Chinese telegraph code
Encyclopedia
The Chinese Telegraph Code, Chinese Telegraphic Code, or Chinese Commercial Code ( or ) is a four-digit decimal code (character encoding
) for electrically telegraphing
messages written with Chinese character
s.
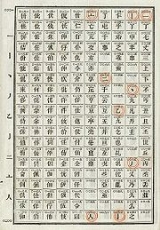
and strokes. Each page of the book shows 100 pairs of a Chinese character and a number in a 10×10 table. The most significant two digits of a code matches the page number, the next digit matches the row number, and the least significant digit matches the column number. For example, the code
Senders convert their messages written with Chinese characters to a sequence of digits according to the codebook. For instance, the phrase (Zhōngwén xìnxī), meaning “information in Chinese,” is rendered into the code as
. Receivers decode the Morse code to get a sequence of digits, chop it into an array of quadruplets, and then decode them one by one referring to the book.
Senders may translate their messages into numbers by themselves, or pay a small charge to have them translated by a telegrapher. Chinese expert telegraphers used to remember several thousands of codes of the most frequent use.
The Standard Telegraph Codebook gives alternative three-letter code (
However, looking up a number given a character is more difficult, as it requires analyzing the character. The four corner method
was developed in the 1920s to allow people to more easily look up characters by the shape, and remains in use today as a Chinese input method for computers
.
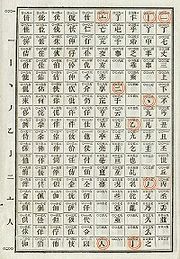 The first telegraph code for Chinese was brought into use soon after the Great Northern Telegraph Company
The first telegraph code for Chinese was brought into use soon after the Great Northern Telegraph Company
( / Dàběi Diànbào Gōngsī) introduced telegraphy to China in 1871. Septime Auguste Viguier, a Frenchman and customs officer in Shanghai, published a codebook (Viguier 1872), succeeding Danish astronomer Hans Carl Frederik Christian Schjellerup’s earlier work.
In consideration of the former code’s insufficiency and disorder of characters, Zheng Guanying ( / Zhèng Guānyīng) compiled a new codebook in 1881. It remained in effect until the Ministry of Transportation and Communications printed a new book in 1929. In 1933, a supplement was added to the book.
After the establishment of the People’s Republic of China in 1949, the codebook forked into two different versions, due to revisions made in the Mainland China and Taiwan independently from each other. The Mainland version, the Standard Telegraph Codebook, adopted the simplified Chinese character
s in 1981.
. Ordinary computer users today hardly master it because it needs a lot of rote memorization. However, the related four corner method
, which allows one to look up characters by shape, is used.
The Hong Kong residents’ identification cards
have the Chinese telegraph code for the holder’s Chinese name (Immigration Department of Hong Kong 2006). Business forms provided by the government and corporations in Hong Kong often require filling out telegraph codes for Chinese names. The codes help inputting Chinese characters to a computer.
Chinese telegraph code is used extensively in law enforcement investigations worldwide that involve ethnic Chinese subjects where variant phonetic spellings of Chinese names can create confusion. Dialectical differences (Mr. Wu in Mandarin becomes Mr. Ng in Cantonese) and differing romanization
systems (Mr. Xiao in the Hanyu pinyin system, and Mr. Hsiao in the Wade Giles system) can create serious problems for investigators, but can be remedied by application of Chinese telegraph code. For instance, investigators following a subject in Taiwan named Hsiao Ai-Kuo might not know this is the same person known in mainland China as Xiao Ai Guo and Hong Kong as Siu Oi-Kwok until codes are checked for the actual Chinese characters to determine all match as CTC: 5618/1947/0948 for 萧爱国.
Chinese telegraph code is also used on occasion in U.S. Immigration documents. For example, the DS-230 form for K1/K2 visa applicants requires the telegraph code of the applicant's name (as of 8 March 2009).
Character encoding
A character encoding system consists of a code that pairs each character from a given repertoire with something else, such as a sequence of natural numbers, octets or electrical pulses, in order to facilitate the transmission of data through telecommunication networks or storage of text in...
) for electrically telegraphing
Electrical telegraph
An electrical telegraph is a telegraph that uses electrical signals, usually conveyed via telecommunication lines or radio. The electromagnetic telegraph is a device for human-to-human transmission of coded text messages....
messages written with Chinese character
Chinese character
Chinese characters are logograms used in the writing of Chinese and Japanese , less frequently Korean , formerly Vietnamese , or other languages...
s.
Encoding and decoding
A codebook is provided for encoding and decoding the Chinese telegraph code. It shows one-to-one correspondence between Chinese characters and four-digit numbers from0000 to 9999. Chinese characters are arranged and numbered in dictionary order according to their radicalsRadical (Chinese character)
A Chinese radical is a component of a Chinese character. The term may variously refer to the original semantic element of a character, or to any semantic element, or, loosely, to any element whatever its origin or purpose...
and strokes. Each page of the book shows 100 pairs of a Chinese character and a number in a 10×10 table. The most significant two digits of a code matches the page number, the next digit matches the row number, and the least significant digit matches the column number. For example, the code
0022 for the character (zhōng), meaning “center,” is given in page 00, row 2, column 2 of the codebook, and the code 2429 for the character (wén), meaning “script,” is given in page 24, row 2, column 9. The PRC’s Standard Telegraph Codebook (Ministry of Post and Telecommunications 2002) provides codes for approximately 7,000 Chinese characters.Senders convert their messages written with Chinese characters to a sequence of digits according to the codebook. For instance, the phrase (Zhōngwén xìnxī), meaning “information in Chinese,” is rendered into the code as
0022 2429 0207 1873. It is transmitted using the Morse codeMorse code
Morse code is a method of transmitting textual information as a series of on-off tones, lights, or clicks that can be directly understood by a skilled listener or observer without special equipment...
. Receivers decode the Morse code to get a sequence of digits, chop it into an array of quadruplets, and then decode them one by one referring to the book.
Senders may translate their messages into numbers by themselves, or pay a small charge to have them translated by a telegrapher. Chinese expert telegraphers used to remember several thousands of codes of the most frequent use.
The Standard Telegraph Codebook gives alternative three-letter code (
AAA, AAB, …) for Chinese characters. It compresses telegram messages and cuts international fees by 25% as compared to the four-digit code. The codebook also defines codes for Zhuyin alphabet, Latin alphabet, Cyrillic alphabet, and various symbols including special symbols for months, days in a month, and hours.Use
Looking up a character given a number is straightforward: page, row, column.However, looking up a number given a character is more difficult, as it requires analyzing the character. The four corner method
Four corner method
The Four Corner Method is a character input method used for encoding Chinese characters into either a computer or a manual typewriter, using four or five numerical digits per character. The Four Corner Method is also known as the Four Corner System.The four digits encode the shapes found in the...
was developed in the 1920s to allow people to more easily look up characters by the shape, and remains in use today as a Chinese input method for computers
Chinese input methods for computers
Hundreds of Chinese input methods are available for entry of Chinese characters into computers, but most keyboard-based methods rely on either pinyin phonetic readings or root shapes in Chinese characters...
.
History

Great Northern Telegraph Company
The Great Northern Telegraph Company was a Danish telegraph company founded in June 1869...
( / Dàběi Diànbào Gōngsī) introduced telegraphy to China in 1871. Septime Auguste Viguier, a Frenchman and customs officer in Shanghai, published a codebook (Viguier 1872), succeeding Danish astronomer Hans Carl Frederik Christian Schjellerup’s earlier work.
In consideration of the former code’s insufficiency and disorder of characters, Zheng Guanying ( / Zhèng Guānyīng) compiled a new codebook in 1881. It remained in effect until the Ministry of Transportation and Communications printed a new book in 1929. In 1933, a supplement was added to the book.
After the establishment of the People’s Republic of China in 1949, the codebook forked into two different versions, due to revisions made in the Mainland China and Taiwan independently from each other. The Mainland version, the Standard Telegraph Codebook, adopted the simplified Chinese character
Simplified Chinese character
Simplified Chinese characters are standardized Chinese characters prescribed in the Xiandai Hanyu Tongyong Zibiao for use in Mainland China. Along with traditional Chinese characters, it is one of many standard character sets of the contemporary Chinese written language...
s in 1981.
Application
The Chinese telegraph code can be used for a Chinese input method for computersChinese input methods for computers
Hundreds of Chinese input methods are available for entry of Chinese characters into computers, but most keyboard-based methods rely on either pinyin phonetic readings or root shapes in Chinese characters...
. Ordinary computer users today hardly master it because it needs a lot of rote memorization. However, the related four corner method
Four corner method
The Four Corner Method is a character input method used for encoding Chinese characters into either a computer or a manual typewriter, using four or five numerical digits per character. The Four Corner Method is also known as the Four Corner System.The four digits encode the shapes found in the...
, which allows one to look up characters by shape, is used.
The Hong Kong residents’ identification cards
Hong Kong Identity Card
The Hong Kong Identity Card is an official identity document issued by the Immigration Department of Hong Kong. The Hong Kong Permanent Identity Card is a class of HKID issued to Hong Kong residents who have the right of abode in Hong Kong SAR. According to the Registration of Persons Ordinance...
have the Chinese telegraph code for the holder’s Chinese name (Immigration Department of Hong Kong 2006). Business forms provided by the government and corporations in Hong Kong often require filling out telegraph codes for Chinese names. The codes help inputting Chinese characters to a computer.
Chinese telegraph code is used extensively in law enforcement investigations worldwide that involve ethnic Chinese subjects where variant phonetic spellings of Chinese names can create confusion. Dialectical differences (Mr. Wu in Mandarin becomes Mr. Ng in Cantonese) and differing romanization
Romanization
In linguistics, romanization or latinization is the representation of a written word or spoken speech with the Roman script, or a system for doing so, where the original word or language uses a different writing system . Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written...
systems (Mr. Xiao in the Hanyu pinyin system, and Mr. Hsiao in the Wade Giles system) can create serious problems for investigators, but can be remedied by application of Chinese telegraph code. For instance, investigators following a subject in Taiwan named Hsiao Ai-Kuo might not know this is the same person known in mainland China as Xiao Ai Guo and Hong Kong as Siu Oi-Kwok until codes are checked for the actual Chinese characters to determine all match as CTC: 5618/1947/0948 for 萧爱国.
Chinese telegraph code is also used on occasion in U.S. Immigration documents. For example, the DS-230 form for K1/K2 visa applicants requires the telegraph code of the applicant's name (as of 8 March 2009).
See also
- Code pointCode pointIn character encoding terminology, a code point or code position is any of the numerical values that make up the code space . For example, ASCII comprises 128 code points in the range 0hex to 7Fhex, Extended ASCII comprises 256 code points in the range 0hex to FFhex, and Unicode comprises 1,114,112...
- Telegraph codeTelegraph codeA telegraph code is a character encoding used to transmit information through telegraphy machines. The most famous such code is Morse code.-Manual telegraph codes:Morse code can be transmitted and received with very primitive equipment....
- Four corner methodFour corner methodThe Four Corner Method is a character input method used for encoding Chinese characters into either a computer or a manual typewriter, using four or five numerical digits per character. The Four Corner Method is also known as the Four Corner System.The four digits encode the shapes found in the...
, a 4-digit structural encoding method designed to aid lookup of telegraph codes
External links
- Chinese Commercial/Telegraph Code Lookup by NJStar
- Standard telegraph code (Chinese commercial code)
- Standard telegraph code (Chinese commercial code)Search

