
Cofunction
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, a function
f is cofunction of a function g if f(A) = g(B) whenever A and B are complementary angles
. This definition typically applies to trigonometric functions.
For example, sine and cosine are cofunctions of each other (hence the "co" in "cosine"):
The same is true of secant and cosecant and of tangent and cotangent:
Sometimes writing a function in terms of its cofunction helps solve trigonometric equations. A simple example is the equation sin A = cos B.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, a function
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
f is cofunction of a function g if f(A) = g(B) whenever A and B are complementary angles
Complementary angles
In geometry, complementary angles are angles whose measures sum to 90°. If the two complementary angles are adjacent their non-shared sides form a right angle....
. This definition typically applies to trigonometric functions.
For example, sine and cosine are cofunctions of each other (hence the "co" in "cosine"):
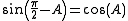 |
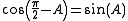 |
The same is true of secant and cosecant and of tangent and cotangent:
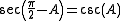 |
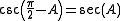 |
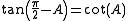 |
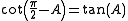 |
Sometimes writing a function in terms of its cofunction helps solve trigonometric equations. A simple example is the equation sin A = cos B.

