiology, medical or surgical critical care and extracorporeal perfusion technology.
Fellows are trained to provide anesthesia for Coronary artery bypass surgery
(CABG) on CPB and on beating heart, valvular heart surgery, aortic surgeries, heart transplant, lung transplant, heart and lung transplant. Adequate exposure and experience provided in the management of adult patients for cardiac pacemaker and automatic implantable cardiac defibrillator placement, surgical treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. The fellow will gain sufficient experience to independently manage intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation and patients with ventricular assist devices. The Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory will enable the fellow to gain expertise in the care of patients undergoing invasive cardiologic and electrophysiologic therapies.
Additional clinical experience within the full one-year fellowship will include anesthetic management of adult patients undergoing thoracic and vascular surgery. Fellows are trained to manage all type of thoracic surgeries which include video assisted thoracoscopy (VAT ),Thoracotomy and aortic surgery. Fellows will achieve expertise in different techniques of lung isolation like Double-lumen endotracheal tube, bronchial blocker, Univent Tube under guidance of fiber optic bronchoscopy
Fellows are trained to achieve expertise in the advanced monitoring techniques including but not limited to invasive blood pressure, arterial blood gas analysis, pulmonary artery catheterisation, cardiac output monitoring, cerebral oximetry, jugular venous oxygen saturation, cerebral oximetry, Bispectral Index (BIS), Transcranial doppler (TCD), Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Additional clinical experience during this fellowship include successful completion of advanced perioperative echocardiography education according to training guidelines from American society of Echocardiography and Society of cardiovascular Anesthesisologists.
Fellow conferences are held once a week to discuss interesting cases and review selected topics relevant to cardiothoracic anesthesia & intraoperative TEE.
Fellows are trained to manage cardiothoracic cases in the postoperative care unit.
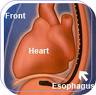
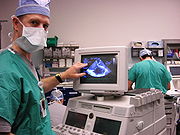
 Echocardiogram is basically a sonography which produces a real-time image of the heart by using standard ultrasound technique. There are two way of performing echocardiography depending on placement of echocardiography probe. One is Transthoracic echocardiography(TTE) in which the probe is placed over the patient chest wall, also called standard echocardiography, and other is transesophageal echocardiography or TEE (called TOE in the UK), in which the probe is placed into the patient's esophagus. The probe contains a transducer; when transmitting it converts electrical energy to acoustic energy, and when receiving it converts acoustic energy to electrical energy, which is processed by the machine in forming an image. The direction of flow and velocity of blood can be assessed by using Doppler ultrasound.
Echocardiogram is basically a sonography which produces a real-time image of the heart by using standard ultrasound technique. There are two way of performing echocardiography depending on placement of echocardiography probe. One is Transthoracic echocardiography(TTE) in which the probe is placed over the patient chest wall, also called standard echocardiography, and other is transesophageal echocardiography or TEE (called TOE in the UK), in which the probe is placed into the patient's esophagus. The probe contains a transducer; when transmitting it converts electrical energy to acoustic energy, and when receiving it converts acoustic energy to electrical energy, which is processed by the machine in forming an image. The direction of flow and velocity of blood can be assessed by using Doppler ultrasound.
Transoesophageal echocardiography (TEE) has rapidly become the most powerful monitoring technique and diagnostic tool for the management of cardiac surgical patients. It provides the detailed information about the structure and function of heart and great vessels. Because of the proximity of esophagus to heart TEE provide better image of heart as compare to standard echocardiography (TTE).
TEE provides timely information about filling status, systolic and diastolic function, valvular function, presence of fluid in pericardial cavity and state of great vessels. TEE has significant influence on surgical and medical decision making, which may lead to changes in therapy.
After successful completion of the fellowship with subspecialty training in TEE, the fellows are eligble for board certification for perioperative Transesophageal Echocardiography Examination ( PTEeXAM ) http://www.echoboards.org/pte/exam.html offered by the National Board of Echocardiography (NBE).
http://www.echoboards.org/pte/exam.html.
Fellows need to perform and interpret at least 150 comprehensive intraoperative TEE examination in order to apply for Advanced PTEexam Board certification.
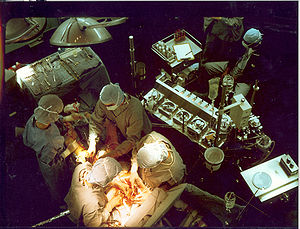
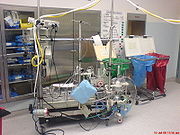 Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a technique in which heart-lung machine temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during surgery. This machine drains deoxygenated blood from the patient, oxygenates and pumps it back into the arterial system thereby bypassing the heart and lungs and maintaining the perfusion of the vital organs. CPB is team effort including the cardiac surgeon, perfusionist, and anesthesiologist.
Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a technique in which heart-lung machine temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during surgery. This machine drains deoxygenated blood from the patient, oxygenates and pumps it back into the arterial system thereby bypassing the heart and lungs and maintaining the perfusion of the vital organs. CPB is team effort including the cardiac surgeon, perfusionist, and anesthesiologist.
The surgeon places a cannula in right atrium, vena cava, or femoral vein to withdraw blood from the body. Venous blood that is removed from the body by the cannula is filtered, oxygenated, cooled or warmed, and then returned to the body. The cannula used to return oxygenated blood is usually inserted in the ascending aorta, but it may be inserted in the femoral artery.
The management of the patient undergoing cardiopulmonay bypass (CPB) is one of the defining characteristics of cardiac anesthesia. This demands that the cardiac anesthesiologist have a thorough knowledge of the basic physiology, principles, practical application and management of CPB.
For the cardiac anesthesiologist it is convenient to think of cardiac operations requiring CPB as occurring in six sequential phases: 1) pre bypass period; 2) initiation of bypass; 3) maintenance of bypass; 4) preparation for separation: 5) separation from bypass; and 6) postbypass period.
The main objective of pre bypass period is to prepare patient for CPB which include anticoagulation and vascular cannulation. A prebypass TEE evaluation of the heart give anesthesiologist valuable information regarding the management of patient in the post bypass period.
Once all preparatory steps have been taken, and CPB initiated, the anesthesiologist has to monitor this transition and assess whether CPB is adequate, and when it is, has to discontinue ventilation of the patient’s lungs. When CPB machine takes over the function of heart and lung, the primary objective is to maintain adequate perfusion to the vital organs. During this period the anesthesiologist should ascertain that the patient is adequately anesthetised, as chances of awareness are quite high during bypass.
Emergence from bypass is the most crucial period when clear communication between surgeon, perfusionist and anesthesiologist is required. Prior to discontinuation of CPB, temperature, acid base status, hematocrite etc. must be restored for optimal cardiac and pulmonary function. At this stage anesthesiologist makes functional assessment of the heart and peripheral vasculature based on visual inspection, hemodynamic indices, and metabolic parameters. Based on this assessment, inotropes, vasodilators, and vasopressers should be prepared.
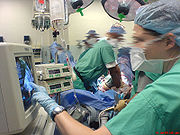 Cardiac anesthesiologists not only provide anesthesia care for cardiac surgery
Cardiac anesthesiologists not only provide anesthesia care for cardiac surgery
, they also have specific role in providing anesthesia care for patients having complex cardiac disease like valvular heart disease, adult congenital heart disease, congestive heart failure etc.undergoing non-cardiac surgery.
Patient with cardiac disease presenting for non-cardiac surgery are at increase risk for serious perioperative complication including myocardial infarction , arrythmia , pulmonary edema. The cardiac anesthesiologist is able to give expert opinion during intraoperative hemodynamic instability/cardiac arrest
by evaluating heart function with the help of TEE and advanced hemodynamic monitering.
Anesthesiologist
An anesthesiologist or anaesthetist is a physician trained in anesthesia and peri-operative medicine....
devoted to the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care of adult patients undergoing cardiothoracic surgery and related invasive procedures. It is the most intellectually challenging and demanding subspecialty in anesthesiology.
It deals with the anesthesia
Anesthesia
Anesthesia, or anaesthesia , traditionally meant the condition of having sensation blocked or temporarily taken away...
aspects of care related to surgical
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
cases such as, but not limited to, open heart surgery
Open Heart Surgery
Open Heart Surgery was released on August 8, 2000 by rock band Virginwool. The band signed to Breaking/Atlantic Records after initially beginning signed to Universal Records. The album was produced and mixed by Brad Wood....
, lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
surgery, and other operations of the human chest
Chest
The chest is a part of the anatomy of humans and various other animals. It is sometimes referred to as the thorax or the bosom.-Chest anatomy - Humans and other hominids:...
.
Most cardiac procedures require a machine that takes over the functions of the heart and lungs while the heart is repaired. The responsibility of a cardiovascular and thoracic (CVT) anesthesiologist is to supervise the "bypass" (or heart-lung) machine and to control the patient's physiology (blood pressure, pulse, respiration, fluid status, temperature, coagulation, etc.) and manage any problems that may arise through use of invasive monitors and pharmacology during the pre- and post- bypass portions of the case, as well as in the cardiothoracic intensive care unit.

CVT fellowship (U.S.)

Residency (medicine)
Residency is a stage of graduate medical training. A resident physician or resident is a person who has received a medical degree , Podiatric degree , Dental Degree and who practices...
program in anesthesiology formal advanced training in cardiac, vascular, and thoracic anesthesia is available via a one-year fellowship
Fellowship (medicine)
A fellowship is the period of medical training in the United States and Canada that a physician may undertake after completing a specialty training program . During this time , the physician is known as a fellow...
.http://anesthesiology.med.miami.edu/x161.xmlhttp://www.scahq.org/sca3/fellowships/.The Adult Cardiothoracic Anesthesiology fellowship program has been Governed by Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesioloist http://www.scahq.org/ which is an international organization of over 6000 cardiac, vascular and thoracic anesthesiologists. Adult Cardiothoracic Anesthesiology became an ACGME approved fellowship in 2006 and there are 44 ACGME accredited programs for current academic year(2008–2009).
This fellowship consists of at least eight months of adult cardiothoracic anesthesiology, one month dedicated to transesophageal echocardiography, one month in surgical intensive care unit and two months of elective rotation which includes inpatient or outpatient cardiology or pulmonary medicine, invasive cardiology, medical or surgical critical care and extracorporeal perfusion technology.
Fellows are trained to provide anesthesia for Coronary artery bypass surgery
Coronary artery bypass surgery
Coronary artery bypass surgery, also coronary artery bypass graft surgery, and colloquially heart bypass or bypass surgery is a surgical procedure performed to relieve angina and reduce the risk of death from coronary artery disease...
(CABG) on CPB and on beating heart, valvular heart surgery, aortic surgeries, heart transplant, lung transplant, heart and lung transplant. Adequate exposure and experience provided in the management of adult patients for cardiac pacemaker and automatic implantable cardiac defibrillator placement, surgical treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. The fellow will gain sufficient experience to independently manage intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation and patients with ventricular assist devices. The Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory will enable the fellow to gain expertise in the care of patients undergoing invasive cardiologic and electrophysiologic therapies.
Additional clinical experience within the full one-year fellowship will include anesthetic management of adult patients undergoing thoracic and vascular surgery. Fellows are trained to manage all type of thoracic surgeries which include video assisted thoracoscopy (VAT ),Thoracotomy and aortic surgery. Fellows will achieve expertise in different techniques of lung isolation like Double-lumen endotracheal tube, bronchial blocker, Univent Tube under guidance of fiber optic bronchoscopy
Fellows are trained to achieve expertise in the advanced monitoring techniques including but not limited to invasive blood pressure, arterial blood gas analysis, pulmonary artery catheterisation, cardiac output monitoring, cerebral oximetry, jugular venous oxygen saturation, cerebral oximetry, Bispectral Index (BIS), Transcranial doppler (TCD), Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Additional clinical experience during this fellowship include successful completion of advanced perioperative echocardiography education according to training guidelines from American society of Echocardiography and Society of cardiovascular Anesthesisologists.
Fellow conferences are held once a week to discuss interesting cases and review selected topics relevant to cardiothoracic anesthesia & intraoperative TEE.
Fellows are trained to manage cardiothoracic cases in the postoperative care unit.
Research
The recent developments in cardiac surgery expanded the scope of research including neuroprotection, myocardial protection, blood conservation strategies, port access surgery in this young subspeciality. Fellows are offered the opportunity to participate in clinical research and encouraged to present at national or international conference after completion of a research project.Ultrasound - TEE



Transoesophageal echocardiography (TEE) has rapidly become the most powerful monitoring technique and diagnostic tool for the management of cardiac surgical patients. It provides the detailed information about the structure and function of heart and great vessels. Because of the proximity of esophagus to heart TEE provide better image of heart as compare to standard echocardiography (TTE).
TEE provides timely information about filling status, systolic and diastolic function, valvular function, presence of fluid in pericardial cavity and state of great vessels. TEE has significant influence on surgical and medical decision making, which may lead to changes in therapy.
After successful completion of the fellowship with subspecialty training in TEE, the fellows are eligble for board certification for perioperative Transesophageal Echocardiography Examination ( PTEeXAM ) http://www.echoboards.org/pte/exam.html offered by the National Board of Echocardiography (NBE).
http://www.echoboards.org/pte/exam.html.
Fellows need to perform and interpret at least 150 comprehensive intraoperative TEE examination in order to apply for Advanced PTEexam Board certification.
Cardio-pulmonary bypass (CPB)



The surgeon places a cannula in right atrium, vena cava, or femoral vein to withdraw blood from the body. Venous blood that is removed from the body by the cannula is filtered, oxygenated, cooled or warmed, and then returned to the body. The cannula used to return oxygenated blood is usually inserted in the ascending aorta, but it may be inserted in the femoral artery.
The management of the patient undergoing cardiopulmonay bypass (CPB) is one of the defining characteristics of cardiac anesthesia. This demands that the cardiac anesthesiologist have a thorough knowledge of the basic physiology, principles, practical application and management of CPB.
For the cardiac anesthesiologist it is convenient to think of cardiac operations requiring CPB as occurring in six sequential phases: 1) pre bypass period; 2) initiation of bypass; 3) maintenance of bypass; 4) preparation for separation: 5) separation from bypass; and 6) postbypass period.
The main objective of pre bypass period is to prepare patient for CPB which include anticoagulation and vascular cannulation. A prebypass TEE evaluation of the heart give anesthesiologist valuable information regarding the management of patient in the post bypass period.
Once all preparatory steps have been taken, and CPB initiated, the anesthesiologist has to monitor this transition and assess whether CPB is adequate, and when it is, has to discontinue ventilation of the patient’s lungs. When CPB machine takes over the function of heart and lung, the primary objective is to maintain adequate perfusion to the vital organs. During this period the anesthesiologist should ascertain that the patient is adequately anesthetised, as chances of awareness are quite high during bypass.
Emergence from bypass is the most crucial period when clear communication between surgeon, perfusionist and anesthesiologist is required. Prior to discontinuation of CPB, temperature, acid base status, hematocrite etc. must be restored for optimal cardiac and pulmonary function. At this stage anesthesiologist makes functional assessment of the heart and peripheral vasculature based on visual inspection, hemodynamic indices, and metabolic parameters. Based on this assessment, inotropes, vasodilators, and vasopressers should be prepared.
Role of cardiac anesthesiologists in non-cardiac surgery

Cardiac surgery
Cardiovascular surgery is surgery on the heart or great vessels performed by cardiac surgeons. Frequently, it is done to treat complications of ischemic heart disease , correct congenital heart disease, or treat valvular heart disease from various causes including endocarditis, rheumatic heart...
, they also have specific role in providing anesthesia care for patients having complex cardiac disease like valvular heart disease, adult congenital heart disease, congestive heart failure etc.undergoing non-cardiac surgery.
Patient with cardiac disease presenting for non-cardiac surgery are at increase risk for serious perioperative complication including myocardial infarction , arrythmia , pulmonary edema. The cardiac anesthesiologist is able to give expert opinion during intraoperative hemodynamic instability/cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest, is the cessation of normal circulation of the blood due to failure of the heart to contract effectively...
by evaluating heart function with the help of TEE and advanced hemodynamic monitering.
External links
- Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists
- Cardiothoracic & Vascular Anesthesia Fellowship Programs
- American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) Home Page
- Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia (JCTVA)
- Annals of Cardiac Anaesthesia (ACA)
- NBE/SCA Examination of Special Competence in Perioperative Transesophageal Echocardiography (PTEeXAM)
- ASA TEE Practice Guidelines
- VIRTUAL TEE, an educational resource for learning about TEE (rich media including Flash support required)
- ASA PAC Practice Guidelines

