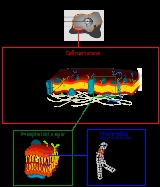
Cell membrane
Overview
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane
that separates the interior
of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable
to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell from outside forces. It consists of the lipid bilayer
with embedded protein
s. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion
, ion conductivity and cell signaling
and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall
, glycocalyx
, and intracellular cytoskeleton
.
The cell membrane surrounds the cytoplasm
of a cell and, in animal cells, physically separates the intracellular
components from the extracellular
environment.
Biological membrane
A biological membrane or biomembrane is an enclosing or separatingmembrane that acts as a selective barrier, within or around a cell. It consists of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins that may constitute close to 50% of membrane content...
that separates the interior
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable
Semipermeable membrane
A semipermeable membrane, also termed a selectively permeable membrane, a partially permeable membrane or a differentially permeable membrane, is a membrane that will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by diffusion and occasionally specialized "facilitated diffusion".The rate of...
to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell from outside forces. It consists of the lipid bilayer
Lipid bilayer
The lipid bilayer is a thin membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around cells. The cell membrane of almost all living organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the membranes surrounding the cell nucleus...
with embedded protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion
Cell adhesion
Cellular adhesion is the binding of a cell to a surface, extracellular matrix or another cell using cell adhesion molecules such as selectins, integrins, and cadherins. Correct cellular adhesion is essential in maintaining multicellular structure...
, ion conductivity and cell signaling
Cell signaling
Cell signaling is part of a complex system of communication that governs basic cellular activities and coordinates cell actions. The ability of cells to perceive and correctly respond to their microenvironment is the basis of development, tissue repair, and immunity as well as normal tissue...
and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
, glycocalyx
Glycocalyx
Glycocalyx is a general term referring to extracellular polymeric material produced by some bacteria, epithelia and other cells. The slime on the outside of a fish is considered a glycocalyx. The term was initially applied to the polysaccharide matrix excreted by epithelial cells forming a...
, and intracellular cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a cellular "scaffolding" or "skeleton" contained within a cell's cytoplasm and is made out of protein. The cytoskeleton is present in all cells; it was once thought to be unique to eukaryotes, but recent research has identified the prokaryotic cytoskeleton...
.
The cell membrane surrounds the cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
of a cell and, in animal cells, physically separates the intracellular
Intracellular
Not to be confused with intercellular, meaning "between cells".In cell biology, molecular biology and related fields, the word intracellular means "inside the cell".It is used in contrast to extracellular...
components from the extracellular
Extracellular
In cell biology, molecular biology and related fields, the word extracellular means "outside the cell". This space is usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid...
environment.
Unanswered Questions

