Choking game
Encyclopedia
The fainting game refers to intentionally cutting off oxygen to the brain with the goal of inducing temporary syncope
and euphoria
. There are two distinct methods used to achieve oxygen deprivation: strangulation
and self-induced hypocapnia
.
, which is oxygen deprivation for sexual arousal. Unlike erotic asphyxiation, practice of the fainting game appears to be uncommon in adulthood.
(oxygen deprivation to the brain). The two mechanisms tend to be confused with each other or treated as one but are quite dissimilar although both have the potential to cause permanent brain damage or death. The two mechanisms are strangulation and self-induced hypocapnia
and work as follows:
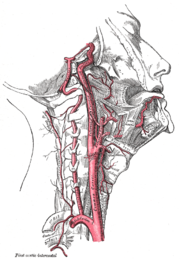
. Apart from the direct restriction of blood to the brain there are two other significant responses produced by pressing on the neck:
This method is responsible for most, but not all, of the reported fatalities.
The method is especially dangerous when practiced alone. Involuntary movements can lead to head trauma and other injuries. If standing, loss of consciousness can result in substantial head trauma through falling. In the event that consciousness is not immediately regained, medical help cannot be sought by a third party, observer, or friends. If the administration of CPR or basic life support is needed due to respiratory or cardiac arrest, help would not be available or quickly summonable when unconscious or not breathing. Also this act could be mistaken for suicide when practiced alone, but accidentally observed by a stranger, to whom the motivation behind the apparent 'strangulation' is not known.
(forced overbreathing) until symptoms of hypocapnia
such as tingling, light-headedness or dizziness are felt, followed by a breath-hold. This alone is enough to cause a blackout, but it is widely believed that the effect is enhanced if lung air pressure is increased by holding the breath "hard" or "bearing down" (tightening the diaphragm as in a forced exhalation while allowing no air to escape or having an assistant apply a bear-hug). These latter actions may augment the effects of hypoxia by approximating the Valsalva maneuver
, causing vagal stimulation.
The hyperventilation leads to an excessive elimination of carbon dioxide
(CO2) whereas no significant additional amounts of oxygen can be stocked in the body. As only carbon dioxide is responsible for the breathing stimulus, after hyperventilation, breath can be held longer until cerebral hypoxia
occurs. The blood also becomes abnormally alkaline as a result of the excessive elimination of carbon dioxide; this subsequent rise in blood pH
is termed alkalosis
. Alkalosis interferes with normal oxygen utilization by the brain. The symptoms of alkalosis are: neuromuscular irritability, muscular spasms, tingling and numbness of the extremities and around the mouth, and a dizziness, or giddiness, often interpreted as a sense of euphoria
. This brief euphoria is what practitioners of the fainting game seek.
In the body alkalosis generally induces vasodilatation (widening of the blood vessels) but in the brain alone it causes vasoconstriction
(narrowing of the blood vessels). This vasoconstriction appears to be made even worse by a sudden increase in blood pressure caused by squeezing or holding the breath ‘hard’. The alkalosis induced euphoria can be followed rapidly by hypoxia-induced unconsciousness. The sequence of events leading to unconsciousness from hyperventilation is as follows:
Because the brain cannot store reserves of oxygen and, unlike other organs, has an exceedingly low tolerance of oxygen deprivation, it is highly vulnerable if vasoconstriction is not reversed. Normally, if the brain is hypoxic, autonomous systems in the body divert blood to the brain at the expense of other organs; because the brain is vasoconstricted this mechanism is not available. Vasoconstriction is only reversed by the build-up of carbon dioxide in the blood through suspension of breathing.
In some versions the bear-hug is replaced by pressure on the neck in which case blackout is a hybrid of strangulation and self-induced hypocapnia.
may induce a syncope (fainting) without any other action at all but this is difficult to reproduce and is not the basis of the game. For those susceptible to carotid sinus syncope, of which most people would be unaware until it occurred, this can be an exceedingly dangerous game.
In both strangulation and self-induced hypocapnia blackouts the victim may experience dreaming or hallucinations, though fleetingly, and regains consciousness with short-term memory loss and involuntary movement of their hands or feet. Full recovery is usually made within seconds but these activities cause many permanent brain injuries or death, particularly when played alone or with a ligature.
study found that at least 79,000 students in the Canadian province of Ontario
participated in this act. The 2006 Youth Health Risk Behavioral Survey in Williams County
, Ohio
found that 11% of youths aged 12–18 years and 19% of youths aged 17–18 reported ever having practiced it.
 Any activity that deprives the brain of oxygen has the potential to cause moderate to severe brain cell death leading to permanent loss of neurological function ranging from difficulty in concentration or loss of short term memory capacity through severe, lifelong mental disability to death.
Any activity that deprives the brain of oxygen has the potential to cause moderate to severe brain cell death leading to permanent loss of neurological function ranging from difficulty in concentration or loss of short term memory capacity through severe, lifelong mental disability to death.
Statistics on fatalities and neurological damage are controversial, no definitive, empirical study exists although the indications are that the practice is a significant contributor to death and disability, particularly among male juveniles
in most developed countries. Many believe that deaths are significantly underreported because of false attributions to suicide.
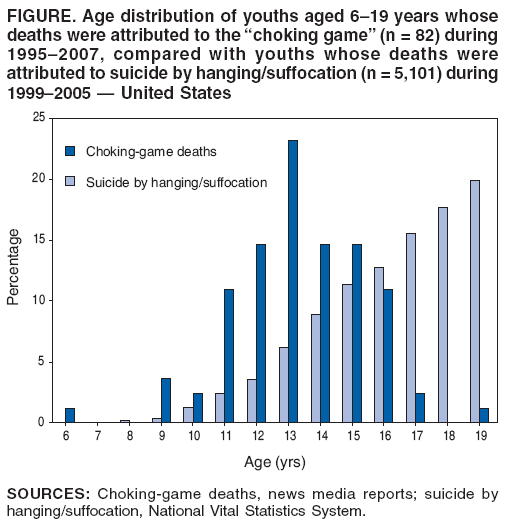
One study by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
(CDC) found sufficient evidence to indicate that since 1995 at least 82 youths between the age of 6 and 19 have died in the United States as a result of the game (being roughly 1% of the deaths attributed to suicide by suffocation in the same age group), see chart on the right. Of these 86.6% were male, the mean age being 13.3. 95.7% of these deaths occurred while the youth was alone; parents of the decedents were unaware of the game in 92.9% of cases. Deaths were recorded in 31 states and were not clustered by location, season or day of week. Neurological damage is harder to attribute accurately because of the difficulty of linking generalised, acquired neurological disability to a specific past event.
Incidental, or indirect, injuries may arise from falling or uncontrolled movements and crushing by a ligature or an assistant. Such injuries may include concussion, bone fracture
s, tongue biting and hemorrhaging of the eye.
The CDC encourages parents, educators and health-care providers to familiarize themselves with the signs of the game. These include: discussion of the game; bloodshot eyes; marks on the neck; severe headaches; disorientation after spending time alone; ropes, scarves, and belts tied to bedroom furniture or doorknobs or found knotted on the floor; and unexplained presence of things like dog leashes, choke collars and bungee cords.
The Fainting Game, Riding a Rocket, Airplaning, America Dream Game, Black Out Game, Breath Play, Bum Rushing, California Choke, California Dreaming, California Headrush, California High, California Knockout, Choking Out, Cloud Nine, Dumbass Game, Dying game, Dream Game, Dreaming Game, Elevator, Flatline Game, Flat Liner, Flatliner Game, Funky Chicken, Harvey Wallbanger, Hyperventilation Game, Indian Headrush, Knockout Game, Pass-out Game, Passing Out Game, Natural High, Sleeper Hold, Space Cowboy, Space Monkey, Suffocation Game, Suffocation Roulette, Teen Choking Game, Rising Sun, High Riser, Tingling Game, Trip to Heaven, Rocket Ride and Speed Dreaming, Wall-Hit, Purple Dragon, Five second high
Syncope (medicine)
Syncope , the medical term for fainting, is precisely defined as a transient loss of consciousness and postural tone characterized by rapid onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery due to global cerebral hypoperfusion that most often results from hypotension.Many forms of syncope are...
and euphoria
Euphoria
Euphoria is an emotional and mental state defined as a sense of great elation and well being.Euphoria may also refer to:* Euphoria , a genus of scarab beetles* Euphoria, a genus name previously used for the longan and other trees...
. There are two distinct methods used to achieve oxygen deprivation: strangulation
Strangling
Strangling is compression of the neck that may lead to unconsciousness or death by causing an increasingly hypoxic state in the brain. Fatal strangling typically occurs in cases of violence, accidents, and as the auxiliary lethal mechanism in hangings in the event the neck does not break...
and self-induced hypocapnia
Hypocapnia
Hypocapnia or hypocapnea also known as hypocarbia, sometimes incorrectly called acapnia, is a state of reduced carbon dioxide in the blood. Hypocapnia usually results from deep or rapid breathing, known as hyperventilation....
.
Differences from erotic asphyxiation
According to Dr. Steve Field, chairman of the Royal College of General Practitioners in London, the fainting game is pursued primarily by children and teens "to get a high without taking drugs." Children "aren't playing this game for sexual gratification." It is frequently confused with erotic asphyxiationErotic asphyxiation
Erotic asphyxiation or breath control play is the intentional restriction of oxygen to the brain for sexual arousal. The sexual preference for that behavior is variously called asphyxiophilia, autoerotic asphyxia, hypoxyphilia. Colloquially, a person engaging in the activity is sometimes called a...
, which is oxygen deprivation for sexual arousal. Unlike erotic asphyxiation, practice of the fainting game appears to be uncommon in adulthood.
Reasons for practice
Limited research has been conducted regarding motivations for practicing the fainting game, although thrill-seeking has been identified as a risk factor, as has the perception that it is a low-risk activity. Anecdotal reasons stated include:- Being released from class during the school day.
- Peer pressure, a challenge or dare, a rite of passageRite of passageA rite of passage is a ritual event that marks a person's progress from one status to another. It is a universal phenomenon which can show anthropologists what social hierarchies, values and beliefs are important in specific cultures....
into a social group or amusement over erratic behavior. - Curiosity in experiencing an altered state of consciousnessAltered state of consciousnessAn altered state of consciousness , also named altered state of mind, is any condition which is significantly different from a normal waking beta wave state. The expression was used as early as 1966 by Arnold M. Ludwig and brought into common usage from 1969 by Charles Tart: it describes induced...
, the experience of a brownoutBrownout (medical)A greyout is a transient loss of vision characterized by a perceived dimming of light and color, sometimes accompanied a loss of peripheral vision...
, or an imagined approximation to a near death experience. - A belief that it can induce a brief sense of euphoriaEuphoria (emotion)Euphoria is medically recognized as a mental and emotional condition in which a person experiences intense feelings of well-being, elation, happiness, ecstasy, excitement and joy...
(a rushing sensation or highAltered state of consciousnessAn altered state of consciousness , also named altered state of mind, is any condition which is significantly different from a normal waking beta wave state. The expression was used as early as 1966 by Arnold M. Ludwig and brought into common usage from 1969 by Charles Tart: it describes induced...
). - The prospect of intoxication, albeit brief, at no financial cost.
Mechanisms behind the activity
There are two main mechanisms behind many variations of this practice, both resulting in cerebral hypoxiaCerebral hypoxia
Cerebral hypoxia refers to a reduced supply of oxygen to the brain. Cerebral anoxia refers to a complete lack of oxygen to the brain. There are four separate categories of cerebral hypoxia; in order of severity they are; diffuse cerebral hypoxia , focal cerebral ischemia, cerebral infarction, and...
(oxygen deprivation to the brain). The two mechanisms tend to be confused with each other or treated as one but are quite dissimilar although both have the potential to cause permanent brain damage or death. The two mechanisms are strangulation and self-induced hypocapnia
Hypocapnia
Hypocapnia or hypocapnea also known as hypocarbia, sometimes incorrectly called acapnia, is a state of reduced carbon dioxide in the blood. Hypocapnia usually results from deep or rapid breathing, known as hyperventilation....
and work as follows:

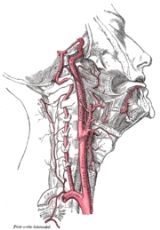
Strangulation
A ligature such as a belt or rope around the neck, or hands or arm pressure on the neck compresses the internal carotid arteryInternal carotid artery
In human anatomy, the internal carotid arteries are two major arteries, one on each side of the head and neck. They arise from the common carotid arteries where these bifurcate into the internal and external carotid artery, and they supply the brain....
. Apart from the direct restriction of blood to the brain there are two other significant responses produced by pressing on the neck:
- Pressing on the carotid arteries also presses on baroreceptors. These bodies then cause vasodilatation (dilation (widening) of the blood vessels) in the brain leading to insufficient blood to perfuse the brain with oxygen and maintain consciousness.
- A message is also sent via the vagus nerveVagus nerveThe vagus nerve , also called pneumogastric nerve or cranial nerve X, is the tenth of twelve paired cranial nerves...
to the main pacemakerCardiac pacemakerright|thumb|350px|Image showing the cardiac pacemaker which is the SA nodeThe contraction of heart muscle in all animals with hearts is initiated by chemical impulses. The rate at which these impulses fire controls the heart rate...
of the heartHeartThe heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
to decrease the rate and volume of the heartbeat, typically by up to a third. In some cases there is evidence that this may escalate into asystoleAsystoleIn medicine, asystole is a state of no cardiac electrical activity, hence no contractions of the myocardium and no cardiac output or blood flow...
, a form of cardiac arrestCardiac arrestCardiac arrest, is the cessation of normal circulation of the blood due to failure of the heart to contract effectively...
that is difficult to treat. There is a dissenting view on the full extent how and when a person reaches a stage of permanent injury, but it is agreed that pressure on the vagus nerve causes changes to pulse rate and blood pressure and is dangerous in cases of carotid sinus hypersensitivity.
This method is responsible for most, but not all, of the reported fatalities.
The method is especially dangerous when practiced alone. Involuntary movements can lead to head trauma and other injuries. If standing, loss of consciousness can result in substantial head trauma through falling. In the event that consciousness is not immediately regained, medical help cannot be sought by a third party, observer, or friends. If the administration of CPR or basic life support is needed due to respiratory or cardiac arrest, help would not be available or quickly summonable when unconscious or not breathing. Also this act could be mistaken for suicide when practiced alone, but accidentally observed by a stranger, to whom the motivation behind the apparent 'strangulation' is not known.
Self-induced hypocapnia
The second mechanism requires hyperventilationHyperventilation
Hyperventilation or overbreathing is the state of breathing faster or deeper than normal, causing excessive expulsion of circulating carbon dioxide. It can result from a psychological state such as a panic attack, from a physiological condition such as metabolic acidosis, can be brought about by...
(forced overbreathing) until symptoms of hypocapnia
Hypocapnia
Hypocapnia or hypocapnea also known as hypocarbia, sometimes incorrectly called acapnia, is a state of reduced carbon dioxide in the blood. Hypocapnia usually results from deep or rapid breathing, known as hyperventilation....
such as tingling, light-headedness or dizziness are felt, followed by a breath-hold. This alone is enough to cause a blackout, but it is widely believed that the effect is enhanced if lung air pressure is increased by holding the breath "hard" or "bearing down" (tightening the diaphragm as in a forced exhalation while allowing no air to escape or having an assistant apply a bear-hug). These latter actions may augment the effects of hypoxia by approximating the Valsalva maneuver
Valsalva maneuver
The Valsalva maneuver or Valsalva manoeuvre is performed by moderately forceful attempted exhalation against a closed airway, usually done by closing one's mouth and pinching one's nose shut...
, causing vagal stimulation.
The hyperventilation leads to an excessive elimination of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
(CO2) whereas no significant additional amounts of oxygen can be stocked in the body. As only carbon dioxide is responsible for the breathing stimulus, after hyperventilation, breath can be held longer until cerebral hypoxia
Cerebral hypoxia
Cerebral hypoxia refers to a reduced supply of oxygen to the brain. Cerebral anoxia refers to a complete lack of oxygen to the brain. There are four separate categories of cerebral hypoxia; in order of severity they are; diffuse cerebral hypoxia , focal cerebral ischemia, cerebral infarction, and...
occurs. The blood also becomes abnormally alkaline as a result of the excessive elimination of carbon dioxide; this subsequent rise in blood pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
is termed alkalosis
Alkalosis
Alkalosis refers to a condition reducing hydrogen ion concentration of arterial blood plasma . Generally, alkalosis is said to occur when pH of the blood exceeds 7.45. The opposite condition is acidosis .-Causes:...
. Alkalosis interferes with normal oxygen utilization by the brain. The symptoms of alkalosis are: neuromuscular irritability, muscular spasms, tingling and numbness of the extremities and around the mouth, and a dizziness, or giddiness, often interpreted as a sense of euphoria
Euphoria (emotion)
Euphoria is medically recognized as a mental and emotional condition in which a person experiences intense feelings of well-being, elation, happiness, ecstasy, excitement and joy...
. This brief euphoria is what practitioners of the fainting game seek.
In the body alkalosis generally induces vasodilatation (widening of the blood vessels) but in the brain alone it causes vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, particularly the large arteries, small arterioles and veins. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels. The process is particularly important in...
(narrowing of the blood vessels). This vasoconstriction appears to be made even worse by a sudden increase in blood pressure caused by squeezing or holding the breath ‘hard’. The alkalosis induced euphoria can be followed rapidly by hypoxia-induced unconsciousness. The sequence of events leading to unconsciousness from hyperventilation is as follows:
- Decrease in partial pressurePartial pressureIn a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture....
of alveolarPulmonary alveolusAn alveolus is an anatomical structure that has the form of a hollow cavity. Found in the lung parenchyma, the pulmonary alveoli are the dead ends of the respiratory tree, which outcrop from either alveolar sacs or alveolar ducts, which are both sites of gas exchange with the blood as well...
CO2. - Decrease in partial pressure of arterial CO2.
- Increase in blood pH, (respiratory alkalosis).
- Vasoconstriction of blood vessels supplying brain.
- Pooling of the blood present in the brain at the time.
- Brain rapidly uses up oxygenOxygenOxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
(O2) available in the pooled blood. - O2 concentration in the brain drops.
- Unconsciousness from hypoxia of cerebral tissue.
Because the brain cannot store reserves of oxygen and, unlike other organs, has an exceedingly low tolerance of oxygen deprivation, it is highly vulnerable if vasoconstriction is not reversed. Normally, if the brain is hypoxic, autonomous systems in the body divert blood to the brain at the expense of other organs; because the brain is vasoconstricted this mechanism is not available. Vasoconstriction is only reversed by the build-up of carbon dioxide in the blood through suspension of breathing.
In some versions the bear-hug is replaced by pressure on the neck in which case blackout is a hybrid of strangulation and self-induced hypocapnia.
Other mechanisms
Unconsciousness may be induced by other methods although these are controversial: Pressure over the carotid sinusCarotid sinus
In human anatomy, the carotid sinus is a localized dilation of the internal carotid artery at its origin, the common carotid artery.-Functions:...
may induce a syncope (fainting) without any other action at all but this is difficult to reproduce and is not the basis of the game. For those susceptible to carotid sinus syncope, of which most people would be unaware until it occurred, this can be an exceedingly dangerous game.
In both strangulation and self-induced hypocapnia blackouts the victim may experience dreaming or hallucinations, though fleetingly, and regains consciousness with short-term memory loss and involuntary movement of their hands or feet. Full recovery is usually made within seconds but these activities cause many permanent brain injuries or death, particularly when played alone or with a ligature.
Prevalence
A 2008 Centre for Addiction and Mental HealthCentre for Addiction and Mental Health
The Centre for Addiction and Mental Health is a consortium of mental health clinics at several sites in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Its name in French is Centre de toxicomanie et de santé mentale...
study found that at least 79,000 students in the Canadian province of Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
participated in this act. The 2006 Youth Health Risk Behavioral Survey in Williams County
Williams County, Ohio
Williams County is a county located in the U.S. state of Ohio. As of 2010, the population was 37,642. Its county seat is Bryan and is named for David Williams, one of the captors of John André in the American Revolutionary War.-Geography:According to the U.S...
, Ohio
Ohio
Ohio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus...
found that 11% of youths aged 12–18 years and 19% of youths aged 17–18 reported ever having practiced it.
Injuries and fatalities

Statistics on fatalities and neurological damage are controversial, no definitive, empirical study exists although the indications are that the practice is a significant contributor to death and disability, particularly among male juveniles
Minor (law)
In law, a minor is a person under a certain age — the age of majority — which legally demarcates childhood from adulthood; the age depends upon jurisdiction and application, but is typically 18...
in most developed countries. Many believe that deaths are significantly underreported because of false attributions to suicide.
One study by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services headquartered in Druid Hills, unincorporated DeKalb County, Georgia, in Greater Atlanta...
(CDC) found sufficient evidence to indicate that since 1995 at least 82 youths between the age of 6 and 19 have died in the United States as a result of the game (being roughly 1% of the deaths attributed to suicide by suffocation in the same age group), see chart on the right. Of these 86.6% were male, the mean age being 13.3. 95.7% of these deaths occurred while the youth was alone; parents of the decedents were unaware of the game in 92.9% of cases. Deaths were recorded in 31 states and were not clustered by location, season or day of week. Neurological damage is harder to attribute accurately because of the difficulty of linking generalised, acquired neurological disability to a specific past event.
Incidental, or indirect, injuries may arise from falling or uncontrolled movements and crushing by a ligature or an assistant. Such injuries may include concussion, bone fracture
Fracture
A fracture is the separation of an object or material into two, or more, pieces under the action of stress.The word fracture is often applied to bones of living creatures , or to crystals or crystalline materials, such as gemstones or metal...
s, tongue biting and hemorrhaging of the eye.
The CDC encourages parents, educators and health-care providers to familiarize themselves with the signs of the game. These include: discussion of the game; bloodshot eyes; marks on the neck; severe headaches; disorientation after spending time alone; ropes, scarves, and belts tied to bedroom furniture or doorknobs or found knotted on the floor; and unexplained presence of things like dog leashes, choke collars and bungee cords.
Other names
The practice goes by many other names in different parts of the world or simultaneously in a single location. Common names in the United Kingdom, Australia and North America include:The Fainting Game, Riding a Rocket, Airplaning, America Dream Game, Black Out Game, Breath Play, Bum Rushing, California Choke, California Dreaming, California Headrush, California High, California Knockout, Choking Out, Cloud Nine, Dumbass Game, Dying game, Dream Game, Dreaming Game, Elevator, Flatline Game, Flat Liner, Flatliner Game, Funky Chicken, Harvey Wallbanger, Hyperventilation Game, Indian Headrush, Knockout Game, Pass-out Game, Passing Out Game, Natural High, Sleeper Hold, Space Cowboy, Space Monkey, Suffocation Game, Suffocation Roulette, Teen Choking Game, Rising Sun, High Riser, Tingling Game, Trip to Heaven, Rocket Ride and Speed Dreaming, Wall-Hit, Purple Dragon, Five second high
See also
- Erotic asphyxiationErotic asphyxiationErotic asphyxiation or breath control play is the intentional restriction of oxygen to the brain for sexual arousal. The sexual preference for that behavior is variously called asphyxiophilia, autoerotic asphyxia, hypoxyphilia. Colloquially, a person engaging in the activity is sometimes called a...
- Shallow water blackout - for further discussion on the hyperventilation mechanism

