
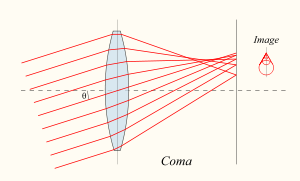
Coma (optics)
Encyclopedia
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
(especially telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
s), the coma (aka comatic aberration) in an optical system refers to aberration
Aberration in optical systems
Aberrations are departures of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. It occurs when light from one point of an object after transmission through the system does not converge...
inherent to certain optical designs or due to imperfection in the lens
Lens (optics)
A lens is an optical device with perfect or approximate axial symmetry which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element...
or other components which results in off-axis point source
Point source
A point source is a localised, relatively small source of something.Point source may also refer to:*Point source , a localised source of pollution**Point source water pollution, water pollution with a localized source...
s such as stars appearing distorted, appearing to have a tail (coma
Coma (cometary)
frame|right|The [[153P/Ikeya-Zhang|comet Ikeya-Zhang]] exhibiting a bright, condensed coma In astronomy, a coma is the nebulous envelope around the nucleus of a comet. It is formed when the comet passes close to the Sun on its highly elliptical orbit; as the comet warms, parts of it sublimate...
) like a comet
Comet
A comet is an icy small Solar System body that, when close enough to the Sun, displays a visible coma and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are both due to the effects of solar radiation and the solar wind upon the nucleus of the comet...
. Specifically, coma is defined as a variation in magnification
Magnification
Magnification is the process of enlarging something only in appearance, not in physical size. This enlargement is quantified by a calculated number also called "magnification"...
over the entrance pupil
Entrance pupil
In an optical system, the entrance pupil is the optical image of the physical aperture stop, as 'seen' through the front of the lens system. The corresponding image of the aperture as seen through the back of the lens system is called the exit pupil...
. In refractive
Refraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
or diffractive
Diffraction
Diffraction refers to various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word "diffraction" and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1665...
optical systems, especially those imaging a wide spectral range, coma can be a function of wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
, in which case it is a form of chromatic aberration
Chromatic aberration
In optics, chromatic aberration is a type of distortion in which there is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same convergence point. It occurs because lenses have a different refractive index for different wavelengths of light...
.
Coma is an inherent property of telescopes using parabolic mirrors. Light from a point source (such as a star) in the center of the field is perfectly focused at the focal point
Focus (optics)
In geometrical optics, a focus, also called an image point, is the point where light rays originating from a point on the object converge. Although the focus is conceptually a point, physically the focus has a spatial extent, called the blur circle. This non-ideal focusing may be caused by...
of the mirror (unlike a spherical mirror, where light from the outer part of the mirror focuses closer to the mirror than light from the center--spherical aberration
Spherical aberration
thumb|right|Spherical aberration. A perfect lens focuses all incoming rays to a point on the [[Optical axis|optic axis]]. A real lens with spherical surfaces suffers from spherical aberration: it focuses rays more tightly if they enter it far from the optic axis than if they enter closer to the...
). However, when the light source is off-center (off-axis), the different parts of the mirror do not reflect the light to the same point. This results in a point of light that is not in the center of the field looking wedge-shaped. The further off-axis, the worse this effect is. This causes stars to appear to have a cometary coma
Coma (cometary)
frame|right|The [[153P/Ikeya-Zhang|comet Ikeya-Zhang]] exhibiting a bright, condensed coma In astronomy, a coma is the nebulous envelope around the nucleus of a comet. It is formed when the comet passes close to the Sun on its highly elliptical orbit; as the comet warms, parts of it sublimate...
, hence the name.
Schemes to reduce spherical aberration without introducing coma include Schmidt, Maksutov
Maksutov telescope
The Maksutov is a catadioptric telescope design that combines a spherical mirror with a weakly negative meniscus lens in a design that takes advantage of all the surfaces being nearly "spherically symmetrical". The negative lens is usually full diameter and placed at the entrance pupil of the...
, ACF and Ritchey-Chrétien
Ritchey-Chrétien telescope
A Ritchey–Chrétien telescope is a specialized Cassegrain telescope designed to eliminate coma, thus providing a large field of view compared to a more conventional configuration. An RCT has a hyperbolic primary and a hyperbolic secondary mirror. It was invented in the early 1910s by American...
optical systems. Correction lenses for Newtonian reflectors have been designed which reduce coma in telescopes below f/6. These work by means of a dual lens system of a plano-convex and a plano-concave lens fitted into an eyepiece adaptor which superficially resembles a Barlow lens
Barlow lens
The Barlow lens, named for its creator, the English engineer Peter Barlow, is a diverging lens which, used in series with other optics in an optical system, increases the effective focal ratio of an optical system as perceived by all components after it in the system...
.
Coma of a single lens or a system of lenses can be minimized (and in some cases eliminated) by choosing the curvature
Curvature
In mathematics, curvature refers to any of a number of loosely related concepts in different areas of geometry. Intuitively, curvature is the amount by which a geometric object deviates from being flat, or straight in the case of a line, but this is defined in different ways depending on the context...
of the lens surfaces to match the application. Lenses in which both spherical aberration and coma are minimized at a single wavelength are called bestform or aplanatic or aspheric
Aspheric lens
An aspheric lens or asphere is a lens whose surface profiles are not portions of a sphere or cylinder. In photography, a lens assembly that includes an aspheric element is often called an aspherical lens....
lenses.
Vertical coma is the most common higher-order aberration in the eyes of patients with keratoconus
Keratoconus
Keratoconus , is a degenerative disorder of the eye in which structural changes within the cornea cause it to thin and change to a more conical shape than its normal gradual curve....
.

