Chess puzzle
Encyclopedia
A chess puzzle is a puzzle
in which knowledge of the pieces
and rules
of chess
is used to solve logically a chess-related problem. The longstanding popularity of chess has paved the way for a rich tradition of such chess-related puzzles and composed problems, which assume a familiarity with the pieces and rules of chess, but can set different objectives than a standard game.
Some chess puzzles may derive from studies which were intended to help a student of the game learn how to seal a victory, but have since evolved into an entirely separate art.
Examples of a chess puzzle include deducing the last move played, the location of a missing piece, or whether a player has lost the right to castle
. Sometimes the objective is antithetical to normal chess, such as helping (or even compelling) the opponent to checkmate
one's own king.
a game, starting with a certain composition of pieces on the chess board, and playing within the standard rules of chess.
Orthodox chess problems involve positions that can arise from actual game play (although the process of getting to that position may be unrealistic). The most common orthodox chess puzzle takes the form of checkmate in n moves. The puzzle positions are seldom similar to positions from actual play, and the challenge is not to find a winning move, but rather to find the (usually unique) move which forces checkmate as rapidly as possible.
Heterodox chess problems involve conditions that are impossible with normal play, such as multiple kings or chess variant
s, while fairy chess problems
employ pieces not used in orthodox chess, such as the amazon (a piece combining the powers of the queen
and the knight
).
. The puzzle is played on 4x4 board. The starting position contains several chess pieces. The solver may play capturing moves only. The goal is to achieve a final position that contains only a single piece (similar to peg solitaire
). There are no pawn promotions
and the king can be captured as other pieces.
An example of Solitaire Chess puzzle is shown at the right. The solution is: 1.Nxb2, 2.Rxb2, 3.Rxb3.
, queen
, rook
, knight
, and bishop
in the five marked squares so that the squares with numbers in them are attacked zero and four times respectively. The solution is to place the queen at a1 (the only place where it doesn't attack a6), king at d6 (the only place where it attacks c6), rook at c8, bishop at a4 and knight at a7.
Some chess problems, like Eight queens puzzle
or Knight's Tour
has connection to mathematics, especially to graph theory
and combinatorics
. Many famous mathematicians studied such problems, for example, Euler
, Legendre
and Gauss
. Besides finding a solution to a particular puzzle, mathematicians are usually interested in counting the total number of possibly solutions, finding solutions with certain properties, as well as generalization of the problems to NxN or rectangular boards.
Puzzle
A puzzle is a problem or enigma that tests the ingenuity of the solver. In a basic puzzle, one is intended to put together pieces in a logical way in order to come up with the desired solution...
in which knowledge of the pieces
Chess piece
Chess pieces or chessmen are the pieces deployed on a chessboard to play the game of chess. The pieces vary in abilities, giving them different values in the game...
and rules
Rules of chess
The rules of chess are rules governing the play of the game of chess. While the exact origins of chess are unclear, modern rules first took form during the Middle Ages. The rules continued to be slightly modified until the early 19th century, when they reached essentially their current form. The...
of chess
Chess
Chess is a two-player board game played on a chessboard, a square-checkered board with 64 squares arranged in an eight-by-eight grid. It is one of the world's most popular games, played by millions of people worldwide at home, in clubs, online, by correspondence, and in tournaments.Each player...
is used to solve logically a chess-related problem. The longstanding popularity of chess has paved the way for a rich tradition of such chess-related puzzles and composed problems, which assume a familiarity with the pieces and rules of chess, but can set different objectives than a standard game.
Some chess puzzles may derive from studies which were intended to help a student of the game learn how to seal a victory, but have since evolved into an entirely separate art.
Examples of a chess puzzle include deducing the last move played, the location of a missing piece, or whether a player has lost the right to castle
Castling
Castling is a special move in the game of chess involving the king and either of the original rooks of the same color. It is the only move in chess in which a player moves two pieces at the same time. Castling consists of moving the king two squares towards a rook on the player's first rank, then...
. Sometimes the objective is antithetical to normal chess, such as helping (or even compelling) the opponent to checkmate
Checkmate
Checkmate is a situation in chess in which one player's king is threatened with capture and there is no way to meet that threat. Or, simply put, the king is under direct attack and cannot avoid being captured...
one's own king.
Chess problems
Whereas the term chess puzzle refers broadly to any puzzle involving aspects of chess, a chess problem is an orthodox puzzle (see below) in which one must play and win or drawDraw (chess)
In chess, a draw is when a game ends in a tie. It is one of the possible outcomes of a game, along with a win for White and a win for Black . Usually, in tournaments a draw is worth a half point to each player, while a win is worth one point to the victor and none to the loser.For the most part,...
a game, starting with a certain composition of pieces on the chess board, and playing within the standard rules of chess.
Orthodox chess problems involve positions that can arise from actual game play (although the process of getting to that position may be unrealistic). The most common orthodox chess puzzle takes the form of checkmate in n moves. The puzzle positions are seldom similar to positions from actual play, and the challenge is not to find a winning move, but rather to find the (usually unique) move which forces checkmate as rapidly as possible.
Heterodox chess problems involve conditions that are impossible with normal play, such as multiple kings or chess variant
Chess variant
A chess variant is a game related to, derived from or inspired by chess. The difference from chess might include one or more of the following:...
s, while fairy chess problems
Fairy chess
Fairy chess comprises chess problems that differ from classical chess problems in that they are not direct mates. The term was introduced before the First World War. While selfmate dates from the Middle Age, helpmate was invented by Max Lange in the late 19th century. Thomas Dawson , pioneer of...
employ pieces not used in orthodox chess, such as the amazon (a piece combining the powers of the queen
Queen (chess)
The queen is the most powerful piece in the game of chess, able to move any number of squares vertically, horizontally, or diagonally. Each player starts the game with one queen, placed in the middle of the first rank next to the king. With the chessboard oriented correctly, the white queen starts...
and the knight
Knight (chess)
The knight is a piece in the game of chess, representing a knight . It is normally represented by a horse's head and neck. Each player starts with two knights, which begin on the row closest to the player, one square from the corner...
).
Tactical puzzles
Chess puzzles can also be regular positions from a game (with normal rules), usually meant as training positions, tactical or positional, from all phases of the game (openings, middlegame of endings). These are known as tactical puzzles. They can range from a simple "Mate in one" combination to a complex attack on the opponent's king. Solving tactical chess puzzles is a very common chess teaching technique. Although it is unlikely that the same position will occur in a game the student plays, the recognition of certain patterns can help to find a good move or plan in another position.Solitaire Chess
Solitaire Chess is a chess puzzle produced by ThinkFunThinkFun
ThinkFun, formerly known as Binary Arts, was founded in 1985 by Bill Ritchie and Andrea Barthello. The two started the company from the basement of their home in Virginia, with a product base that initially consisted of four games invented by a family friend William Keister...
. The puzzle is played on 4x4 board. The starting position contains several chess pieces. The solver may play capturing moves only. The goal is to achieve a final position that contains only a single piece (similar to peg solitaire
Peg solitaire
Peg solitaire is a board game for one player involving movement of pegs on a board with holes. Some sets use marbles in a board with indentations. The game is known simply as Solitaire in the United Kingdom where the card games are called Patience...
). There are no pawn promotions
Promotion (chess)
Promotion is a chess rule describing the transformation of a pawn that reaches its eighth rank into the player's choice of a queen, knight, rook, or bishop of the same color . The new piece replaces the pawn on the same square and is part of the move. Promotion is not limited to pieces that have...
and the king can be captured as other pieces.
An example of Solitaire Chess puzzle is shown at the right. The solution is: 1.Nxb2, 2.Rxb2, 3.Rxb3.
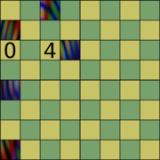
Chess miner
Chess miner is a chess puzzle, where the goal is to deduce the location of invisible pieces based on information about how many times certain squares are attacked. For example, in the position at right, the challenge is to place a white kingKing (chess)
In chess, the king is the most important piece. The object of the game is to trap the opponent's king so that its escape is not possible . If a player's king is threatened with capture, it is said to be in check, and the player must remove the threat of capture on the next move. If this cannot be...
, queen
Queen (chess)
The queen is the most powerful piece in the game of chess, able to move any number of squares vertically, horizontally, or diagonally. Each player starts the game with one queen, placed in the middle of the first rank next to the king. With the chessboard oriented correctly, the white queen starts...
, rook
Rook (chess)
A rook is a piece in the strategy board game of chess. Formerly the piece was called the castle, tower, marquess, rector, and comes...
, knight
Knight (chess)
The knight is a piece in the game of chess, representing a knight . It is normally represented by a horse's head and neck. Each player starts with two knights, which begin on the row closest to the player, one square from the corner...
, and bishop
Bishop (chess)
A bishop is a piece in the board game of chess. Each player begins the game with two bishops. One starts between the king's knight and the king, the other between the queen's knight and the queen...
in the five marked squares so that the squares with numbers in them are attacked zero and four times respectively. The solution is to place the queen at a1 (the only place where it doesn't attack a6), king at d6 (the only place where it attacks c6), rook at c8, bishop at a4 and knight at a7.
Mathematical chess problems
- Main article: Mathematical chess problemMathematical chess problemMathematical chess problem is a mathematical problem which is formulated using chessboard or chess pieces. These problems belong to recreational mathematics. The most known problems of this kind are Eight queens puzzle or Knight's Tour problems, which have connection to graph theory and combinatorics...
Some chess problems, like Eight queens puzzle
Eight queens puzzle
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens attack each other. Thus, a solution requires that no two queens share the same row, column, or diagonal...
or Knight's Tour
Knight's tour
The knight's tour is a mathematical problem involving a knight on a chessboard. The knight is placed on the empty board and, moving according to the rules of chess, must visit each square exactly once. A knight's tour is called a closed tour if the knight ends on a square attacking the square from...
has connection to mathematics, especially to graph theory
Graph theory
In mathematics and computer science, graph theory is the study of graphs, mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects from a certain collection. A "graph" in this context refers to a collection of vertices or 'nodes' and a collection of edges that connect pairs of...
and combinatorics
Combinatorics
Combinatorics is a branch of mathematics concerning the study of finite or countable discrete structures. Aspects of combinatorics include counting the structures of a given kind and size , deciding when certain criteria can be met, and constructing and analyzing objects meeting the criteria ,...
. Many famous mathematicians studied such problems, for example, Euler
Leonhard Euler
Leonhard Euler was a pioneering Swiss mathematician and physicist. He made important discoveries in fields as diverse as infinitesimal calculus and graph theory. He also introduced much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, particularly for mathematical analysis, such as the notion...
, Legendre
Adrien-Marie Legendre
Adrien-Marie Legendre was a French mathematician.The Moon crater Legendre is named after him.- Life :...
and Gauss
Carl Friedrich Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss was a German mathematician and scientist who contributed significantly to many fields, including number theory, statistics, analysis, differential geometry, geodesy, geophysics, electrostatics, astronomy and optics.Sometimes referred to as the Princeps mathematicorum...
. Besides finding a solution to a particular puzzle, mathematicians are usually interested in counting the total number of possibly solutions, finding solutions with certain properties, as well as generalization of the problems to NxN or rectangular boards.
See also
- Wheat and Chessboard ProblemWheat and Chessboard ProblemThe wheat and chessboard problem is a mathematical problem: To solve this, observe that a chess board is an 8×8 square, containing 64 squares...
from the Sassa legend - Mutilated chessboard problemMutilated chessboard problemThe mutilated chessboard problem is a tiling puzzle introduced by and discussed by Martin Gardner in his Scientific American column "Mathematical Games." The problem is as follows:...
- Single player chess variants

