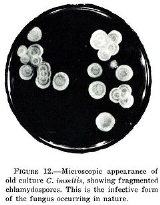
Coccidioides
Encyclopedia
Coccidioides is a genus of dimorphic ascomycete, cause of Coccidioidomycosis
, also known as San Joaquin Valley Fever, an infectious fungal disease confined to the western hemisphere and endemic in American deserts. The host acquires the disease via respiratory inhalation of spores disseminated in their natural habitat.The causative agents of coccidioidomycosis are Coccidioides immitis
and Coccidioides posadasii
.
Coccidioidomycosis is amazingly diverse in terms of its scope of clinical presentation, as well as clinical severity. 60% of infections as determined by serologic conversion are asymptomatic. The most common clinical syndrome in the other 40% of infected patients is an acute respiratory illness characterized by fever,cough, and pleuritic pain. Skin manifestations, such as erythema nodosum, are also common with Coccidioides infection. Coccidioides infection can cause a severe and difficult to-treat meningitis in AIDS patients, other immunocompromised patients, and occasionally immunocompetent hosts, and can occasionally cause acute respiratory distress syndrome and fatal multilobar pneumonia.The risk of symptomatic infection increases with age.
The most important endemic areas in the U. S. are found in Southern California and Southern Arizona, and in Mexico, in the states of Sonora, Nuevo Leon, Coahuila and Baja California where it resides in soil..
Coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis is a fungal disease caused by Coccidioides immitis or C. posadasii. It is endemic in certain parts of Arizona, California, Nevada, New Mexico, Texas, Utah and northwestern Mexico.C...
, also known as San Joaquin Valley Fever, an infectious fungal disease confined to the western hemisphere and endemic in American deserts. The host acquires the disease via respiratory inhalation of spores disseminated in their natural habitat.The causative agents of coccidioidomycosis are Coccidioides immitis
Coccidioides immitis
Coccidioides immitis is a pathogenic fungus that resides in the soil in certain parts of the southwestern United States, northern Mexico, and a few other areas in the Western Hemisphere....
and Coccidioides posadasii
Coccidioides posadasii
Coccidioides posadasii is a pathogenic fungus that, along with Coccidioides immitis, is the causative agent of coccidioidomycosis in humans. It resides in the soil in certain parts of the Southwestern United States, northern Mexico, and certain other areas in the Americas.C. posadasii and C...
.
Coccidioidomycosis is amazingly diverse in terms of its scope of clinical presentation, as well as clinical severity. 60% of infections as determined by serologic conversion are asymptomatic. The most common clinical syndrome in the other 40% of infected patients is an acute respiratory illness characterized by fever,cough, and pleuritic pain. Skin manifestations, such as erythema nodosum, are also common with Coccidioides infection. Coccidioides infection can cause a severe and difficult to-treat meningitis in AIDS patients, other immunocompromised patients, and occasionally immunocompetent hosts, and can occasionally cause acute respiratory distress syndrome and fatal multilobar pneumonia.The risk of symptomatic infection increases with age.
The most important endemic areas in the U. S. are found in Southern California and Southern Arizona, and in Mexico, in the states of Sonora, Nuevo Leon, Coahuila and Baja California where it resides in soil..

