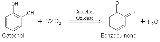
Catechol oxidase
Overview
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyses
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the oxidation of phenol
Phenol
Phenol, also known as carbolic acid, phenic acid, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid. The molecule consists of a phenyl , bonded to a hydroxyl group. It is produced on a large scale as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds...
s such as catechol. Catechol oxidase is a copper-containing enzyme whose activity is similar to that of tyrosinase
Tyrosinase
Tyrosinase also known as monophenol monooxygenase is an enzyme that catalyses the oxidation of phenols and is widespread in plants and animals...
, a related class of copper oxidase
Oxidase
An oxidase is any enzyme that catalyzes an oxidation-reduction reaction involving molecular oxygen as the electron acceptor. In these reactions, oxygen is reduced to water or hydrogen peroxide ....
s.
Catechol oxidase carries out the oxidation of phenols such as catechol, using dioxygen (O2). In the presence of catechol, benzoquinone is formed (see reaction below).

