Cellulitis
Encyclopedia
Cellulitis is a diffuse inflammation
of connective tissue
with severe inflammation of dermal and subcutaneous layers of the skin
. Cellulitis can be caused by normal skin flora
or by exogenous bacteria
, and often occurs where the skin has previously been broken: cracks in the skin, cuts, blister
s, burns
, insect bite
s, surgical wounds, intravenous drug injection
or sites of intravenous catheter
insertion. Skin on the face or lower legs is most commonly affected by this infection, though cellulitis can occur on any part of the body. The mainstay of therapy remains treatment with appropriate antibiotic
s, and recovery periods last from 48 hours to six months.
Erysipelas
is the term used for a more superficial infection of the dermis and upper subcutaneous layer that presents clinically with a well-defined edge. Erysipelas and cellulitis often coexist, so it is often difficult to make a distinction between the two.
Cellulitis is unrelated (except etymologically) to cellulite
, a cosmetic condition featuring dimpling of the skin.
Streptococcus
and Staphylococcus
are the most common of these bacteria, which are part of the normal flora of the skin, but normally cause no actual infection while on the skin's outer surface.
Predisposing conditions for cellulitis include insect or spider bite
, blister
ing, animal bite, tattoos, pruritic
(itchy) skin rash, recent surgery
, athlete's foot
, dry skin
, eczema
, injecting drugs (especially subcutaneous or intramuscular injection or where an attempted intravenous injection "misses" or blows the vein), pregnancy, diabetes and obesity, which can affect circulation, as well as burns and boil
s, though there is debate as to whether minor foot lesions contribute.
Occurrences of cellulitis may also be associated with the rare condition hidradenitis suppurativa
.
The appearance of the skin will assist a doctor in determining a diagnosis. A doctor may also suggest blood tests, a wound culture or other tests to help rule out a blood clot deep in the veins of the legs. Cellulitis in the lower leg is characterized by signs and symptoms similar to those of a deep vein thrombosis
, such as warmth, pain and swelling (inflammation).
This reddened skin or rash may signal a deeper, more serious infection of the inner layers of skin. Once below the skin, the bacteria can spread rapidly, entering the lymph nodes and the bloodstream and spreading throughout the body. This can result in influenza-like symptoms with a high temperature and sweating or feeling very cold with shaking, as the sufferer cannot get warm.
In rare cases, the infection can spread to the deep layer of tissue called the fascial lining. Necrotizing fasciitis
, also called by the media "flesh-eating bacteria", is an example of a deep-layer infection. It is a medical emergency
.
(a weakened immune system) are especially vulnerable to contracting cellulitis. Diabetics
are more susceptible to cellulitis than the general population because of impairment of the immune system; they are especially prone to cellulitis in the feet, because the disease causes impairment of blood circulation in the legs, leading to diabetic foot/foot ulcers. Poor control of blood glucose levels allows bacteria to grow more rapidly in the affected tissue, and facilitates rapid progression if the infection enters the bloodstream. Neural degeneration in diabetes means these ulcers may not be painful and thus often become infected. Those who have suffered poliomyelitis
are also prone because of circulatory problems, especially in the legs.
Immunosuppressive drugs, and other illnesses or infections that weaken the immune system, are also factors that make infection more likely. Chickenpox
and shingles often result in blisters that break open, providing a gap in the skin through which bacteria can enter. Lymphedema
, which causes swelling on the arms and/or legs, can also put an individual at risk.
Diseases that affect blood circulation in the legs and feet, such as chronic venous insufficiency
and varicose veins
, are also risk factors for cellulitis.
Cellulitis is also extremely prevalent among dense populations sharing hygiene facilities and common living quarters, such as military installations, college dormitories, nursing homes, oil platforms and homeless shelters. It is advised if a cabin is shared with a sufferer, urgent medical treatment should be given.
s usually are positive only if the patient develops generalized sepsis
. Conditions that may resemble cellulitis include deep vein thrombosis
, which can be diagnosed with a compression leg ultrasound
, and stasis dermatitis
, which is inflammation of the skin from poor blood flow. Associated musculoskeletal findings are sometimes reported. When it occurs with acne conglobata
, hidradenitis suppurativa
, and pilonidal cyst
s, the syndrome is referred to as the follicular occlusion triad or tetrad.
There have been many cases where Lyme disease
has been misdiagnosed as staphylococcal- or streptococcal-induced cellulitis. Because the characteristic bullseye rash
does not always appear in patients infected with Lyme disease
, the similar set of symptoms may be misdiagnosed as cellulitis. Standard treatments for cellulitis are not sufficient for curing Lyme disease. The only way to rule out Lyme disease is with a blood test, which is recommended during warm months in areas where the disease is endemic.
or dicloxacillin
monotherapy (to cover staphylococcal infection) is often sufficient in mild cellulitis, but in more moderate cases, or where streptococcal infection is suspected, then this course is usually combined with oral phenoxymethylpenicillin
or intravenous benzylpenicillin
, or ampicillin
/amoxicillin
. Pain relief is also often prescribed, but excessive pain should always be investigated as it is a symptom of necrotizing fasciitis
.
Elevation of the affected area is also important.
As in other maladies characterized by wounds or tissue destruction, hyperbaric oxygen treatment can be a valuable adjunctive therapy, but is not widely available.
(grade 1-2 out of 5) than that caused by septic arthritis (grade 4-5 lameness). The horse will exhibit inflammatory edema, which is marked by hot, painful swelling. This swelling differs from stocking up in that the horse will not display symmetrical swelling in two or four legs, but in only one leg. This swelling begins near the source of infection, but will eventually continue down the leg. In some cases, the swelling will also travel upward. Treatment includes cleaning the wound and caring for it properly, the administration of NSAIDs, such as phenylbutazone
, cold hosing, applying a sweat wrap or a poultice
, and mild exercise. Veterinarians may also prescribe antibiotic
s. Recovery is usually quick, and the prognosis is very good if the cellulitis is secondary to skin infection.
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
of connective tissue
Connective tissue
"Connective tissue" is a fibrous tissue. It is one of the four traditional classes of tissues . Connective Tissue is found throughout the body.In fact the whole framework of the skeleton and the different specialized connective tissues from the crown of the head to the toes determine the form of...
with severe inflammation of dermal and subcutaneous layers of the skin
Skin
-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
. Cellulitis can be caused by normal skin flora
Skin flora
The skin flora are the microorganisms which reside on the skin. Most research has been upon those that reside upon the 2 square metres of human skin. Many of them are bacteria of which there are around 1000 species upon human skin from 19 phyla. The total number of bacteria on an average human has...
or by exogenous bacteria
Exogenous bacteria
Exogenous bacteria are bacteria introduced to closed biological systems from the external world. They exist in water, earth, and the air. Examples are cholera, Legionella, salmonella, rickettsia, mycobacterium, and bacillus anthracis. Endogenous bacteria are part of our normal internal flora....
, and often occurs where the skin has previously been broken: cracks in the skin, cuts, blister
Blister
A blister is a small pocket of fluid within the upper layers of the skin, typically caused by forceful rubbing , burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled with a clear fluid called serum or plasma...
s, burns
Burn (injury)
A burn is a type of injury to flesh caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, light, radiation or friction. Most burns affect only the skin . Rarely, deeper tissues, such as muscle, bone, and blood vessels can also be injured...
, insect bite
Insect bite
Insect bites and stings occur when an insect is agitated and seeks to defend itself through its natural defense mechanisms, or when an insect seeks to feed off the bitten person. Some insects inject formic acid, which can cause an immediate skin reaction often resulting in redness and swelling in...
s, surgical wounds, intravenous drug injection
Drug injection
In substance dependence and recreational drug use, drug injection is a method of introducing a drug into the body with a hollow needle and a syringe which is pierced through the skin into the body...
or sites of intravenous catheter
Catheter
In medicine, a catheter is a tube that can be inserted into a body cavity, duct, or vessel. Catheters thereby allow drainage, administration of fluids or gases, or access by surgical instruments. The process of inserting a catheter is catheterization...
insertion. Skin on the face or lower legs is most commonly affected by this infection, though cellulitis can occur on any part of the body. The mainstay of therapy remains treatment with appropriate antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s, and recovery periods last from 48 hours to six months.
Erysipelas
Erysipelas
Erysipelas is an acute streptococcus bacterial infection of the deep epidermis with lymphatic spread.-Risk factors:...
is the term used for a more superficial infection of the dermis and upper subcutaneous layer that presents clinically with a well-defined edge. Erysipelas and cellulitis often coexist, so it is often difficult to make a distinction between the two.
Cellulitis is unrelated (except etymologically) to cellulite
Cellulite
Cellulite is a topographic skin change that occurs in most postpubertal females. It presents as a modification of skin topography evident by skin dimpling and nodularity that occurs mainly in women on the pelvic region, lower limbs, and abdomen, and is caused by the herniation of subcutaneous fat...
, a cosmetic condition featuring dimpling of the skin.
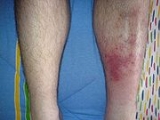
Signs and symptoms
The typical symptoms of cellulitis is an area which is red, hot, and tender. The photos shown here of cellulitis are of mild cases, and are not representative of earlier stages of the disease.Causes
Cellulitis is caused by a type of bacteria entering the skin, usually by way of a cut, abrasion, or break in the skin. This break does not need to be visible. Group AGroup A streptococcal infection
The group A streptococcus bacterium is a form of β-hemolytic Streptococcus bacteria responsible for most cases of streptococcal illness. Other types may also cause infection...
Streptococcus
Streptococcus
Streptococcus is a genus of spherical Gram-positive bacteria belonging to the phylum Firmicutes and the lactic acid bacteria group. Cellular division occurs along a single axis in these bacteria, and thus they grow in chains or pairs, hence the name — from Greek στρεπτος streptos, meaning...
and Staphylococcus
Staphylococcus
Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria. Under the microscope they appear round , and form in grape-like clusters....
are the most common of these bacteria, which are part of the normal flora of the skin, but normally cause no actual infection while on the skin's outer surface.
Predisposing conditions for cellulitis include insect or spider bite
Spider bite
A spider bite is an injury resulting from the bites of spiders or other closely related arachnids.Spiders are active hunters and rely heavily on their bites to paralyze and kill their prey before consuming it. They also bite in self defense...
, blister
Blister
A blister is a small pocket of fluid within the upper layers of the skin, typically caused by forceful rubbing , burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled with a clear fluid called serum or plasma...
ing, animal bite, tattoos, pruritic
Itch
Itch is a sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to classify it as any one type of sensory experience. Modern science has shown that itch has many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant sensory experiences, their behavioral response...
(itchy) skin rash, recent surgery
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
, athlete's foot
Athlete's foot
Athlete's foot is a fungal infection of the skin that causes scaling, flaking, and itch of affected areas. It is caused by fungi in the genus Trichophyton and is typically transmitted in moist areas where people walk barefoot, such as showers or bathhouses...
, dry skin
Xeroderma
Xeroderma, literally meaning "dry skin", is a condition involving the integumentary system, which in most cases can safely be treated with emollients and/or moisturizers. Xeroderma occurs most commonly on the scalp, lower legs, arms, the knuckles, the sides of the abdomen and thighs...
, eczema
Eczema
Eczema is a form of dermatitis, or inflammation of the epidermis . In England, an estimated 5.7 million or about one in every nine people have been diagnosed with the disease by a clinician at some point in their lives.The term eczema is broadly applied to a range of persistent skin conditions...
, injecting drugs (especially subcutaneous or intramuscular injection or where an attempted intravenous injection "misses" or blows the vein), pregnancy, diabetes and obesity, which can affect circulation, as well as burns and boil
Boil
A boil, also called a furuncle, is a deep folliculitis, infection of the hair follicle. It is always caused by infection by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, resulting in a painful swollen area on the skin caused by an accumulation of pus and dead tissue...
s, though there is debate as to whether minor foot lesions contribute.
Occurrences of cellulitis may also be associated with the rare condition hidradenitis suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a skin disease that most commonly affects areas bearing apocrine sweat glands or sebaceous glands, such as the underarms, breasts, inner thighs, groin and buttocks.-Overview:...
.
The appearance of the skin will assist a doctor in determining a diagnosis. A doctor may also suggest blood tests, a wound culture or other tests to help rule out a blood clot deep in the veins of the legs. Cellulitis in the lower leg is characterized by signs and symptoms similar to those of a deep vein thrombosis
Thrombosis
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel is injured, the body uses platelets and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss...
, such as warmth, pain and swelling (inflammation).
This reddened skin or rash may signal a deeper, more serious infection of the inner layers of skin. Once below the skin, the bacteria can spread rapidly, entering the lymph nodes and the bloodstream and spreading throughout the body. This can result in influenza-like symptoms with a high temperature and sweating or feeling very cold with shaking, as the sufferer cannot get warm.
In rare cases, the infection can spread to the deep layer of tissue called the fascial lining. Necrotizing fasciitis
Necrotizing fasciitis
Necrotizing fasciitis , commonly known as flesh-eating disease or Flesh-eating bacteria syndrome, is a rare infection of the deeper layers of skin and subcutaneous tissues, easily spreading across the fascial plane within the subcutaneous tissue.Necrotizing fasciitis is a quickly progressing and...
, also called by the media "flesh-eating bacteria", is an example of a deep-layer infection. It is a medical emergency
Medical emergency
A medical emergency is an injury or illness that is acute and poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long term health. These emergencies may require assistance from another person, who should ideally be suitably qualified to do so, although some of these emergencies can be dealt with by the...
.
Risk factors
The elderly and those with immunodeficiencyImmunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious disease is compromised or entirely absent. Immunodeficiency may also decrease cancer immunosurveillance. Most cases of immunodeficiency are acquired but some people are born with defects in their immune system,...
(a weakened immune system) are especially vulnerable to contracting cellulitis. Diabetics
Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, often simply referred to as diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced...
are more susceptible to cellulitis than the general population because of impairment of the immune system; they are especially prone to cellulitis in the feet, because the disease causes impairment of blood circulation in the legs, leading to diabetic foot/foot ulcers. Poor control of blood glucose levels allows bacteria to grow more rapidly in the affected tissue, and facilitates rapid progression if the infection enters the bloodstream. Neural degeneration in diabetes means these ulcers may not be painful and thus often become infected. Those who have suffered poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis, often called polio or infantile paralysis, is an acute viral infectious disease spread from person to person, primarily via the fecal-oral route...
are also prone because of circulatory problems, especially in the legs.
Immunosuppressive drugs, and other illnesses or infections that weaken the immune system, are also factors that make infection more likely. Chickenpox
Chickenpox
Chickenpox or chicken pox is a highly contagious illness caused by primary infection with varicella zoster virus . It usually starts with vesicular skin rash mainly on the body and head rather than at the periphery and becomes itchy, raw pockmarks, which mostly heal without scarring...
and shingles often result in blisters that break open, providing a gap in the skin through which bacteria can enter. Lymphedema
Lymphedema
Lymphedema , also known as lymphatic obstruction, is a condition of localized fluid retention and tissue swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system....
, which causes swelling on the arms and/or legs, can also put an individual at risk.
Diseases that affect blood circulation in the legs and feet, such as chronic venous insufficiency
Venous insufficiency
Venous insufficiency can refer to:* varicose veins* chronic venous insufficiency...
and varicose veins
Varicose veins
Varicose veins are veins that have become enlarged and tortuous. The term commonly refers to the veins on the leg, although varicose veins can occur elsewhere. Veins have leaflet valves to prevent blood from flowing backwards . Leg muscles pump the veins to return blood to the heart, against the...
, are also risk factors for cellulitis.
Cellulitis is also extremely prevalent among dense populations sharing hygiene facilities and common living quarters, such as military installations, college dormitories, nursing homes, oil platforms and homeless shelters. It is advised if a cabin is shared with a sufferer, urgent medical treatment should be given.
Diagnosis
Cellulitis is most often a clinical diagnosis, and local cultures do not always identify the causative organism. Blood cultureBlood culture
Blood culture is a microbiological culture of blood. It is employed to detect infections that are spreading through the bloodstream...
s usually are positive only if the patient develops generalized sepsis
Sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially deadly medical condition that is characterized by a whole-body inflammatory state and the presence of a known or suspected infection. The body may develop this inflammatory response by the immune system to microbes in the blood, urine, lungs, skin, or other tissues...
. Conditions that may resemble cellulitis include deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein. Deep vein thrombosis commonly affects the leg veins or the deep veins of the pelvis. Occasionally the veins of the arm are affected...
, which can be diagnosed with a compression leg ultrasound
Medical ultrasonography
Diagnostic sonography is an ultrasound-based diagnostic imaging technique used for visualizing subcutaneous body structures including tendons, muscles, joints, vessels and internal organs for possible pathology or lesions...
, and stasis dermatitis
Stasis dermatitis
Stasis dermatitis refers to the skin changes that occur in the leg as a result of "stasis" or blood pooling from insufficient venous return; the alternative name of varicose eczema comes from a common cause of this being varicose veins.Insufficient venous...
, which is inflammation of the skin from poor blood flow. Associated musculoskeletal findings are sometimes reported. When it occurs with acne conglobata
Acne conglobata
Acne conglobata is a highly inflammatory disease presenting with comedones, nodules, abscesses, and draining sinus tracts.This condition generally begins between the ages of 18 and 30. It usually persists for a very long time, and often until the patient is around 40 years old...
, hidradenitis suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a skin disease that most commonly affects areas bearing apocrine sweat glands or sebaceous glands, such as the underarms, breasts, inner thighs, groin and buttocks.-Overview:...
, and pilonidal cyst
Pilonidal cyst
A pilonidal cyst, also referred to as a pilonidal abscess, pilonidal sinus or sacrococcygeal fistula, is a cyst or abscess near or on the natal cleft of the buttocks that often contains hair and skin debris.-Etymology:...
s, the syndrome is referred to as the follicular occlusion triad or tetrad.
There have been many cases where Lyme disease
Lyme disease
Lyme disease, or Lyme borreliosis, is an emerging infectious disease caused by at least three species of bacteria belonging to the genus Borrelia. Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto is the main cause of Lyme disease in the United States, whereas Borrelia afzelii and Borrelia garinii cause most...
has been misdiagnosed as staphylococcal- or streptococcal-induced cellulitis. Because the characteristic bullseye rash
Erythema chronicum migrans
Erythema chronicum migrans refers to the rash often seen in the early stage of Lyme disease. It can appear anywhere from one day to one month after a tick bite. This rash does not represent an allergic reaction to the bite, but rather an actual skin infection with the Lyme bacteria, Borrelia...
does not always appear in patients infected with Lyme disease
Lyme disease
Lyme disease, or Lyme borreliosis, is an emerging infectious disease caused by at least three species of bacteria belonging to the genus Borrelia. Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto is the main cause of Lyme disease in the United States, whereas Borrelia afzelii and Borrelia garinii cause most...
, the similar set of symptoms may be misdiagnosed as cellulitis. Standard treatments for cellulitis are not sufficient for curing Lyme disease. The only way to rule out Lyme disease is with a blood test, which is recommended during warm months in areas where the disease is endemic.
Treatment
Treatment consists of resting the affected area, cutting away dead tissue, and antibiotics (either oral or intravenous). FlucloxacillinFlucloxacillin
Flucloxacillin or floxacillin is a narrow-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. It is used to treat infections caused by susceptible Gram-positive bacteria. Unlike other penicillins, flucloxacillin has activity against beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as Staphylococcus...
or dicloxacillin
Dicloxacillin
Dicloxacillin is a narrow-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. It is used to treat infections caused by susceptible Gram-positive bacteria. It is active against beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus, which would otherwise be resistant to most...
monotherapy (to cover staphylococcal infection) is often sufficient in mild cellulitis, but in more moderate cases, or where streptococcal infection is suspected, then this course is usually combined with oral phenoxymethylpenicillin
Phenoxymethylpenicillin
Phenoxymethylpenicillin, commonly known as penicillin V, is a penicillin antibiotic that is orally active. It is less active than benzylpenicillin against Gram-negative bacteria. Phenoxymethylpenicillin is more acid-stable than benzylpenicillin, which allows it to be given orally...
or intravenous benzylpenicillin
Benzylpenicillin
Benzylpenicillin, commonly known as penicillin G, is the gold standard type of penicillin. 'G' in the name 'Penicillin G' refers to 'Gold Standard'. Penicillin G is typically given by a parenteral route of administration because it is unstable in the hydrochloric acid of the stomach...
, or ampicillin
Ampicillin
Ampicillin is a beta-lactam antibiotic that has been used extensively to treat bacterial infections since 1961. Until the introduction of ampicillin by the British company Beecham, penicillin therapies had only been effective against Gram-positive organisms such as staphylococci and streptococci...
/amoxicillin
Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin , formerly amoxycillin , and abbreviated amox, is a moderate-spectrum, bacteriolytic, β-lactam antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections caused by susceptible microorganisms. It is usually the drug of choice within the class because it is better absorbed, following oral...
. Pain relief is also often prescribed, but excessive pain should always be investigated as it is a symptom of necrotizing fasciitis
Necrotizing fasciitis
Necrotizing fasciitis , commonly known as flesh-eating disease or Flesh-eating bacteria syndrome, is a rare infection of the deeper layers of skin and subcutaneous tissues, easily spreading across the fascial plane within the subcutaneous tissue.Necrotizing fasciitis is a quickly progressing and...
.
Elevation of the affected area is also important.
As in other maladies characterized by wounds or tissue destruction, hyperbaric oxygen treatment can be a valuable adjunctive therapy, but is not widely available.
In animals
Horses may acquire cellulitis, usually secondary to a wound (which can be extremely small and superficial) or to a deep-tissue infection, such as an abscess or infected bone, tendon sheath, or joint. Cellulitis from a superficial wound will usually create less lamenessLameness (equine)
Lameness in horses and other equidae is a term used to refer to any number of conditions where the animal fails to travel in a regular and sound manner on all four feet...
(grade 1-2 out of 5) than that caused by septic arthritis (grade 4-5 lameness). The horse will exhibit inflammatory edema, which is marked by hot, painful swelling. This swelling differs from stocking up in that the horse will not display symmetrical swelling in two or four legs, but in only one leg. This swelling begins near the source of infection, but will eventually continue down the leg. In some cases, the swelling will also travel upward. Treatment includes cleaning the wound and caring for it properly, the administration of NSAIDs, such as phenylbutazone
Phenylbutazone
Phenylbutazone, often referred to as bute, is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug for the short-term treatment of pain and fever in animals. In the United States, it is no longer approved for human use.-In humans:...
, cold hosing, applying a sweat wrap or a poultice
Poultice
A poultice, also called cataplasm, is a soft moist mass, often heated and medicated, that is spread on cloth over the skin to treat an aching, inflamed, or painful part of the body. It can be used on wounds such as cuts...
, and mild exercise. Veterinarians may also prescribe antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s. Recovery is usually quick, and the prognosis is very good if the cellulitis is secondary to skin infection.
See also
- Haemophilus influenzae cellulitisHaemophilus influenzae cellulitisHaemophilus influenzae cellulitis is a cutaneous condition characterized by a distinctive bluish or purplish-red cellulitis of the face.- References :...
- Vibrio vulnificus infection
- Aeromonas infectionAeromonas infectionAeromonas infections may cause skin infections manifesting as cellulitis, pustules, and furuncles....
- Helicobacter cellulitisHelicobacter cellulitisHelicobacter cellulitis is a cutaneous condition caused by Helicobacter cinaedi....
- Tuberculous cellulitisTuberculous cellulitisTuberculous cellulitis is a skin condition resulting from infection with mycobacterium, and presenting as cellulitis.- See also :* Lupus vulgaris* Metastatic tuberculous abscess or ulceration* Miliary tuberculosis* Skin lesion- References :...
- List of cutaneous conditions
External links
- Cellulitis Treatment
- Cellulitis Basics - Basic description of cellulitis medical condition with pictures included.
- First hand account of Severe Cellulitis of the leg (with pictures).

