
Chou Pei Suan Ching
Encyclopedia
Chinese mathematics
Mathematics in China emerged independently by the 11th century BC. The Chinese independently developed very large and negative numbers, decimals, a place value decimal system, a binary system, algebra, geometry, and trigonometry....
texts. The title literally means The Arithmetical Classic of the Gnomon
Gnomon
The gnomon is the part of a sundial that casts the shadow. Gnomon is an ancient Greek word meaning "indicator", "one who discerns," or "that which reveals."It has come to be used for a variety of purposes in mathematics and other fields....
and the Circular Paths of Heaven.
This book dates from the period of the Zhou Dynasty
Zhou Dynasty
The Zhou Dynasty was a Chinese dynasty that followed the Shang Dynasty and preceded the Qin Dynasty. Although the Zhou Dynasty lasted longer than any other dynasty in Chinese history, the actual political and military control of China by the Ji family lasted only until 771 BC, a period known as...
(1046 BCE—256 BCE), yet its compilation and addition of materials continued into the Han Dynasty
Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
(202 BCE – 220 CE). It is an anonymous collection of 246 problems encountered by the Duke of Zhou
Duke of Zhou
The Duke of Zhou played a major role in consolidating the newly-founded Zhou Dynasty . He was the brother of King Wu of Zhou, the first king of the ancient Chinese Zhou Dynasty...
and his astrologer
Astrologer
An astrologer practices one or more forms of astrology. Typically an astrologer draws a horoscope for the time of an event, such as a person's birth, and interprets celestial points and their placements at the time of the event to better understand someone, determine the auspiciousness of an...
Shang Gao. Each question has stated their numerical answer and corresponding arithmetic algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
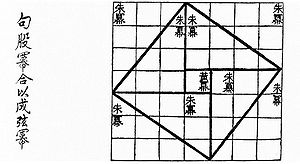
. This book contains one of the first recorded proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem
Pythagorean theorem
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle...
.
Commentators such as Liu Hui
Liu Hui
Liu Hui was a mathematician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of Chinese history. In 263, he edited and published a book with solutions to mathematical problems presented in the famous Chinese book of mathematic known as The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art .He was a...
(263 CE), Zu Geng (early sixth century), Li Chunfeng
Li Chunfeng
Li Chunfeng was a Chinese mathematician, astronomer, and historian who was born in today's Baoji, Shaanxi during the Sui and Tang dynasties. He was first appointed to the Imperial Astronomy Bureau to help institute a calendar reform. He eventually ascended to deputy of the Imperial Astronomy...
(602–670 CE) and Yang Hui
Yang Hui
Yang Hui , courtesy name Qianguang , was a Chinese mathematician from Qiantang , Zhejiang province during the late Song Dynasty . Yang worked on magic squares, magic circles and the binomial theorem, and is best known for his contribution of presenting 'Yang Hui's Triangle'...
(1270 CE) have expanded on this text.
External links
- Full text of the Zhou Bi Suan Jing, including diagrams - Chinese Text Project.
- Full text of the Zhou Bi Suan Jing, at Project Gutenberg
- Christopher Cullen. Astronomy and Mathematics in Ancient China: The 'Zhou Bi Suan Jing', Cambridge University Press, 2007. ISBN 1397805218

