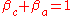Charge transfer coefficient
Encyclopedia
Charge transfer coefficient, and symmetry factor (symbols α and β, respectively) are two related parameters used in description of the kinetics
of electrochemical
reactions. They appear in the Butler-Volmer equation and related expressions.
The symmetry factor and the charge transfer coefficient are dimensionless.

The anodic transfer coefficient (αa) is defined by analogy::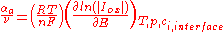
where:
-electrolyte
interface that helps in lowering the free energy barrier for the electrochemical reaction. The electroactive ion
present in the interfacial region experiences the interfacial potential and electrostatic work in done on the ion by a part of the interfacial electric field. It is charge transfer coefficient that signifies this part that is utilized in activating the ion to the top of the free energy barrier.
and fuel cell
s, charge transfer coefficient is the parameter that signifies the fraction of overpotential
that affects the current density
. This parameter has had a mysterious significance in electrochemical kinetics for over three quarters of the previous century. It can also be said that charge transfer coefficient is the heart of electrode kinetics.
The sum of anodic symmetry factor and cathodic symmetry factor are equal to one:
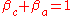
Chemical kinetics
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the study of rates of chemical processes. Chemical kinetics includes investigations of how different experimental conditions can influence the speed of a chemical reaction and yield information about the reaction's mechanism and transition...
of electrochemical
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place in a solution at the interface of an electron conductor and an ionic conductor , and which involve electron transfer between the electrode and the electrolyte or species in solution.If a chemical reaction is...
reactions. They appear in the Butler-Volmer equation and related expressions.
The symmetry factor and the charge transfer coefficient are dimensionless.
Charge transfer coefficient
According to an IUPAC definition, for a reaction with a single rate-determining step, the charge transfer coefficient for a cathodic reaction (the cathodic transfer coefficient, αc) is defined as:
The anodic transfer coefficient (αa) is defined by analogy::
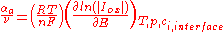
where:
 : stoichometric number, i.e., the number of activated complexes formed and destroyed in the overall reaction (with n electrons)
: stoichometric number, i.e., the number of activated complexes formed and destroyed in the overall reaction (with n electrons)-
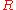 : universal gas constant
: universal gas constant -
 : absolute temperature
: absolute temperature -
 : number of electrons involved in the electrode reaction
: number of electrons involved in the electrode reaction -
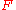 : Faraday constant
: Faraday constant -
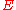 : electrode potentialElectrode potentialElectrode potential, E, in electrochemistry, according to an IUPAC definition, is the electromotive force of a cell built of two electrodes:* on the left-hand side is the standard hydrogen electrode, and...
: electrode potentialElectrode potentialElectrode potential, E, in electrochemistry, according to an IUPAC definition, is the electromotive force of a cell built of two electrodes:* on the left-hand side is the standard hydrogen electrode, and... -
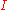 : partial cathodic (anodic) current
: partial cathodic (anodic) current
Interpretation
The charge transfer coefficient signifies the fraction of the interfacial potential at an electrodeElectrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
-electrolyte
Electrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
interface that helps in lowering the free energy barrier for the electrochemical reaction. The electroactive ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
present in the interfacial region experiences the interfacial potential and electrostatic work in done on the ion by a part of the interfacial electric field. It is charge transfer coefficient that signifies this part that is utilized in activating the ion to the top of the free energy barrier.
Batteries and fuel cells
In operating batteriesBattery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
and fuel cell
Fuel cell
A fuel cell is a device that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Hydrogen is the most common fuel, but hydrocarbons such as natural gas and alcohols like methanol are sometimes used...
s, charge transfer coefficient is the parameter that signifies the fraction of overpotential
Overpotential
Overpotential is an electrochemical term which refers to the potential difference between a half-reaction's thermodynamically determined reduction potential and the potential at which the redox event is experimentally observed. The term is directly related to a cell's voltage efficiency...
that affects the current density
Current density
Current density is a measure of the density of flow of a conserved charge. Usually the charge is the electric charge, in which case the associated current density is the electric current per unit area of cross section, but the term current density can also be applied to other conserved...
. This parameter has had a mysterious significance in electrochemical kinetics for over three quarters of the previous century. It can also be said that charge transfer coefficient is the heart of electrode kinetics.
Symmetry factor
The symmetry factor (or barrier symmetry factor) is a coefficient similar to the transfer coefficient, but applicable only to a single-step reactions.The sum of anodic symmetry factor and cathodic symmetry factor are equal to one: