
Carrier-to-noise ratio
Encyclopedia
In telecommunications, the carrier-to-noise ratio, often written CNR or C/N, is the signal-to-noise ratio
(SNR) of a modulated
signal. The term is used to distinguish the CNR of the radio frequency passband
signal from the SNR of an analogue base band message signal after demodulation
, for example an audio frequency analogue message signal. If this distinction is not necessary, the term SNR is often used instead of CNR, with the same definition.
Digitally modulated signals (e.g. QAM or PSK
) are basically made of two CW
carriers (the I and Q components, which are out-of-phase carriers) . In fact, the information (bits or symbols) is carried by given combinations of phase and/or amplitude of the I and Q components. It is for this reason that, in the context of digital modulations, digitally modulated signals are usually referred to as carriers. Therefore, the term carrier-to-noise-ratio (CNR), instead of signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) is preferred to express the signal quality when the signal has been digitally modulated.
High C/N ratios provide good quality of reception, for example low bit error rate (BER) of a digital message signal, or high SNR of an analogue message signal.
C to the received noise power N after the receive filters: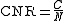 .
.
When both carrier and noise are measured across the same impedance
, this ratio can equivalently be given as: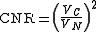 ,
,
where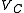 and
and 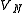 are the root mean square
are the root mean square
(RMS) voltage levels of the carrier signal and noise respectively.
C/N ratios are often specified in decibel
s (dB):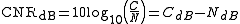
or in term of voltage:
The C/N ratio is measured in a manner similar to the way the signal-to-noise ratio
(S/N) is measured, and both specifications give an indication of the quality of a communications channel.
In the famous Shannon–Hartley theorem
, the C/N ratio is equivalent to the S/N ratio. The C/N ratio resembles the carrier-to-interference ratio (C/I, CIR), and the carrier-to-noise-and-interference ratio, C/(N+I) or CNIR.
Signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...
(SNR) of a modulated
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
signal. The term is used to distinguish the CNR of the radio frequency passband
Passband
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter without being attenuated.A bandpass filtered signal , is known as a bandpass signal, as opposed to a baseband signal....
signal from the SNR of an analogue base band message signal after demodulation
Demodulation
Demodulation is the act of extracting the original information-bearing signal from a modulated carrier wave.A demodulator is an electronic circuit that is used to recover the information content from the modulated carrier wave.These terms are traditionally used in connection with radio receivers,...
, for example an audio frequency analogue message signal. If this distinction is not necessary, the term SNR is often used instead of CNR, with the same definition.
Digitally modulated signals (e.g. QAM or PSK
Phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by changing, or modulating, the phase of a reference signal ....
) are basically made of two CW
Continuous wave
A continuous wave or continuous waveform is an electromagnetic wave of constant amplitude and frequency; and in mathematical analysis, of infinite duration. Continuous wave is also the name given to an early method of radio transmission, in which a carrier wave is switched on and off...
carriers (the I and Q components, which are out-of-phase carriers) . In fact, the information (bits or symbols) is carried by given combinations of phase and/or amplitude of the I and Q components. It is for this reason that, in the context of digital modulations, digitally modulated signals are usually referred to as carriers. Therefore, the term carrier-to-noise-ratio (CNR), instead of signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) is preferred to express the signal quality when the signal has been digitally modulated.
High C/N ratios provide good quality of reception, for example low bit error rate (BER) of a digital message signal, or high SNR of an analogue message signal.
Definition
The carrier-to-noise ratio is defined as the ratio of the received modulated carrier signal powerPower (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
C to the received noise power N after the receive filters:
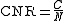 .
.When both carrier and noise are measured across the same impedance
Characteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance of a uniform transmission line, usually written Z_0, is the ratio of the amplitudes of a single pair of voltage and current waves propagating along the line in the absence of reflections. The SI unit of characteristic impedance is the ohm...
, this ratio can equivalently be given as:
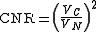 ,
,where
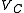 and
and 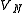 are the root mean square
are the root mean squareRoot mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
(RMS) voltage levels of the carrier signal and noise respectively.
C/N ratios are often specified in decibel
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
s (dB):
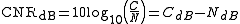
or in term of voltage:

The C/N ratio is measured in a manner similar to the way the signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...
(S/N) is measured, and both specifications give an indication of the quality of a communications channel.
In the famous Shannon–Hartley theorem
Shannon–Hartley theorem
In information theory, the Shannon–Hartley theorem tells the maximum rate at which information can be transmitted over a communications channel of a specified bandwidth in the presence of noise. It is an application of the noisy channel coding theorem to the archetypal case of a continuous-time...
, the C/N ratio is equivalent to the S/N ratio. The C/N ratio resembles the carrier-to-interference ratio (C/I, CIR), and the carrier-to-noise-and-interference ratio, C/(N+I) or CNIR.
See also
- Signal-to-noise ratioSignal-to-noise ratioSignal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...
(SNR or S/N) - Signal-to-interference ratioSignal-to-interference ratioThe signal-to-interference ratio , also known as the carrier-to-interference ratio , is the quotient between the average received modulated carrier power S or C and the average received co-channel interference power I, i.e...
(SIR or S/I) - SINADSINADSINAD stands for Signal-to-noise and distortion ratio. It is a measure of the quality of a signal from a communications device, often defined as:...
(ratio of signal-plus-noise-plus-distortion to noise-plus-distortion) - Eb/N0 (energy per bit relative to noise power spectral density)
- Es/N0 (energy per symbol relative to noise power spectral density)
- Carrier-to-receiver noise densityCarrier-to-receiver noise densityIn satellite communications, carrier-to-receiver noise density is the ratio of the received carrier power to the receiver noise power density.The carrier-to-receiver noise density ratio is usually expressed in dBHz....
C/N0

