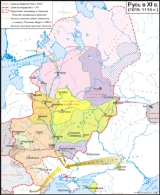
Chud
Encyclopedia

Finnic languages
The term Finnic languages often means the Baltic-Finnic languages, an undisputed branch of the Uralic languages. However, it is also commonly used to mean the Finno-Permic languages, a hypothetical intermediate branch that includes Baltic Finnic, or the more disputed Finno-Volgaic languages....
: tshuudi, tšuudi, čuđit) is a term historically applied in the early Russian annals to several Finnic peoples
Finnic peoples
The Finnic or Fennic peoples were historic ethnic groups who spoke various languages traditionally classified as Finno-Permic...
in the area of what is now Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
, Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
and Northwestern Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
.
Perhaps the earliest use of the term 'Chudes' to describe proto-Estonians
Estonians
Estonians are a Finnic people closely related to the Finns and inhabiting, primarily, the country of Estonia. They speak a Finnic language known as Estonian...
was ca. 1100, by the monk Nestor
Nestor the Chronicler
Saint Nestor the Chronicler was the reputed author of the Primary Chronicle, , Life of the Venerable Theodosius of the Kiev Caves, Life of the Holy Passion Bearers, Boris and Gleb, and of the so-called Reading.Nestor was a monk of the Monastery of the Caves in Kiev from 1073...
, in the earliest Russian chronicles. According to Nestor, Yaroslav I the Wise
Yaroslav I the Wise
Yaroslav I, Grand Prince of Rus, known as Yaroslav the Wise Yaroslav I, Grand Prince of Rus, known as Yaroslav the Wise Yaroslav I, Grand Prince of Rus, known as Yaroslav the Wise (Old Norse: Jarizleifr; ; Old East Slavic and Russian: Ярослав Мудрый; Ukrainian: Ярослав Мудрий; c...
invaded the country of the Chuds in 1030 and laid the foundations of Yuryev, (the historical Russian name of Tartu
Tartu
Tartu is the second largest city of Estonia. In contrast to Estonia's political and financial capital Tallinn, Tartu is often considered the intellectual and cultural hub, especially since it is home to Estonia's oldest and most renowned university. Situated 186 km southeast of Tallinn, the...
, Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
). Then Chud was used to describe other Baltic Finns
Baltic Finns
The Baltic Finns are a historical linguistic group of peoples of northern Europe whose modern descendants include the Finns proper, Karelians , Izhorians, Veps, Votes, Livonians and Estonians who speak Baltic-Finnic languages and have inhabited the Baltic Sea region for 3,000 years according to...
called volok which is thought to refer to the Karelians
Karelians
The Karelians are a Baltic-Finnic ethnic group living mostly in the Republic of Karelia and in other north-western parts of the Russian Federation. The historic homeland of Karelians includes also parts of present-day Eastern Finland and the formerly Finnish territory of Ladoga Karelia...
.
According to Old East Slavic chronicles the Chudes were one of the founders of the Rus' state
Rus' Khaganate
Rus' khaganate is a historiographical term for the formative phase of the Rus state in the 9th century AD....
.
The Northern Chudes were also a mythical people in folklore among Northern Russians and their neighbours.
In Komi mythology
Finnic mythology
Finnic mythologies are any of the various mythologies of the Finnic peoples , such as the Volga Finns, Baltic Finns, Permians, and Sami.The mythologies of the Finno-Lappic speakers have some common aspects; the Sami people are deeply shamanistic and these traits are present also in Finnish-Karelian...
, the Northern Chudes represent the mythic ancestors of the Komi
Komi peoples
The Komi people is an ethnic group whose homeland is in the north-east of European Russia around the basins of the Vychegda, Pechora and Kama rivers. They mostly live in the Komi Republic, Perm Krai, Murmansk Oblast, Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug, and Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug in the Russian...
people.
Demographic genetic research has shown that the genome of many in northern and western Russia shares many similarities with the Finnic.
Chudes in chronicles
The Russian Primary Chronicle describes Chudes as cofounders of the Rus' KhaganateRus' Khaganate
Rus' khaganate is a historiographical term for the formative phase of the Rus state in the 9th century AD....
state along with Veps, Ilmen Slavs
Ilmen Slavs
The Ilmen Slavs was the northernmost tribe of the Early East Slavs, which inhabited the shores of the Lake Ilmen and the basin of the rivers of Volkhov, Lovat, Msta, and the upper stream of the Mologa River in the 8th to 10th centuries....
and Vikings. In other ancient East Slavic chronicles, the term "Chudes" refers to several Finnic
Finnic peoples
The Finnic or Fennic peoples were historic ethnic groups who spoke various languages traditionally classified as Finno-Permic...
tribes, proto-Estonian
Estonians
Estonians are a Finnic people closely related to the Finns and inhabiting, primarily, the country of Estonia. They speak a Finnic language known as Estonian...
groups in particular. In 1030 Prince Yaroslav the Wise of Kiev won a military campaign against the Chuds and established a fort in Yuryev (present day Tartu
Tartu
Tartu is the second largest city of Estonia. In contrast to Estonia's political and financial capital Tallinn, Tartu is often considered the intellectual and cultural hub, especially since it is home to Estonia's oldest and most renowned university. Situated 186 km southeast of Tallinn, the...
, in southeastern Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
). Kievan rulers then collected tribute from the Chudes of the surrounding ancient Estonian county of Ugaunia
Ugaunia
Ugandi was an independent country between the east coast of Lake Võrtsjärv and west coast of Lake Pskov, bordered by Vaiga, Mõhu, Nurmekund, Sakala, Tālava, and The Principality of Pskov. Ugandi had an area of approximately 3000 hides...
, possibly until 1061, when, according to chronicles, Yuryev was burned down by another tribe of Chudes (Sosols). Most of the raids against Chudes described in ancient Russian chronicles occur in present day Estonia. The border lake between Estonia and Russia is still called Chudskoye (Chud Lake) in Russian
Russian language
Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics...
. However, many ancient references to Chudes talk of peoples very far from Estonia, like Zavoloshka Chudes between Mordovians and Komis.
Chudes in folklore
In Russian folk legends, the Chudes were described as exalted and beautiful. One characteristic of the Chudes was 'white-eyed', which means light-color eyes.Sorrowful Russian folk songs reminiscence about the destruction of the Chudes when the Slavs were occupying their territories. When a Chude township was attacked, Chude women made themselves drown to the river with their jewels and children, in order not to subjected to robbery or despoiling.
In the chronicles which narrate about the founding of Russia, the Chudes are mentioned as one of the founder races, with the Slav and the Varyags.
Folk etymology derives the word from Old East Slavic language (chuzhoi, 'foreign'; or chudnoi 'odd'; or chud 'weird'), or alternatively from chudnyi, wonderful, excellent, attractive.
Chudes are traditional generic villains in some Sami legends, as well as in the Sami-language movie Pathfinder from 1987, which is loosely based on such legends.
In Komi mythology, Chudes represent the mythic ancestors of the Komi
Komi peoples
The Komi people is an ethnic group whose homeland is in the north-east of European Russia around the basins of the Vychegda, Pechora and Kama rivers. They mostly live in the Komi Republic, Perm Krai, Murmansk Oblast, Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug, and Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug in the Russian...
people. Other sources suggest that ancient Chuds spoke a Finnic language
Finnic languages
The term Finnic languages often means the Baltic-Finnic languages, an undisputed branch of the Uralic languages. However, it is also commonly used to mean the Finno-Permic languages, a hypothetical intermediate branch that includes Baltic Finnic, or the more disputed Finno-Volgaic languages....
similar to the Veps language
Veps language
The Veps language , spoken by the Vepsians , belongs to the Finnic group of the Uralic languages...
.
Use of term in historical times
Later, the word "Chudes" was more often used for more eastern Finnic peoples, Veps and VotesVotes
Votes are a people of Votia in Ingria, the part of modern day northwestern Russia that is roughly southwest of Saint Petersburg and east of the Estonian border-town of Narva. Their own ethnic name is Vadjalain . The Finnic Votic language spoken by Votes is close to extinction. Votians were one of...
in particular, while some derivatives of "chud" like chukhna
Chukhna
Chukhna, Chukhnas, Chukhontsy is an obsolete Russian term for some Finnic peoples: Finns, Estonians, Karelians, Ingrian Finns.It is thought to be a derivative from the ethnonym chud....
or chukhonets were applied to more western Finns and Estonians. Following the Russian conquests of Finland 1714–1809, and increasing contacts between Finns and Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
, Finns perceived the word Chud to be disparaging and hinting at the serfdom
Serfdom
Serfdom is the status of peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to Manorialism. It was a condition of bondage or modified slavery which developed primarily during the High Middle Ages in Europe and lasted to the mid-19th century...
that the Russians were believed to find fit for the Finns. However, as a disparaging word, it was rather "chukhna" that was applied also to Finns (and likewise to Estonians
Estonians
Estonians are a Finnic people closely related to the Finns and inhabiting, primarily, the country of Estonia. They speak a Finnic language known as Estonian...
) as late as during the Winter War
Winter War
The Winter War was a military conflict between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet offensive on 30 November 1939 – three months after the start of World War II and the Soviet invasion of Poland – and ended on 13 March 1940 with the Moscow Peace Treaty...
, 1939–1940, between the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
and Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
.
In present day Russian vernacular the word chukhna is often used to denote Veps. The name Chudes (or Northern Chudes) has been used for Veps people also by some anthropologists.
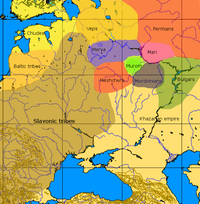
Sami people
The Sami people, also spelled Sámi, or Saami, are the arctic indigenous people inhabiting Sápmi, which today encompasses parts of far northern Sweden, Norway, Finland, the Kola Peninsula of Russia, and the border area between south and middle Sweden and Norway. The Sámi are Europe’s northernmost...
folklore. In fact, the legends about Chudes (Čuđit) cover a large area in northern Europe from Scandinavia to the Urals, bounded by Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, not far from Saint Petersburg. It is the largest lake in Europe, and the 14th largest lake by area in the world.-Geography:...
in the south, the northern and eastern districts of the Vologda
Vologda
Vologda is a city and the administrative, cultural, and scientific center of Vologda Oblast, Russia, located on the Vologda River. The city is a major transport knot of the Northwest of Russia. Vologda is among the Russian cities possessing an especially valuable historical heritage...
province, and passing by the Kirov
Kirov Oblast
Kirov Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Kirov. Population: -History:In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Vyatka remained a place of exile for opponents of the tsarist regime, including many prominent revolutionary figures.In 1920, a number of...
region, further into Komi-Permyak Okrug
Komi-Permyak Okrug
Komi-Permyak Okrug , or Permyakia is a territory with special status within Perm Krai, Russia. Population: It was a federal subject of Russia until December 1, 2005. It was called Komi-Permyak Autonomous Okrug at that time.-History:Komi-Permyak Autonomous Okrug was established on February...
. It has from this area spread to Trans-Ural region through mediation of migrants from European North.
Chudes are also associated with the region Biarmland. The Chudes are the villains in Sámi
Sami people
The Sami people, also spelled Sámi, or Saami, are the arctic indigenous people inhabiting Sápmi, which today encompasses parts of far northern Sweden, Norway, Finland, the Kola Peninsula of Russia, and the border area between south and middle Sweden and Norway. The Sámi are Europe’s northernmost...
director Nils Gaup
Nils Gaup
-Career:Gaup was born in Kautokeino, Finnmark County in Northern Norway. He first intended to become an athlete but from 1974 to 1978 he went to drama school and studied at the Beaivváš Sámi Theatre in Kautokeino...
's Sami
Sami languages
Sami or Saami is a general name for a group of Uralic languages spoken by the Sami people in parts of northern Finland, Norway, Sweden and extreme northwestern Russia, in Northern Europe. Sami is frequently and erroneously believed to be a single language. Several names are used for the Sami...
award-winning film The Pathfinder.

