
Castability
Encyclopedia
Castability is the ease of forming a casting
. Castability can be thought of as how easy is it to cast a quality part. A very castable part design is easily developed, incurs minimal tooling costs, requires minimal energy, and has few rejections.
Castability can refer to a part design or a material property.
If the design has undercut
s or interior cavities it decreases castability due to tooling complexity. Long thin sections in a design are hard to fill. Sudden changes in wall thickness reduce castability because it induces turbulence
during filling; fillet
s should be added to avoid this. Annulars in the path of flow should be avoided because they can cause cold shuts or misruns. A design that causes isolated hot spots decreases castability. An ideal design would have progressive directional solidification
from the thinnest section to the thickest.
Location of the mold's parting line
also affects castability, because a non-planar parting line also increases tooling complexity.
If a design requires a high degree of accuracy, fine surface finish
or defect free surface it reduces the castability of the part. However, the casting process can be very economical for part designs that require intricate contoured surfaces, thickness variations, and internal features.
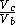
Where Vc is the volume of the casting and Vb is the volume of the smallest box that the casting could fit in.
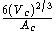
Where Vc is the volume of the casting and Ac is the surface area of the casting
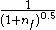
Where nf is the number of features (holes, pockets, slots, bosses, ribs, etc.)
, solidification shrinkage, and slag
/dross
formation tendencies.
Casting
In metalworking, casting involves pouring liquid metal into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowing it to cool and solidify. The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process...
. Castability can be thought of as how easy is it to cast a quality part. A very castable part design is easily developed, incurs minimal tooling costs, requires minimal energy, and has few rejections.
Castability can refer to a part design or a material property.
Part design
Part design and geometry directly affect the castability, with volume, surface area and the number of features being the most important attributes.If the design has undercut
Undercut (manufacturing)
In manufacturing, an undercut is a special type of recessed surface. In turning it refers to a recess in a diameter. In machining it refers to a recess in a corner. In molding it refers to a feature that cannot be molded using only a single pull mold...
s or interior cavities it decreases castability due to tooling complexity. Long thin sections in a design are hard to fill. Sudden changes in wall thickness reduce castability because it induces turbulence
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...
during filling; fillet
Fillet (mechanics)
In mechanical engineering, a fillet is a concave easing of an interior corner of a part design. A rounding of an exterior corner is called a "round" or a "chamfer".-Applications:...
s should be added to avoid this. Annulars in the path of flow should be avoided because they can cause cold shuts or misruns. A design that causes isolated hot spots decreases castability. An ideal design would have progressive directional solidification
Directional solidification
Directional solidification and progressive solidification describe types of solidification within castings. Directional solidification describes solidification that occurs from farthest end of the casting and works its way towards the sprue...
from the thinnest section to the thickest.
Location of the mold's parting line
Parting line
A parting line in moldmaking is the place where two or more parts of the mold meet. At times, either because the mold halves do not meet with enough precision or because injection pressure is high, material will creep into the space between the molds. This material is generally called molding...
also affects castability, because a non-planar parting line also increases tooling complexity.
If a design requires a high degree of accuracy, fine surface finish
Surface finish
Surface finish, also known as surface texture, is the characteristics of a surface. It has three components: lay, surface roughness, and waviness.-Lay:...
or defect free surface it reduces the castability of the part. However, the casting process can be very economical for part designs that require intricate contoured surfaces, thickness variations, and internal features.
Quantitative analysis
The castability of a design can be partially quantitatively determined by the following three equations. Better castability is denoted by a larger number.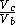
Where Vc is the volume of the casting and Vb is the volume of the smallest box that the casting could fit in.
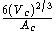
Where Vc is the volume of the casting and Ac is the surface area of the casting
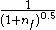
Where nf is the number of features (holes, pockets, slots, bosses, ribs, etc.)
Material properties
Material properties that influence their castability include their pouring temperature, fluidityFluidity
Fluidity may refer toIn science*reciprocal of viscosity*Cognitive fluidity*Membrane fluidity*Sexual fluidityOthers*Fluidity *Dark Fluidity – a literature magazine*Empire Fane ship...
, solidification shrinkage, and slag
Slag
Slag is a partially vitreous by-product of smelting ore to separate the metal fraction from the unwanted fraction. It can usually be considered to be a mixture of metal oxides and silicon dioxide. However, slags can contain metal sulfides and metal atoms in the elemental form...
/dross
Dross
Dross is a mass of solid impurities floating on a molten metal. It appears usually on the melting of low-melting-point metals or alloys such as tin, lead, zinc or aluminium, or by oxidation of the metal. It can also consist of impurities such as paint leftovers...
formation tendencies.

