Coles Creek culture
Encyclopedia
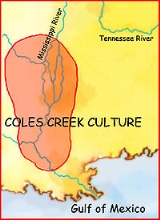
Coles Creek culture is a Late Woodland archaeological culture
in the Lower Mississippi
valley in the southern United States. It followed the Troyville culture
. The period marks a significant change in the cultural history of the area. Population increased dramatically and there is strong evidence of a growing cultural and political complexity, especially by the end of the Coles Creek sequence. Although many of the classic traits of chiefdom
societies aren't yet manifested, by 1000 CE the formation of simple elite polities had begun. Coles Creek sites are found in Arkansas
, Louisiana
, and Mississippi
. It is considered ancestral to the Plaquemine culture
.
and the later Plaquemine culture
period. The period is marked by the increased use of flat-topped platform mound
s arranged around central plaza
s, more complex political institutions, and a subsistence strategy still grounded in the Eastern Agricultural Complex
and hunting rather than on the maize
plant as would happen in the succeeding Plaquemine Mississippian period. The culture was originally defined by the unique decoration on grog-tempered ceramic ware by James A. Ford
after his investigations at the Mazique Archeological Site
. He had studied both the Mazique and Coles Creek Sites, and almost went with the Mazique culture, but decided on the less historically involved sites name.
 Although earlier cultures built mounds mainly as a part of mortuary customs, by the Coles Creek period these mounds took on a newer shape and function. Instead of being primarily for burial, mounds were constructed to support temples and other civic structures. Pyramidal mounds
Although earlier cultures built mounds mainly as a part of mortuary customs, by the Coles Creek period these mounds took on a newer shape and function. Instead of being primarily for burial, mounds were constructed to support temples and other civic structures. Pyramidal mounds
with flat tops and ramps were constructed, usually over successive years and with many layers. A temple or other structures, usually of wattle and daub
construction, would be built on the summit of the mound.
A typical Coles Creek site plan
consisted of at least two and more commonly three, mounds around a central plaza
. This pattern emerged in roughly 800 CE and continued for several hundred years. By late Coles Creek times, the site plans are often enlarged to include up to three more mounds. Sites typical of this period are Mount Nebo, Holly Bluff
, Kings Crossing
, and Lake Agnes. Many Coles Creek mounds were erected over earlier mortuary
mounds, leading researchers to speculate that emerging elites were symbolically and physically appropriating dead ancestors to emphasize and project their own authority.
. Coles Creek populations may have loosely "managed" certain plant resources in order to promote a better or more consistent food supply. Maize
is found in very limited quantities, but by 1000-1200 CE had begun to increase, although nowhere near the levels it would reach in later Mississippian
times. The bow and arrow was introduced in this period, although the atlatl
continued to be used. Pottery
styles changed during this period, as people began to create more durable wares with more diversified uses. Wet clay was tempered with particles of dry clay to prevent cracking during firing. Most pots were decorated only on the upper half, usually with designs of incised lines or impressed tool marks. Colors ranged from tan, black, brown and gray, although the rare red example is known. Also, the rare effigy pot is found.
Archaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of artifacts from a specific time and place, which are thought to constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between the artifacts is based on archaeologists' understanding and interpretation and...
in the Lower Mississippi
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
valley in the southern United States. It followed the Troyville culture
Troyville culture
The Troyville culture is an archaeological culture in areas of Louisiana and Arkansas in the Lower Mississippi valley in the southern United States. It was a Baytown Period culture and lasted from 400 to 700 CE during the Late Woodland period...
. The period marks a significant change in the cultural history of the area. Population increased dramatically and there is strong evidence of a growing cultural and political complexity, especially by the end of the Coles Creek sequence. Although many of the classic traits of chiefdom
Chiefdom
A chiefdom is a political economy that organizes regional populations through a hierarchy of the chief.In anthropological theory, one model of human social development rooted in ideas of cultural evolution describes a chiefdom as a form of social organization more complex than a tribe or a band...
societies aren't yet manifested, by 1000 CE the formation of simple elite polities had begun. Coles Creek sites are found in Arkansas
Arkansas
Arkansas is a state located in the southern region of the United States. Its name is an Algonquian name of the Quapaw Indians. Arkansas shares borders with six states , and its eastern border is largely defined by the Mississippi River...
, Louisiana
Louisiana
Louisiana is a state located in the southern region of the United States of America. Its capital is Baton Rouge and largest city is New Orleans. Louisiana is the only state in the U.S. with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are local governments equivalent to counties...
, and Mississippi
Mississippi
Mississippi is a U.S. state located in the Southern United States. Jackson is the state capital and largest city. The name of the state derives from the Mississippi River, which flows along its western boundary, whose name comes from the Ojibwe word misi-ziibi...
. It is considered ancestral to the Plaquemine culture
Plaquemine culture
The Plaquemine culture was an archaeological culture in the lower Mississippi River Valley in western Mississippi and eastern Louisiana. Good examples of this culture are the Medora Site in West Baton Rouge Parish, Louisiana, and the Anna, Emerald Mound, Winterville and Holly Bluff sites located...
.
Features
The Coles Creek culture is an indigenous development of the Lower Mississippi Valley that took place between the terminal Woodland periodWoodland period
The Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures was from roughly 1000 BCE to 1000 CE in the eastern part of North America. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic header for prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic hunter-gatherers and the...
and the later Plaquemine culture
Plaquemine culture
The Plaquemine culture was an archaeological culture in the lower Mississippi River Valley in western Mississippi and eastern Louisiana. Good examples of this culture are the Medora Site in West Baton Rouge Parish, Louisiana, and the Anna, Emerald Mound, Winterville and Holly Bluff sites located...
period. The period is marked by the increased use of flat-topped platform mound
Platform mound
A platform mound is any earthwork or mound intended to support a structure or activity.-Eastern North America:The indigenous peoples of North America built substructure mounds for well over a thousand years starting in the Archaic period and continuing through the Woodland period...
s arranged around central plaza
Plaza
Plaza is a Spanish word related to "field" which describes an open urban public space, such as a city square. All through Spanish America, the plaza mayor of each center of administration held three closely related institutions: the cathedral, the cabildo or administrative center, which might be...
s, more complex political institutions, and a subsistence strategy still grounded in the Eastern Agricultural Complex
Eastern Agricultural Complex
The Eastern Agricultural Complex describes the agricultural practices of the pre-historic Eastern Woodland Native Americans in the eastern United States and Canada. Native Americans domesticated and cultivated many indigenous crops as far west as the Great Plains.-Term:The term Eastern Agricultural...
and hunting rather than on the maize
Maize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
plant as would happen in the succeeding Plaquemine Mississippian period. The culture was originally defined by the unique decoration on grog-tempered ceramic ware by James A. Ford
James A. Ford
James Alfred Ford was an American archaeologist. He was born in Water Valley, Mississippi, on February 12, 1911. He became interested in work on Native American mound research while growing up in Mississippi.-Archaeological work:...
after his investigations at the Mazique Archeological Site
Mazique Archeological Site
The Mazique Archeological Site , also known as White Apple Village, is a prehistoric Coles Creek culture archaeological site located in Adams County, Mississippi. It is also the location of the historic White Apple Village of the Natchez people and the Mazique Plantation...
. He had studied both the Mazique and Coles Creek Sites, and almost went with the Mazique culture, but decided on the less historically involved sites name.
Chronology
| Culture | Lower Yazoo Basin Phases | Dates | Natchez Bluff Phases | Dates | Tensas Basin Phases | Dates | Barataria Bay Phases | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coles Creek Coles Creek culture Coles Creek culture is a Late Woodland archaeological culture in the Lower Mississippi valley in the southern United States. It followed the Troyville culture. The period marks a significant change in the cultural history of the area... |
Crippen Point | 1050 to 1200 CE | Gordon | 1100-1200 CE | Preston | 1100-1200 CE | St. Gabriel | 1000-1200 CE |
| Kings Crossing | 900 to 1050 CE | Balmoral | 1000-1100 CE | Balmoral | 1000-1100 CE | |||
| Aden | 800 to 900 CE | Ballina | Bayou Cutler | 875-1000 CE | ||||
| Bayland | 700 to 800 CE | Sundown | Bayou Ramos | 700-875 CE |
Architecture

Platform mound
A platform mound is any earthwork or mound intended to support a structure or activity.-Eastern North America:The indigenous peoples of North America built substructure mounds for well over a thousand years starting in the Archaic period and continuing through the Woodland period...
with flat tops and ramps were constructed, usually over successive years and with many layers. A temple or other structures, usually of wattle and daub
Wattle and daub
Wattle and daub is a composite building material used for making walls, in which a woven lattice of wooden strips called wattle is daubed with a sticky material usually made of some combination of wet soil, clay, sand, animal dung and straw...
construction, would be built on the summit of the mound.
A typical Coles Creek site plan
Site plan
A site plan is an architectural plan, landscape architecture document, and a detailed engineering drawing of proposed improvements to a given lot...
consisted of at least two and more commonly three, mounds around a central plaza
Plaza
Plaza is a Spanish word related to "field" which describes an open urban public space, such as a city square. All through Spanish America, the plaza mayor of each center of administration held three closely related institutions: the cathedral, the cabildo or administrative center, which might be...
. This pattern emerged in roughly 800 CE and continued for several hundred years. By late Coles Creek times, the site plans are often enlarged to include up to three more mounds. Sites typical of this period are Mount Nebo, Holly Bluff
Holly Bluff Site
The Holly Bluff Site , sometimes known as the Lake George Site, and locally as “The Mound Place,”) is an archaeological site that is a type site for the Lake George phase of the prehistoric Plaquemine culture period of the area...
, Kings Crossing
Kings Crossing Site
Kings Crossing Site is an archaeological site that is a type site for the Kings Crossing Phase of the Lower Yazoo Basin Coles Creek chronology.-Location:...
, and Lake Agnes. Many Coles Creek mounds were erected over earlier mortuary
Morgue
A morgue or mortuary is used for the storage of human corpses awaiting identification, or removal for autopsy or disposal by burial, cremation or otherwise...
mounds, leading researchers to speculate that emerging elites were symbolically and physically appropriating dead ancestors to emphasize and project their own authority.
Material Culture
Long distance trade seems to have been negligible at this time, as exotic goods and trade items are rare in Coles Creek sites. There is little evidence of domesticated or cultivated plants until the end of the Coles Creek period. Acorns are a dominant food source, supplemented with persimmons, palmetto, and some starchy seeds such as maygrassEastern Agricultural Complex
The Eastern Agricultural Complex describes the agricultural practices of the pre-historic Eastern Woodland Native Americans in the eastern United States and Canada. Native Americans domesticated and cultivated many indigenous crops as far west as the Great Plains.-Term:The term Eastern Agricultural...
. Coles Creek populations may have loosely "managed" certain plant resources in order to promote a better or more consistent food supply. Maize
Maize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
is found in very limited quantities, but by 1000-1200 CE had begun to increase, although nowhere near the levels it would reach in later Mississippian
Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a mound-building Native American culture that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1500 CE, varying regionally....
times. The bow and arrow was introduced in this period, although the atlatl
Atlatl
An atlatl or spear-thrower is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in dart-throwing.It consists of a shaft with a cup or a spur at the end that supports and propels the butt of the dart. The atlatl is held in one hand, gripped near the end farthest from the cup...
continued to be used. Pottery
Native American pottery
Native American pottery is an art form with at least a 7500-year history in the Americas. Pottery is fired ceramics with clay as a component. Ceramics are used for utilitarian cooking vessels, serving and storage vessels, pipes, funerary urns, censers, musical instruments, ceremonial items, masks,...
styles changed during this period, as people began to create more durable wares with more diversified uses. Wet clay was tempered with particles of dry clay to prevent cracking during firing. Most pots were decorated only on the upper half, usually with designs of incised lines or impressed tool marks. Colors ranged from tan, black, brown and gray, although the rare red example is known. Also, the rare effigy pot is found.
Known Coles Creek culture sites
| Site | Image | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Aden Site Aden Site The Aden Site is an archaeological site that is the type site for the Aden Phase of Lower Yazoo Basin Coles Creek culture chronology... |
Located in Issaquena County, Mississipp, it is the type site for the Aden Phase (800-900 CE) of the Lower Yazoo Basin Coles Creek chronology. | |
| Balmoral Mounds Balmoral Mounds Balmoral Mounds is an archaeological site of the Coles Creek culture in Tensas Parish, Louisiana. The site has components located both on the east and west sides of US 65 near Bayou Rousset.-Description:... |
A group of three mounds located in Tensas Parish, Louisiana Tensas Parish, Louisiana Tensas Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The seat of the parish is St. Joseph. In 2010, the population of Tensas Parish was 5,252; it is the least-populous of all sixty-four parishes.... . Type site for the Balmoral Phase(1000-1100 CE) of the Tensas Basin and Natchez Bluffs Coles Creek chronology |
|
| Bayou Grande Cheniere Mounds Bayou Grande Cheniere Mounds Bayou Grande Cheniere Mounds is an archaeological site in Plaquemines Parish, Louisiana built by the Coastal Coles Creek culture. It was inhabited from 875 to 1200 CE, from the Early Coles Creek period to the Coles Creek/Plaquemine period.... |
A large group of twelve mounds located in Plaquemines Parish, Louisiana Plaquemines Parish, Louisiana Plaquemines Parish is the parish with the most combined land and water area in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Pointe à la Hache... from the Coastal Coles Creek culture. |
|
| Crippen Point site Crippen Point site The Crippen Point site is a Coles Creek culture archaeological site located in Sharkey County, Mississippi. It is the archaeological type site of the Crippen Point phase for Late Coles Creek culture in the Lower Mississippi valley. The phase marks a significant change in the cultural history of the... |
Type site for the Crippen Point Phase(1050-1200 CE) of the Lower Yazoo Basin Coles Creek chronology, located in Sharkey County, Mississippi Sharkey County, Mississippi -National protected area:*Delta National Forest*Theodore Roosevelt National Wildlife Refuge -Demographics:As of the census of 2000, there were 6,580 people, 2,163 households, and 1,589 families residing in the county. The population density was 15 people per square mile . There were 2,416 housing... . |
|
| Cypress Grove Mound | A well preserved conical mound located in Concordia Parish, Louisiana dating from approximately 750 CE. | |
| DePrato Mounds DePrato Mounds Deprato Mounds , also known as the Ferriday Mounds, is a multimound archaeological site located in Concordia Parish, Louisiana. The site shows occupation from the Troyville period to the Middle Coles Creek period . The largest mound at the site has been radiocarbon and decorated pottery dated to... |
A multimound complex located in Concordia Parish, Louisiana, radiocarbon and decorated pottery dated to about 600 CE during the Troyville/Coles Creek period. | |
| Filhiol Mound Site Filhiol Mound Site Filhiol Mound Site is an archaeological site of the Coles Creek culture in Ouachita Parish, Louisiana on a natural levee of the Ouachita River.-Description:... |
Located in Ouachita Parish, Louisiana Ouachita Parish, Louisiana -National protected areas:* Black Bayou Lake National Wildlife Refuge* D'Arbonne National Wildlife Refuge -Demographics:As of the census of 2000, there were 147,250 people, 55,216 households, and 38,319 families residing in the parish. The population density was 241 people per square mile... on a natural levee of the Ouachita River Ouachita River The Ouachita River is a river that runs south and east through the U.S. states of Arkansas and Louisiana, joining the Tensas River to form the Black River near Jonesville, Louisiana.-Course:... |
|
| Flowery Mound Flowery Mound Flowery Mound is an archaeological site in Tensas Parish, Louisiana with components from the Late Coles Creek and Plaquemine-Mississippian culture which dates from approximately 950–1541.-Description:... |
A single mound Late Coles Creek to Plaquemine/Mississippian site in Tensas Parish, Louisiana which dates from approximately 950–1541. | |
| Frogmore Mound Site Frogmore Mound Site Frogmore Mound Site is an archaeological site of the Late Coles Creek culture in Concordia Parish, Louisiana. It was added to the NRHP on July 28, 2004 as NRIS number 04000740.-Description:... |
A Late Coles Creek site in Concordia Parish, Louisiana Concordia Parish, Louisiana Concordia Parish borders the Mississippi River in eastern Louisiana. The parish seat is Vidalia. As of 2000, the population was 20,247. It is part of the Natchez, MS–LA Micropolitan Statistical Area.-Prehistory:... . |
|
| Ghost Site Mounds Ghost Site Mounds Ghost Site Mounds is an archaeological site in Tensas Parish, Louisiana with an Early to Middle Coles Creek culture component and a Late Coles Creek to Plaquemine culture component .-Description:... |
A site in Tensas Parish, Louisiana Tensas Parish, Louisiana Tensas Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The seat of the parish is St. Joseph. In 2010, the population of Tensas Parish was 5,252; it is the least-populous of all sixty-four parishes.... with an Early to Middle Coles Creek component(700–1200)and a Late Coles Creek to Plaquemine component(1200 to 1541) |
|
| Greenhouse Site Greenhouse Site The Greenhouse Site is an archaeological site of the Troyville-Coles Creek culture in Avoyelles Parish, Louisiana.-Description:... |
A multimound site in Avoyelles Parish, Louisiana Avoyelles Parish, Louisiana Avoyelles is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Marksville. In 2000, its population was 41,481. The parish is named for the Avoyel Indian tribe.-History:... from the Troyville-Coles Creek Period |
|
| Insley Mounds | A multimound site in Richland Parish, Louisiana Richland Parish, Louisiana Richland Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Rayville. As of 2010, the population was 20,725.-History:... with a Poverty Point Poverty Point culture Poverty Point culture is an archaeological culture that corresponds to an ancient group of Indigenous peoples who inhabited the area of the lower Mississippi Valley and surrounding Gulf coast from about 2200 BCE - 700 BCE... period component (1700–1000 BCE) and a Coles Creek component (720 to 1200 CE). |
|
| Kings Crossing Site Kings Crossing Site Kings Crossing Site is an archaeological site that is a type site for the Kings Crossing Phase of the Lower Yazoo Basin Coles Creek chronology.-Location:... |
 |
The type site for the Kings Crossing phase (900 -1050 CE), a multimound site located near Vicksburg Vicksburg, Mississippi Vicksburg is a city in Warren County, Mississippi, United States. It is the only city in Warren County. It is located northwest of New Orleans on the Mississippi and Yazoo rivers, and due west of Jackson, the state capital. In 1900, 14,834 people lived in Vicksburg; in 1910, 20,814; in 1920,... in Warren County, Mississippi Warren County, Mississippi -National protected areas:* Theodore Roosevelt National Wildlife Refuge * Vicksburg National Military Park -Demographics:As of the census of 2000, there were 49,644 people, 18,756 households, and 13,222 families residing in the county. The population density was 85 people per square mile... |
| Lamarque Landing Mound | A single mound site in Concordia Parish, Louisiana dating to about 1000 CE. | |
| Marsden Mounds Marsden Mounds Marsden Mounds is an archaeological site with components from the Poverty Point culture and the Troyville-Coles Creek period . It is located in Richland Parish, Louisiana near Delhi It was added to the NRHP on August 4, 2004 as NRIS number 04000803... |
A multimound site in West Carroll Parish, Louisiana near Delhi, Louisiana Delhi, Louisiana Delhi, originally called Deerfield, is a town in Richland Parish, Louisiana, in the United States. As of the 2000 census, the town population was 3,066.-History:... , with a Poverty Point Poverty Point culture Poverty Point culture is an archaeological culture that corresponds to an ancient group of Indigenous peoples who inhabited the area of the lower Mississippi Valley and surrounding Gulf coast from about 2200 BCE - 700 BCE... period component (1500 BCE) and a Coles Creek component (400 to 1200 CE). |
|
| Mazique Archeological Site Mazique Archeological Site The Mazique Archeological Site , also known as White Apple Village, is a prehistoric Coles Creek culture archaeological site located in Adams County, Mississippi. It is also the location of the historic White Apple Village of the Natchez people and the Mazique Plantation... |
A multimound site in Adams County, Mississippi southeast of Natchez, Mississippi Natchez, Mississippi Natchez is the county seat of Adams County, Mississippi, United States. With a total population of 18,464 , it is the largest community and the only incorporated municipality within Adams County... , with components from both the Coles Creek period (700-1000 CE) and the later Plaquemine Mississippian period (1000-1680 CE), when it was recorded in historic times as the White Apple village of the Natchez people Natchez people The Natchez are a Native American people who originally lived in the Natchez Bluffs area, near the present-day city of Natchez, Mississippi. They spoke a language isolate that has no known close relatives, although it may be very distantly related to the Muskogean languages of the Creek... . |
|
| Mott Mounds Mott Archaeological Preserve The Mott Archaeological Preserve or Mott Mounds Site is an archaeological site in Franklin Parish, Louisiana on the west bank of Bayou Macon. It originally had eleven mounds with components from the Marksville, Troyville, Coles Creek, and Plaquemine periods... |
A large multimound site with components from the Late Marksville to the Plaquemine period but with its main occupation during the Coles Creek period, located in Franklin Parish, Louisiana Franklin Parish, Louisiana -Demographics:As of the census of 2000, there were 21,263 people, 7,754 households, and 5,706 families residing in the parish. The population density was 34 people per square mile . There were 8,623 housing units at an average density of 14 per square mile... . |
|
| Peck Mounds Peck Mounds Peck Mounds is an archaeological site of the Late Troyville-Early Coles Creek culture in Catahoula Parish, Louisiana.-Description:... |
A multimound site from the Late Troyville-Early Coles Creek period located in Catahoula Parish, Louisiana Catahoula Parish, Louisiana Catahoula Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. Its seat is Harrisonburg, located on the Ouachita River, which forms the eastern boundary of the parish. In 2000, the population of the parish was 10,920.-Prehistory:... |
|
| Raffman Site Raffman Site The Raffman Site is an archaeological site located in Madison Parish, Louisiana and constructed between 700 and 1200 CE. It has components from the Tchefuncte culture and the Coles Creek culture, whose main period of occupation was during the Balmoral Phase of the Tensas Basin and Natchez Bluffs... |
A multimound site whose main period of occupation was during the Balmoral Phase(1000-1100 CE) of the Tensas Basin and Natchez Bluffs Coles Creek chronology, located in Madison Parish, Louisiana Madison Parish, Louisiana -National protected areas:* Tensas River National Wildlife Refuge * Vicksburg National Military Park -Demographics:-2010:Whereas according to the 2010 U.S... and constructed between 700 and 1000 CE |
|
| Scott Place Mounds Scott Place Mounds Scott Place Mounds is an archaeological site in Union Parish, Louisiana from the Late Coles Creek-Early Plaquemine period, dating to approximately 1200 CE. The site is one of the few such sites in north-central Louisiana.-Description:... |
A multimound site from the Late Coles Creek-Early Plaquemine period located in Union Parish, Louisiana Union Parish, Louisiana Union Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Farmerville.... |
|
| Sundown Mounds Sundown Mounds Sundown Mounds is an multimound archaeological site in Tensas Parish, Louisiana from the Early Coles Creek culture.It is the type site for the Sundown Phase of the Tensas Basin and Natchez Bluff Coles Creek chronology.-Description:... |
A multimound site from the Early Coles Creek in Tensas Parish, Louisiana that is the type site for the Sundown Phase(700-800 CE) | |
| Transylvania Mounds Transylvania Mounds Translyvania Mounds is an archaeological site in East Carroll Parish, Louisiana with components from the Coles Creek CE and Plaquemine/Mississippi periods... |
A large multimound site with 2 plaza Plaza Plaza is a Spanish word related to "field" which describes an open urban public space, such as a city square. All through Spanish America, the plaza mayor of each center of administration held three closely related institutions: the cathedral, the cabildo or administrative center, which might be... s and components from the Coles Creek (700–1200) and Plaquemine/Mississippian periods (1200–1541). It located in East Carroll Parish, Louisiana East Carroll Parish, Louisiana East Carroll Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Lake Providence and as of 2010, the population was 7,759.-Law and government:In the 2004 presidential race, East Carroll gave the George W. Bush - Richard B... It is the type site Type site In archaeology a type site is a site that is considered the model of a particular archaeological culture... for the Translyvania Phase of the Tensas Basin Plaquemine Mississippian chronology. |
|
| Troyville Earthworks Troyville Earthworks Troyville Earthworks is a Woodland period Native American archaeological site with components dating from 100 BCE to 700 CE during the Baytown to the Troyville-Coles Creek periods. It once had the tallest mound in Louisiana at in height. It is located in Catahoula Parish, Louisiana in the town of... |
A large multimound site with components dating from 100 BCE to 700 CE. It once had the tallest mound in Louisiana at 82 feet (25 m) in height. It is located in Catahoula Parish, Louisiana in the town of Jonesville Jonesville, Louisiana Jonesville is a town in Catahoula Parish, Louisiana, at the confluence of the Ouachita, Tensas, and Little rivers. The three rivers become the Black River at Jonesville though the "Black" is primarily the continuation of the Ouachita River. A new bridge has been built over the Black River... . |
|
| Venable Mound Venable Mound Venable Mound is an archaeological site in Morehouse Parish, Louisiana with a single mound with components from the Troyville, Coles Creek and Plaquemine period.-Description:... |
A single mound site with components from the Troyville, Coles Creek and Plaquemine periods, located in Morehouse Parish, Louisiana Morehouse Parish, Louisiana Morehouse Parish is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. The parish seat is Bastrop. In 2000, the parish population was 31,021.... |
|
| Wade Landing Mound Wade Landing Mound Wade Landing Mound is an archaeological site of the Coles Creek culture in Caldwell Parish, Louisiana.-Description:The site contains a tall rectangular platform mound with a base measuring by . Archaeologists have done core samples of the mound and determined that it was built in two stages... |
A single mound site located in Caldwell Parish, Louisiana Caldwell Parish, Louisiana -Demographics:As of the census of 2000, there were 10,560 people, 3,941 households, and 2,817 families residing in the parish. The population density was 20 people per square mile . There were 5,035 housing units at an average density of 10 per square mile... |
|
See also
- Plum Bayou culturePlum Bayou culturePlum Bayou culture is a Pre-Columbian Native American culture that lived in what is now east-central Arkansas from 650—1050 CE, a time known as the Late Woodland Period...
- Culture, phase, and chronological table for the Mississippi Valley

