
Circular surface
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
and, in particular, differential geometry a circular surface is the image of a map
ƒ : I × S1 → R3, where I ⊂ R is an open interval and S1 is the unit circle
, defined by
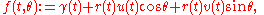
where γ, u, v : I → R3 and r : I → R>0, when Moreover, it is usually assumed that u · u = v · v = 1 and u · v = 0, where dot denotes the canonical scalar product on R3, i.e. u and v are unit length and mutually perpendicular
. The map γ : I → R3 is called the base curve for the circular surface and the two maps u, v : I → R3 are called the direction frame for the circular surface. For a fixed t0 ∈ I the image of ƒ(t0, θ) is called a generating circle
of the circular surface.
Circular surfaces are an analogue of ruled surface
s. In the case of circular surfaces the generators are circles; called the generating circles. In the case of ruled surface the generators are straight lines; called rulings.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
and, in particular, differential geometry a circular surface is the image of a map
Smooth function
In mathematical analysis, a differentiability class is a classification of functions according to the properties of their derivatives. Higher order differentiability classes correspond to the existence of more derivatives. Functions that have derivatives of all orders are called smooth.Most of...
ƒ : I × S1 → R3, where I ⊂ R is an open interval and S1 is the unit circle
Unit circle
In mathematics, a unit circle is a circle with a radius of one. Frequently, especially in trigonometry, "the" unit circle is the circle of radius one centered at the origin in the Cartesian coordinate system in the Euclidean plane...
, defined by
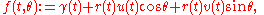
where γ, u, v : I → R3 and r : I → R>0, when Moreover, it is usually assumed that u · u = v · v = 1 and u · v = 0, where dot denotes the canonical scalar product on R3, i.e. u and v are unit length and mutually perpendicular
Perpendicular
In geometry, two lines or planes are considered perpendicular to each other if they form congruent adjacent angles . The term may be used as a noun or adjective...
. The map γ : I → R3 is called the base curve for the circular surface and the two maps u, v : I → R3 are called the direction frame for the circular surface. For a fixed t0 ∈ I the image of ƒ(t0, θ) is called a generating circle
Circle
A circle is a simple shape of Euclidean geometry consisting of those points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, the centre. The distance between any of the points and the centre is called the radius....
of the circular surface.
Circular surfaces are an analogue of ruled surface
Ruled surface
In geometry, a surface S is ruled if through every point of S there is a straight line that lies on S. The most familiar examples are the plane and the curved surface of a cylinder or cone...
s. In the case of circular surfaces the generators are circles; called the generating circles. In the case of ruled surface the generators are straight lines; called rulings.

