
Chalicothere
Encyclopedia
Chalicotheres were a group of herbivorous, odd-toed ungulate
(perissodactyl) mammal
s spread throughout North America
, Europe
, Asia
, and Africa
during the Early Eocene to Early Pleistocene
subepochs living from 55.8 mya—781,000 years ago, existing for approximately .
They evolved around 40 million years ago from small, forest animals similar to the early horse
s. Many chalicotheres, including such animals as Moropus
and Chalicotherium
, reached the size of a horse
. By the late Oligocene
, they had divided into two groups: one that grazed in open areas and another that was more adapted to woodlands. They died out around 3.5 million years ago, and are related to the extinct brontotheres, as well as modern day horse
s, rhinoceros
es, and tapir
s.
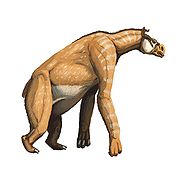
s today. Fossil
remains have shown thick, developed front knuckles, much like gorilla
s. It was once thought that the claws were used to dig up roots and tubers, however, the wear on the claws and teeth do not suggest that they dug or ate dirt-rich foods such as tubers. The chalicotheres probably used their claws to strip vegetation from trees and to forage for food.
Chalicotheres did not have front teeth
in their upper jaw, and their back teeth show little wear, suggesting that they probably were selective browsers.
from Africa
, the Nandi Bear
, could be a chalicothere.
Odd-toed ungulate
An odd-toed ungulate is a mammal with hooves that feature an odd number of toes. Odd-toed ungulates comprise the order Perissodactyla . The middle toe on each hoof is usually larger than its neighbours...
(perissodactyl) mammal
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
s spread throughout North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
, Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
, and Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
during the Early Eocene to Early Pleistocene
Early Pleistocene
Calabrian is a subdivision of the Pleistocene Epoch of the Geologic time scale. ~1.8 Ma.—781,000 years ago ± 5,000 years, a period of ~.The end of the stage is defined by the last magnetic pole reversal and plunge in to an ice age and global drying possibly colder and drier than the late Miocene ...
subepochs living from 55.8 mya—781,000 years ago, existing for approximately .
They evolved around 40 million years ago from small, forest animals similar to the early horse
Hyracotherium
Hyracotherium , also known as Eohippus or the dawn horse, is an extinct genus of very small perissodactyl ungulates that lived in the woodlands of the northern hemisphere, with species ranging throughout Asia, Europe, and North America during the early Tertiary Period and the early to mid Eocene...
s. Many chalicotheres, including such animals as Moropus
Moropus
Moropus is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to a group called chalicotheres, which were perissodactyl mammals, endemic to North America during the Miocene from ~23.0—13.6 Mya, existing for approximately ....
and Chalicotherium
Chalicotherium
Chalicotherium is a genus of extinct browsing odd-toed ungulates of the order Perissodactyla and family Chalicotheriidae, found in Europe, Africa, and Asia during the Late Oligocene to Lower Pliocene, living from 16—7.75 mya, existing for approximately .This animal...
, reached the size of a horse
Horse
The horse is one of two extant subspecies of Equus ferus, or the wild horse. It is a single-hooved mammal belonging to the taxonomic family Equidae. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature into the large, single-toed animal of today...
. By the late Oligocene
Oligocene
The Oligocene is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 34 million to 23 million years before the present . As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the period are slightly...
, they had divided into two groups: one that grazed in open areas and another that was more adapted to woodlands. They died out around 3.5 million years ago, and are related to the extinct brontotheres, as well as modern day horse
Horse
The horse is one of two extant subspecies of Equus ferus, or the wild horse. It is a single-hooved mammal belonging to the taxonomic family Equidae. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature into the large, single-toed animal of today...
s, rhinoceros
Rhinoceros
Rhinoceros , also known as rhino, is a group of five extant species of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. Two of these species are native to Africa and three to southern Asia....
es, and tapir
Tapir
A Tapir is a large browsing mammal, similar in shape to a pig, with a short, prehensile snout. Tapirs inhabit jungle and forest regions of South America, Central America, and Southeast Asia. There are four species of Tapirs: the Brazilian Tapir, the Malayan Tapir, Baird's Tapir and the Mountain...
s.

Description
Unlike modern perissodactyls, chalicotheres had long forelimbs and short hind limbs. Consequently, chalicotheres probably moved with most of their weight on their short, strong hind legs. Their front legs had long, curved claws indicating they knuckle-walked like giant anteaterGiant Anteater
The Giant Anteater, Myrmecophaga tridactyla, is the largest species of anteater. It is the only species in the genus Myrmecophaga. It is found in Central and South America from Honduras to northern Argentina...
s today. Fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
remains have shown thick, developed front knuckles, much like gorilla
Gorilla
Gorillas are the largest extant species of primates. They are ground-dwelling, predominantly herbivorous apes that inhabit the forests of central Africa. Gorillas are divided into two species and either four or five subspecies...
s. It was once thought that the claws were used to dig up roots and tubers, however, the wear on the claws and teeth do not suggest that they dug or ate dirt-rich foods such as tubers. The chalicotheres probably used their claws to strip vegetation from trees and to forage for food.
Chalicotheres did not have front teeth
Tooth
Teeth are small, calcified, whitish structures found in the jaws of many vertebrates that are used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores, also use teeth for hunting or for defensive purposes. The roots of teeth are embedded in the Mandible bone or the Maxillary bone and are...
in their upper jaw, and their back teeth show little wear, suggesting that they probably were selective browsers.
Cryptozoology
Some cryptozoologists have hypothesised that (the supposedly carnivorous) cryptidCryptid
In cryptozoology and sometimes in cryptobotany, a cryptid is a creature or plant whose existence has been suggested but is unrecognized by scientific consensus and often regarded as highly unlikely. Famous examples include the Yeti in the Himalayas and the Loch Ness Monster in...
from Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, the Nandi Bear
Nandi Bear
The Nandi Bear, also known as Ngoloko is a cryptid, or unconfirmed animal, reported to live in Africa. It takes its name from the Nandi people who live in western Kenya, near where the Nandi Bear is reported as living....
, could be a chalicothere.
See also
- MoropusMoropusMoropus is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to a group called chalicotheres, which were perissodactyl mammals, endemic to North America during the Miocene from ~23.0—13.6 Mya, existing for approximately ....
- AncylotheriumAncylotheriumAncylotherium is an extinct genus of the family Chalicotheriidae, subfamily Schizotheriinae, endemic to Europe, Asia, and Africa during the Late Miocene-Pliocene , existing for approximately .-Taxonomy:...

