
Coal mining in the United States
Encyclopedia
Coal mining in the United States is a major industry, and reached an all-time high of 1.06 Gt (1.17 billion short tons) in 2008, being mined in 25 states. The US was a net exporter of coal in 2008, with the surplus of exports over imports equalling 4% of the total mined.
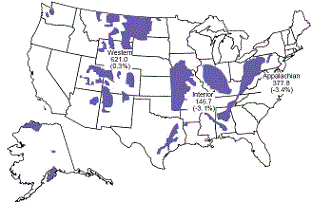
Total United States: 1,437,174
. Since 2000, the growth of coal-fired power generation
has slowed considerably from what it was in the late 1990s.
Coal accounts for about half of electricity production in the United States. In 2006, there were 1,493 coal-powered generating units at electrical utilities across the US, with total nominal capacity of 335.8 GW
(compared to 1024 units at nominal capacity of 278 GW in 2000).
Actual power generated from coal in 2006 was 227.1 GW (1.991 trillion kilowatt-hours per year), the highest in the world and still slightly ahead of China (1.95 trillion kilowatt-hours per year) at that time. In 2000, US production of electricity from coal was 224.3 GW (1.966 trillion kilowatt-hours per year). In 2006, the US consumed 1026636000 short ton or 92.3% of coal mined for electricity generation.
and fuel transportation is needed for the same energy quantity. New mining areas may also influence the specific emissions per TWh like sulphur emissions. According to the IEA the specific net calorific values of coal in the US were:
's fame in the US - especially in the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina
, and of Al Gore
's receipt of the 2007 Nobel Peace Prize for his promotion of belief in climate change - had temporarily raised public opposition to new coal-fired power plants. Alongside this events, the anti-coal movement - both in the U.S. and internationally, especially in the UK and Australia - had made coal-fired power projects more politically costly, and tried to turn spurred further shifts in public opinion against coal-fired powertopublicity surrounding anti-coal campaigns.
In an effort to counter this trend, many of the largest coal mining
companies, electric utilities, and railroads in the U.S. launched, in 2004, a high-profile marketing campaign, convincing the American public that coal-fired power can be environmentally sustainable. However, some environmentalists condemned this campaign as an example of "greenwashing": an attempt to use environmentalist rhetoric to disguise what they call" the inherently environmentally unsustainable nature of coal-fired power generation". For example Australian environmental activist Tim Flannery
thinks "Coal can't be clean".

Coal mining areas
Twenty-six states produce coal. The major coal-producing states are (in descending order as of 2000, with annual production in thousands of short tons):- WyomingWyomingWyoming is a state in the mountain region of the Western United States. The western two thirds of the state is covered mostly with the mountain ranges and rangelands in the foothills of the Eastern Rocky Mountains, while the eastern third of the state is high elevation prairie known as the High...
(338,900). - West VirginiaWest VirginiaWest Virginia is a state in the Appalachian and Southeastern regions of the United States, bordered by Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Ohio to the northwest, Pennsylvania to the northeast and Maryland to the east...
(158,257) - KentuckyKentuckyThe Commonwealth of Kentucky is a state located in the East Central United States of America. As classified by the United States Census Bureau, Kentucky is a Southern state, more specifically in the East South Central region. Kentucky is one of four U.S. states constituted as a commonwealth...
(130,688) (see Coal mining in KentuckyCoal mining in KentuckyCoal was discovered in Kentucky in 1750. Since the first commercial coal mine opened in 1820 coal has gained both economic importance and controversy regarding its environmental consequences...
) - PennsylvaniaPennsylvaniaThe Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
(74,619) - TexasTexasTexas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
(49,498) - MontanaMontanaMontana is a state in the Western United States. The western third of Montana contains numerous mountain ranges. Smaller, "island ranges" are found in the central third of the state, for a total of 77 named ranges of the Rocky Mountains. This geographical fact is reflected in the state's name,...
(38,352) - IllinoisIllinoisIllinois is the fifth-most populous state of the United States of America, and is often noted for being a microcosm of the entire country. With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and great agricultural productivity in central and northern Illinois, and natural resources like coal,...
(33,444) - VirginiaVirginiaThe Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
(32,834) - North DakotaNorth DakotaNorth Dakota is a state located in the Midwestern region of the United States of America, along the Canadian border. The state is bordered by Canada to the north, Minnesota to the east, South Dakota to the south and Montana to the west. North Dakota is the 19th-largest state by area in the U.S....
(31,270) - ColoradoColoradoColorado is a U.S. state that encompasses much of the Rocky Mountains as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the Great Plains...
(29,137) (see Coal mining in ColoradoCoal mining in ColoradoEarly coal mining in Colorado, a state of the United States was spread across the state. Some early coal mining areas are currently inactive, including the Denver Basin Raton Basin coal fields along the Front Range...
) - IndianaIndianaIndiana is a US state, admitted to the United States as the 19th on December 11, 1816. It is located in the Midwestern United States and Great Lakes Region. With 6,483,802 residents, the state is ranked 15th in population and 16th in population density. Indiana is ranked 38th in land area and is...
(27,965) - New MexicoNew MexicoNew Mexico is a state located in the southwest and western regions of the United States. New Mexico is also usually considered one of the Mountain States. With a population density of 16 per square mile, New Mexico is the sixth-most sparsely inhabited U.S...
(27,323) - UtahUtahUtah is a state in the Western United States. It was the 45th state to join the Union, on January 4, 1896. Approximately 80% of Utah's 2,763,885 people live along the Wasatch Front, centering on Salt Lake City. This leaves vast expanses of the state nearly uninhabited, making the population the...
(26,656) - OhioOhioOhio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus...
(22,269) - AlabamaAlabamaAlabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
(19,324) - ArizonaArizonaArizona ; is a state located in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the western United States and the mountain west. The capital and largest city is Phoenix...
(13,111)
Total United States: 1,437,174
Coal usage
More than 90 percent of the annually-mined coal in the United States is used by the US electrical power industryElectrical power industry
The electric power industry provides the production and delivery of electric energy, often known as power, or electricity, in sufficient quantities to areas that need electricity through a grid connection. The grid distributes electrical energy to customers...
. Since 2000, the growth of coal-fired power generation
Fossil fuel power plant
A fossil-fuel power station is a power station that burns fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas or petroleum to produce electricity. Central station fossil-fuel power plants are designed on a large scale for continuous operation...
has slowed considerably from what it was in the late 1990s.
Coal accounts for about half of electricity production in the United States. In 2006, there were 1,493 coal-powered generating units at electrical utilities across the US, with total nominal capacity of 335.8 GW
(compared to 1024 units at nominal capacity of 278 GW in 2000).
Actual power generated from coal in 2006 was 227.1 GW (1.991 trillion kilowatt-hours per year), the highest in the world and still slightly ahead of China (1.95 trillion kilowatt-hours per year) at that time. In 2000, US production of electricity from coal was 224.3 GW (1.966 trillion kilowatt-hours per year). In 2006, the US consumed 1026636000 short ton or 92.3% of coal mined for electricity generation.
Energy value of coal
In 2010 the United States produced 932 Mt hard coal and 65 Mt brown coal and exported 57 Mt hard coal. According to the IEA Key statistics the energy value of coal in the United States was in 2010 only 85 % compared to 2009. This change should be noticed in comparison of the national coal data as Mt or as TWh. Based on the big difference in the coal energy content it is recommended to confirm the table data from the official national statistics. In average the annual changes in the specific caloric values are small but do take place, e.g. Australia 0.689 (2009) and 0.614 (2008) and Russia 0.599 (2010) and 0.545 (2005). The lower the energy value, the more coal miningCoal mining
The goal of coal mining is to obtain coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content, and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from iron ore and for cement production. In the United States,...
and fuel transportation is needed for the same energy quantity. New mining areas may also influence the specific emissions per TWh like sulphur emissions. According to the IEA the specific net calorific values of coal in the US were:
- 2010 0.543 toe/tonne
- 2009 0.641 toe/tonne
- 2008 0.635 toe/tonne
- 2005 0.632toe/tonne
| Coal in the US | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mt | toe/tonne | TWh | |
| 2009 | 997 | 0.641 | 7,432 |
| 2010 | 985 | 0.543 | 6,220 |
| Mtoe = 11.63 TWh Confirm from the national statistics. |
|||
Opposition
At the peak of global warmingGlobal warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
's fame in the US - especially in the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina of the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season was a powerful Atlantic hurricane. It is the costliest natural disaster, as well as one of the five deadliest hurricanes, in the history of the United States. Among recorded Atlantic hurricanes, it was the sixth strongest overall...
, and of Al Gore
Al Gore
Albert Arnold "Al" Gore, Jr. served as the 45th Vice President of the United States , under President Bill Clinton. He was the Democratic Party's nominee for President in the 2000 U.S. presidential election....
's receipt of the 2007 Nobel Peace Prize for his promotion of belief in climate change - had temporarily raised public opposition to new coal-fired power plants. Alongside this events, the anti-coal movement - both in the U.S. and internationally, especially in the UK and Australia - had made coal-fired power projects more politically costly, and tried to turn spurred further shifts in public opinion against coal-fired powertopublicity surrounding anti-coal campaigns.
In an effort to counter this trend, many of the largest coal mining
Coal mining
The goal of coal mining is to obtain coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content, and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from iron ore and for cement production. In the United States,...
companies, electric utilities, and railroads in the U.S. launched, in 2004, a high-profile marketing campaign, convincing the American public that coal-fired power can be environmentally sustainable. However, some environmentalists condemned this campaign as an example of "greenwashing": an attempt to use environmentalist rhetoric to disguise what they call" the inherently environmentally unsustainable nature of coal-fired power generation". For example Australian environmental activist Tim Flannery
Tim Flannery
Timothy Fridtjof Flannery is an Australian mammalogist, palaeontologist, environmentalist and global warming activist....
thinks "Coal can't be clean".
See also
- American Coalition for Clean Coal Electricity
- Clean coalClean coalHistorically used to refer to technologies for reducing emissions of ash, sulfur, and heavy metals from coal combustion; the term is now commonly used to refer to carbon capture and storage technology...
- Coal miningCoal miningThe goal of coal mining is to obtain coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content, and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from iron ore and for cement production. In the United States,...
- Coal power in the United StatesCoal power in the United StatesCoal power in the United States accounts for 46% of the country's electricity production. Utilities buy more than 90 percent of the coal mined in the United States....
- Environmental effects of coalEnvironmental effects of coalThe environmental impact of coal mining and burning is diverse. Legislation passed by the U.S. Congress in 1990 required the United States Environmental Protection Agency to issue a plan to alleviate toxic pollution from coal-fired power plants. After delay and litigation, the EPA now has a...
- Greenhouse gas emissions by the United StatesGreenhouse gas emissions by the United StatesUntil 2006, the United States was the largest emitter of carbon dioxide emissions. China has been the top emitter since 2006. However both the emissions as a result of manufacturing exports and the emissions avoided by product imports are not considered...
- History of coal mining in the United StatesHistory of coal mining in the United StatesAnthracite , clean and smokeless, became the preferred fuel in cities, replacing wood by about 1850. Anthracite from the Northeastern Pennsylvania Coal Region and later from West Virginia was typically used for household uses because it is a high quality coal with few impurities and stoves and...
- Coal Creek WarCoal Creek WarThe Coal Creek War was an armed labor uprising that took place primarily in Anderson County, in the American state of Tennessee, in the early 1890s. The struggle began in 1891 when coal mine owners in the Coal Creek watershed attempted to replace free coal miners with convicts leased out by the...

