
Caroli disease
Encyclopedia
Caroli disease is a rare inherited disorder characterized by dilatation of the intrahepatic bile ducts. There are two types of Caroli disease, the most common being the simple, or isolated case where the bile ducts are widened by ectasia
. The second, more complex, cause is commonly known as Caroli Syndrome. This complex form is also linked with portal hypertension
and congenital hepatic fibrosis
.
The differences between the causes of the two cases have not yet been discovered. Caroli disease is also associated with liver failure
and polycystic kidney disease. The disease affects about 1 in 1,000,000 people, with more reported cases of Caroli syndrome than of Caroli disease.
Caroli disease also is known as communicating cavernous ectasia, or congenital cystic dilatation of the intrahepatic biliary tree
. Caroli disease is distinct from other diseases that cause ductal dilatation caused by obstruction, in that it is not one of the many choledochal cyst derivatives.
, France
.
He described it as "nonobstructive saccular or fusiform multi-focal segmental dilatation of the intra-hepatic bile ducts"; basically, he observed cavernous ectasia in the biliary tree causing a chronic, often life-threatening hepatobiliary disease.
Caroli, born in France
in 1902, learned and practiced medicine in Angers
. After World War II
he was chief of service for 30 years at Saint-Antoine
in Paris
. Before dying in 1979, he was honored with the rank of commander in the Legion of Honour in 1976.
, intermittent abdominal pain
, and hepatomegaly
. Occasionally jaundice
occurs.
Caroli disease usually occurs in the presence of other diseases, such as autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
, cholangitis, gallstones, bilary abscess, septicemia, liver cirrhosis
, renal failure
, and cholangiocarcinoma
(7% affected). People with Caroli disease are 100 times more at risk for cholangiocarcinoma than the general population. After recognizing symptoms of related diseases, Caroli disease can be diagnosed.
, or MRI will show enlarged intrahepatic (in the liver) bile ducts due to ectasia. Using an ultrasound
, tubular dilation of the bile ducts can be seen. On a CT-Scan, Caroli disease can be observed by noting the many fluid-filled, tubular structures extending to the liver. A high contrast CT must be used to distinguish the difference between stones and widened ducts. Bowel gas and digestive habits make it difficult to obtain a clear sonogram
, therefore, a CT scan is a good substitution. When the intrahepatic bile duct wall has protrusions, it is clearly seen as central dots or a linear streak. Caroli disease is commonly diagnosed after this “central dot sign” is detected on a CT scan or ultrasound. However, cholangiography
is the best, and final, approach to show the enlarged bile ducts as a result of Caroli disease.
and diagnosed in persons under the age of 22. Cases have also been found in both infants and adults. As medical imaging technology improves, diagnostic age decreases. Morbidity is common and is caused by complications of cholangitis, sepsis
, choledocholithiasis, and cholangiocarcinoma
. These morbid conditions often prompt the diagnosis. Portal hypertension may be present, resulting in other conditions including splenomegaly
, hematemesis
and melena
. These problems can severely affect the patient's quality of life. In a ten year period between 1995 and 2005, only ten patients were surgically treated for Caroli disease, with an average patient age of 45.8 years.
After reviewing 46 cases of Caroli disease before 1990, it was found that 21.7% of the cases were the result of an intraheptic cyst or non-obstructive biliary tree dilation, 34.7% were linked with congenital hepatic fibrosis
, 13% were isolated choledochal cystic dilation, and the remaining 24.6% had a combination of all three.
Mortality is indirect and caused by complications. After cholangitis occurs, patients typically die within approximately 5–10 years.
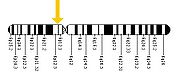 The cause appears to be genetic; the simple form is an autosomal dominant trait while the complex form is an autosomal recessive trait. Females are more prone to Caroli disease than males. Family history may include kidney and liver disease due to the link between Caroli Disease and ARPKD. PKHD1, the gene linked to ARPKD, has been found mutated in patients with Caroli syndrome. PKHD1 is expressed primarily in the kidneys with lower levels in the liver
The cause appears to be genetic; the simple form is an autosomal dominant trait while the complex form is an autosomal recessive trait. Females are more prone to Caroli disease than males. Family history may include kidney and liver disease due to the link between Caroli Disease and ARPKD. PKHD1, the gene linked to ARPKD, has been found mutated in patients with Caroli syndrome. PKHD1 is expressed primarily in the kidneys with lower levels in the liver
, pancreas
, and lungs, a pattern consistent with phenotype of the disease, which primarily affects the liver and kidneys. The genetic basis for the difference between Caroli disease and Caroli syndrome has not been defined.
relieves symptoms and appears to remove the risk of malignancy. Sometimes, if the disease is isolated in one specific area, a lobectomy
may be performed to remove the affected lobe, relieving symptoms and removing the risk of malignancy. There is good evidence that malignancy complicates Caroli disease in approximately 7% of cases.
Antibiotics are used to treat the inflammation of the bile duct, and ursodeoxycholic acid for hepatolithiasis. Ursodiol
is given to treat cholelithiasis. In diffuse cases of Caroli disease, treatment options include conservative or endoscopic therapy, internal biliary bypass procedures and liver transplantation in carefully selected cases. Surgical resection has been used successfully in patients with monolobar disease. An orthotopic liver transplant is another option, used only when antibiotics have no effect, in combination with recurring cholangitis. With a liver transplant, cholangiocarcinoma is usually avoided in the long run.
Family studies are necessary to determine if Caroli disease is due to inheritable causes. Regular follow-ups, including ultrasounds and liver biopsies, are performed.
Ectasia
Dilation or distention of a tubular structure. It occurs as part of a pathophysiological process.-Specific conditions:* Duct ectasia of breast, a dilated milk duct...
. The second, more complex, cause is commonly known as Caroli Syndrome. This complex form is also linked with portal hypertension
Hypertension
Hypertension or high blood pressure is a cardiac chronic medical condition in which the systemic arterial blood pressure is elevated. What that means is that the heart is having to work harder than it should to pump the blood around the body. Blood pressure involves two measurements, systolic and...
and congenital hepatic fibrosis
Congenital hepatic fibrosis
Congenital hepatic fibrosis is an inherited fibrocystic liver disease associated with proliferation of interlobular bile ducts within the portal areas and fibrosis that do not alter hepatic lobular architecture. The fibrosis would affect resistance in portal veins leading to portal...
.
The differences between the causes of the two cases have not yet been discovered. Caroli disease is also associated with liver failure
Liver failure
Acute liver failure is the appearance of severe complications rapidly after the first signs of liver disease , and indicates that the liver has sustained severe damage . The complications are hepatic encephalopathy and impaired protein synthesis...
and polycystic kidney disease. The disease affects about 1 in 1,000,000 people, with more reported cases of Caroli syndrome than of Caroli disease.
Caroli disease also is known as communicating cavernous ectasia, or congenital cystic dilatation of the intrahepatic biliary tree
Biliary tree
The biliary tract is the common anatomical term for the path by which bile is secreted by the liver then transported to the first part of the small intestine, also known as the duodenum...
. Caroli disease is distinct from other diseases that cause ductal dilatation caused by obstruction, in that it is not one of the many choledochal cyst derivatives.
History
Jacques Caroli, a gastroenterologist, first described a rare congenital condition in 1958 in ParisParis
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
.
He described it as "nonobstructive saccular or fusiform multi-focal segmental dilatation of the intra-hepatic bile ducts"; basically, he observed cavernous ectasia in the biliary tree causing a chronic, often life-threatening hepatobiliary disease.
Caroli, born in France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
in 1902, learned and practiced medicine in Angers
Angers
Angers is the main city in the Maine-et-Loire department in western France about south-west of Paris. Angers is located in the French region known by its pre-revolutionary, provincial name, Anjou, and its inhabitants are called Angevins....
. After World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
he was chief of service for 30 years at Saint-Antoine
Saint-Antoine
-Canada:*Saint-Antoine, New Brunswick, a village*Saint-Antoine-de-l'Isle-aux-Grues, Quebec, a parish in Chaudière-Appalaches*Saint-Antoine-de-Tilly, Quebec, a municipality in Chaudière-Appalaches*Saint-Antoine-sur-Richelieu, Quebec, a municipality in Montérégie...
in Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
. Before dying in 1979, he was honored with the rank of commander in the Legion of Honour in 1976.
Symptoms
The first symptoms typically include feverFever
Fever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
, intermittent abdominal pain
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain can be one of the symptoms associated with transient disorders or serious disease. Making a definitive diagnosis of the cause of abdominal pain can be difficult, because many diseases can result in this symptom. Abdominal pain is a common problem...
, and hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly is the condition of having an enlarged liver. It is a nonspecific medical sign having many causes, which can broadly be broken down into infection, direct toxicity, hepatic tumours, or metabolic disorder. Often, hepatomegaly will present as an abdominal mass...
. Occasionally jaundice
Jaundice
Jaundice is a yellowish pigmentation of the skin, the conjunctival membranes over the sclerae , and other mucous membranes caused by hyperbilirubinemia . This hyperbilirubinemia subsequently causes increased levels of bilirubin in the extracellular fluid...
occurs.
Caroli disease usually occurs in the presence of other diseases, such as autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
Polycystic kidney disease
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is an inherited systemic disorder that predominantly affects the kidneys, but may affect other organs including the liver, pancreas, brain, and arterial blood vessels...
, cholangitis, gallstones, bilary abscess, septicemia, liver cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a consequence of chronic liver disease characterized by replacement of liver tissue by fibrosis, scar tissue and regenerative nodules , leading to loss of liver function...
, renal failure
Renal failure
Renal failure or kidney failure describes a medical condition in which the kidneys fail to adequately filter toxins and waste products from the blood...
, and cholangiocarcinoma
Cholangiocarcinoma
Cholangiocarcinoma is a cancer of the bile ducts which drain bile from the liver into the small intestine. Other biliary tract cancers include pancreatic cancer, gallbladder cancer, and cancer of the ampulla of Vater...
(7% affected). People with Caroli disease are 100 times more at risk for cholangiocarcinoma than the general population. After recognizing symptoms of related diseases, Caroli disease can be diagnosed.
Detection images
Modern imaging techniques allow the diagnosis to be made more easily and without invasive imaging of the biliary tree. Commonly the disease is limited to the left lobe of the liver. Images taken by CT-scan, X-rayX-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
, or MRI will show enlarged intrahepatic (in the liver) bile ducts due to ectasia. Using an ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
, tubular dilation of the bile ducts can be seen. On a CT-Scan, Caroli disease can be observed by noting the many fluid-filled, tubular structures extending to the liver. A high contrast CT must be used to distinguish the difference between stones and widened ducts. Bowel gas and digestive habits make it difficult to obtain a clear sonogram
Sonogram
A sonogram may refer to the following:* A diagnostic medical image created using ultrasound echo equipment, see medical ultrasonography...
, therefore, a CT scan is a good substitution. When the intrahepatic bile duct wall has protrusions, it is clearly seen as central dots or a linear streak. Caroli disease is commonly diagnosed after this “central dot sign” is detected on a CT scan or ultrasound. However, cholangiography
Cholangiography
Cholangiography is the imaging of the bile duct by x-rays. There are at least two kinds of cholangiography:* percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography : Examination of liver and bile ducts by x-rays...
is the best, and final, approach to show the enlarged bile ducts as a result of Caroli disease.
Morbidity
Caroli disease is typically found in AsiaAsia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
and diagnosed in persons under the age of 22. Cases have also been found in both infants and adults. As medical imaging technology improves, diagnostic age decreases. Morbidity is common and is caused by complications of cholangitis, sepsis
Sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially deadly medical condition that is characterized by a whole-body inflammatory state and the presence of a known or suspected infection. The body may develop this inflammatory response by the immune system to microbes in the blood, urine, lungs, skin, or other tissues...
, choledocholithiasis, and cholangiocarcinoma
Cholangiocarcinoma
Cholangiocarcinoma is a cancer of the bile ducts which drain bile from the liver into the small intestine. Other biliary tract cancers include pancreatic cancer, gallbladder cancer, and cancer of the ampulla of Vater...
. These morbid conditions often prompt the diagnosis. Portal hypertension may be present, resulting in other conditions including splenomegaly
Splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant of the human abdomen. It is one of the four cardinal signs of hypersplenism, some reduction in the number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any...
, hematemesis
Hematemesis
Hematemesis or haematemesis is the vomiting of blood. The source is generally the upper gastrointestinal tract. Patients can easily confuse it with hemoptysis , although the latter is more common.-Signs:...
and melena
Melena
In medicine, melena or melaena refers to the black, "tarry" feces that are associated with gastrointestinal hemorrhage. The black color is caused by oxidation of the iron in hemoglobin during its passage through the ileum and colon.-Melena vs...
. These problems can severely affect the patient's quality of life. In a ten year period between 1995 and 2005, only ten patients were surgically treated for Caroli disease, with an average patient age of 45.8 years.
After reviewing 46 cases of Caroli disease before 1990, it was found that 21.7% of the cases were the result of an intraheptic cyst or non-obstructive biliary tree dilation, 34.7% were linked with congenital hepatic fibrosis
Congenital hepatic fibrosis
Congenital hepatic fibrosis is an inherited fibrocystic liver disease associated with proliferation of interlobular bile ducts within the portal areas and fibrosis that do not alter hepatic lobular architecture. The fibrosis would affect resistance in portal veins leading to portal...
, 13% were isolated choledochal cystic dilation, and the remaining 24.6% had a combination of all three.
Mortality is indirect and caused by complications. After cholangitis occurs, patients typically die within approximately 5–10 years.
Causes

Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
, pancreas
Pancreas
The pancreas is a gland organ in the digestive and endocrine system of vertebrates. It is both an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin, as well as a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist...
, and lungs, a pattern consistent with phenotype of the disease, which primarily affects the liver and kidneys. The genetic basis for the difference between Caroli disease and Caroli syndrome has not been defined.
Treatment
The treatment depends on clinical features and the location of the biliary abnormality. When the disease is localized to one hepatic lobe, hepatectomyHepatectomy
Hepatectomy consists on the surgical resection of the liver. While the term is often employed for the removal of the liver from a liver transplant recipient, this article will focus on partial resections of hepatic tissue.-History:...
relieves symptoms and appears to remove the risk of malignancy. Sometimes, if the disease is isolated in one specific area, a lobectomy
Lobectomy
Lobectomy means surgical excision of a lobe. This may refer to a lobe of the lung, a lobe of the thyroid , or a lobe of the brain ....
may be performed to remove the affected lobe, relieving symptoms and removing the risk of malignancy. There is good evidence that malignancy complicates Caroli disease in approximately 7% of cases.
Antibiotics are used to treat the inflammation of the bile duct, and ursodeoxycholic acid for hepatolithiasis. Ursodiol
Ursodiol
Ursodiol, also known as ursodeoxycholic acid and the abbreviation UDCA, is one of the secondary bile acids, which are metabolic byproducts of intestinal bacteria.-Endogenous effects:...
is given to treat cholelithiasis. In diffuse cases of Caroli disease, treatment options include conservative or endoscopic therapy, internal biliary bypass procedures and liver transplantation in carefully selected cases. Surgical resection has been used successfully in patients with monolobar disease. An orthotopic liver transplant is another option, used only when antibiotics have no effect, in combination with recurring cholangitis. With a liver transplant, cholangiocarcinoma is usually avoided in the long run.
Family studies are necessary to determine if Caroli disease is due to inheritable causes. Regular follow-ups, including ultrasounds and liver biopsies, are performed.

