Catalytic cycle
Encyclopedia
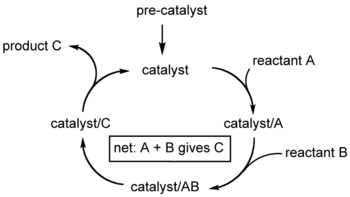
A catalytic cycle in chemistry
is a term for a multistep reaction mechanism that involves a catalyst . The catalytic cycle is the main method for describing the role of catalysts in biochemistry
, organometallic chemistry
, materials science, etc. Often such cycles show the conversion of a precatalyst to the catalyst. Since catalysts are regenerated, catalytic cycles are usually written as a sequence of chemical reactions in the form of a loop. In such loops, the initial step entails binding of one or more reactants by the catalyst, and the final step is the release of the product and regeneration of the catalyst. Articles on the Monsanto process
, the Wacker process
, and the Heck reaction
show catalytic cycles.
 A catalytic cycle is not necessarily a full reaction mechanism
A catalytic cycle is not necessarily a full reaction mechanism
. For example, it may be that the intermediates have been detected, but it is not known by which mechanisms the actual elementary reactions occur.
quantities compared to the main reactant. Usually the true catalyst is an expensive and complex molecule and added in quantities as small as possible. The stoichiometric catalyst on the other hand should be cheap and abundant.
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
is a term for a multistep reaction mechanism that involves a catalyst . The catalytic cycle is the main method for describing the role of catalysts in biochemistry
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
, organometallic chemistry
Organometallic chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of chemical compounds containing bonds between carbon and a metal. Since many compounds without such bonds are chemically similar, an alternative may be compounds containing metal-element bonds of a largely covalent character...
, materials science, etc. Often such cycles show the conversion of a precatalyst to the catalyst. Since catalysts are regenerated, catalytic cycles are usually written as a sequence of chemical reactions in the form of a loop. In such loops, the initial step entails binding of one or more reactants by the catalyst, and the final step is the release of the product and regeneration of the catalyst. Articles on the Monsanto process
Monsanto process
The Monsanto process is an important method for the manufacture of acetic acid by catalytic carbonylation of methanol. This process operates at a pressure of 30–60 atm and a temperature of 150–200 °C and gives a selectivity greater than 99%. It was developed 1960 by German BASF and...
, the Wacker process
Wacker process
The Wacker process or the Hoechst-Wacker process originally referred to the oxidation of ethylene to acetaldehyde by oxygen in water in the presence of a tetrachloropalladate catalyst...
, and the Heck reaction
Heck reaction
The Heck reaction is the chemical reaction of an unsaturated halide with an alkene and a base and palladium catalyst to form a substituted alkene. Together with the other palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions, this reaction is of great importance, as it allows one to do substitution...
show catalytic cycles.

Reaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs.Although only the net chemical change is directly observable for most chemical reactions, experiments can often be designed that suggest the possible sequence of steps in...
. For example, it may be that the intermediates have been detected, but it is not known by which mechanisms the actual elementary reactions occur.
Sacrificial catalysts
Often a so-called sacrificial catalyst is also part of the reaction system with the purpose of regenerating the true catalyst in each cycle. As the name implies, the sacrificial catalyst is not regenerated and irreversibly consumed. This sacrificial compound is also known as a stoichiometric catalyst when added in stoichiometricStoichiometry
Stoichiometry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions. In a balanced chemical reaction, the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of whole numbers...
quantities compared to the main reactant. Usually the true catalyst is an expensive and complex molecule and added in quantities as small as possible. The stoichiometric catalyst on the other hand should be cheap and abundant.

