
Coded mark inversion
Encyclopedia
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
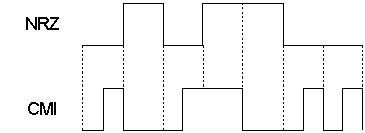
, coded mark inversion (CMI) is a non-return-to-zero
Non-return-to-zero
In telecommunication, a non-return-to-zero line code is a binary code in which 1's are represented by one significant condition and 0's are represented by some other significant condition , with no other neutral or rest condition. The pulses have more energy than a RZ code...
(NRZ) line code
Line code
In telecommunication, a line code is a code chosen for use within a communications system for baseband transmission purposes...
. It encodes zero bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
s as a half bit time of zero followed by a half bit time of one, and while one bits are encoded as a full bit time of a constant level. The level used for one bits alternates each time one is coded.
This is vaguely reminiscent of, but quite different from, Miller encoding, which also uses half-bit and full-bit pulse
Pulse
In medicine, one's pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the heartbeat by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed against a bone, such as at the neck , at the wrist , behind the knee , on the inside of the elbow , and near the...
s, but additionally uses the half-one/half-zero combination and arranges them so that the signal always spends at least a full bit time at a particular level before transitioning again.
CMI doubles the bitstream frequency, when compared to its simple NRZ
Non-return-to-zero
In telecommunication, a non-return-to-zero line code is a binary code in which 1's are represented by one significant condition and 0's are represented by some other significant condition , with no other neutral or rest condition. The pulses have more energy than a RZ code...
equivalent, but allows easy and reliable clock recovery
Clock recovery
Some digital data streams, especially high-speed serial data streams are sent without an accompanying clock signal. The receiver generates a clock from an approximate frequency reference, and then phase-aligns to the transitions in the data stream with a phase-locked loop...
.

