Compass navigation system
Encyclopedia
The COMPASS system is a project by China
to develop an independent global satellite navigation system.
COMPASS is not an extension to the previously deployed Beidou-1
, but a new GNSS
similar in principle to GPS
, GLONASS
, and Galileo.
(GEO) satellites and 30 medium Earth orbit
(MEO) satellites, that will offer complete coverage of the globe. The ranging signals are based on the CDMA principle and have complex structure typical to Galileo
or modernized GPS. Similarly to the other GNSS, there will be two levels of positioning service: open and restricted (military). The public service shall be available globally to general users. When all the currently planned GNSS systems are deployed, the users will benefit from the use of a total constellation of 75+ satellites, which will significantly improve all the aspects of positioning, especially availability of the signals in so-called “urban canyons”. The general designer of Compass navigation system is Sun Jiadong
, who is also the general designer of its predecessor, Beidou navigation system.
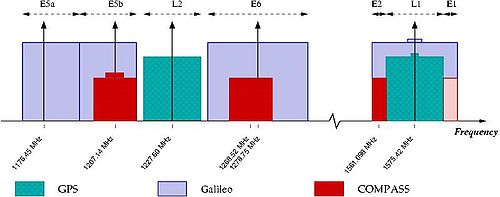 Frequencies
Frequencies
for Compass are allocated in four bands: E1, E2, E5B, and E6 and overlap with Galileo
. The fact of overlapping could be convenient from the point of view of the receiver design, but on the other hand raises the issues of inter-system interference, especially within E1 and E2 bands, which are allocated for Galileo’s
publicly-regulated service. However, under International Telecommunications Union (ITU) policies, the first nation to start broadcasting in a specific frequency will have priority to that frequency, and any subsequent users will be required to obtain permission prior to using that frequency, and otherwise ensure that their broadcasts do not interfere with the original nation's broadcasts. It now appears that Chinese Compass satellites will start transmitting in the E1, E2, E5B, and E6 bands before Europe's Galileo satellites and thus have primary rights to these frequency ranges.
Although almost nothing has yet been officially announced by Chinese authorities about the signals of the new system, the launch of the first Compass satellite permitted independent researchers not only to study general characteristics of the signals but even to build a Compass receiver.
satellites for Galileo
. The signals of Compass-M1 are to a great extent unraveled by independent research. The orbit of Compass-M1 is nearly circular, has an altitude of 21,150 km and an inclination of 55.5 degrees.
Compass-M1 is transmitting in 3 bands: E2, E5B, and E6. In each frequency band two coherent sub-signals have been detected with a phase shift of 90 degrees (in quadrature
). These signal components are further referred to as “I” and “Q”. The “I” components have shorter codes and are likely to be intended for the open service. The “Q” components have much longer codes, are more interference resistive, and are probably intended for the restricted service.
The investigation of the transmitted signals started immediately after the launch of COMPASS-M1 on April 14, 2007. Already in June engineers at CNES
reported the spectrum and structure of the signals. Next month researchers from the Stanford University
reported complete decoding of the “I” signal scomponents. The knowledge of the codes allowed a group of engineers at Septentrio
to build the COMPASS receiver and report tracking and multipath characteristics of the “I” signals on E2 and E5B.
Characteristics of the “I” signals on E2 and E5B are generally similar to the civilian codes of GPS (L1-CA and L2C), but Compass signals have somewhat greater power. The notation of Compass signals used in this page follows the naming of the frequency bands and agrees with the notation used in the American literature on the subject, but the notation used by the Chinese seems to be different and is quoted in the first row of the table.
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
to develop an independent global satellite navigation system.
COMPASS is not an extension to the previously deployed Beidou-1
Beidou navigation system
The BeiDou Navigation System or BeiDou Navigation Satellite System is a project by China to develop an independent satellite navigation system...
, but a new GNSS
Global Navigation Satellite System
A satellite navigation or SAT NAV system is a system of satellites that provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning with global coverage. It allows small electronic receivers to determine their location to within a few metres using time signals transmitted along a line-of-sight by radio from...
similar in principle to GPS
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System is a space-based global navigation satellite system that provides location and time information in all weather, anywhere on or near the Earth, where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites...
, GLONASS
GLONASS
GLONASS , acronym for Globalnaya navigatsionnaya sputnikovaya sistema or Global Navigation Satellite System, is a radio-based satellite navigation system operated for the Russian government by the Russian Space Forces...
, and Galileo.
General
The new system will be a constellation of 35 satellites, which include 5 geostationary orbitGeostationary orbit
A geostationary orbit is a geosynchronous orbit directly above the Earth's equator , with a period equal to the Earth's rotational period and an orbital eccentricity of approximately zero. An object in a geostationary orbit appears motionless, at a fixed position in the sky, to ground observers...
(GEO) satellites and 30 medium Earth orbit
Medium Earth Orbit
Medium Earth orbit , sometimes called intermediate circular orbit , is the region of space around the Earth above low Earth orbit and below geostationary orbit ....
(MEO) satellites, that will offer complete coverage of the globe. The ranging signals are based on the CDMA principle and have complex structure typical to Galileo
Galileo positioning system
Galileo is a global navigation satellite system currently being built by the European Union and European Space Agency . The €20 billion project is named after the famous Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei...
or modernized GPS. Similarly to the other GNSS, there will be two levels of positioning service: open and restricted (military). The public service shall be available globally to general users. When all the currently planned GNSS systems are deployed, the users will benefit from the use of a total constellation of 75+ satellites, which will significantly improve all the aspects of positioning, especially availability of the signals in so-called “urban canyons”. The general designer of Compass navigation system is Sun Jiadong
Sun Jiadong
Sun Jiadong , was born in Fuxian, Liaoning Province. He is a Chinese scientist and an expert in carrier rocket and satellite technology...
, who is also the general designer of its predecessor, Beidou navigation system.

Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
for Compass are allocated in four bands: E1, E2, E5B, and E6 and overlap with Galileo
Galileo positioning system
Galileo is a global navigation satellite system currently being built by the European Union and European Space Agency . The €20 billion project is named after the famous Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei...
. The fact of overlapping could be convenient from the point of view of the receiver design, but on the other hand raises the issues of inter-system interference, especially within E1 and E2 bands, which are allocated for Galileo’s
Galileo positioning system
Galileo is a global navigation satellite system currently being built by the European Union and European Space Agency . The €20 billion project is named after the famous Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei...
publicly-regulated service. However, under International Telecommunications Union (ITU) policies, the first nation to start broadcasting in a specific frequency will have priority to that frequency, and any subsequent users will be required to obtain permission prior to using that frequency, and otherwise ensure that their broadcasts do not interfere with the original nation's broadcasts. It now appears that Chinese Compass satellites will start transmitting in the E1, E2, E5B, and E6 bands before Europe's Galileo satellites and thus have primary rights to these frequency ranges.
Although almost nothing has yet been officially announced by Chinese authorities about the signals of the new system, the launch of the first Compass satellite permitted independent researchers not only to study general characteristics of the signals but even to build a Compass receiver.
Compass-M1
Compass-M1 is an experimental satellite launched for signal testing and validation and for the frequency filing on April 14, 2007. The role of Compass-M1 for Compass is similar to the role of GIOVEGIOVE
GIOVE, or Galileo In-Orbit Validation Element, is the name for each satellite in a series being built for the European Space Agency to test technology in orbit for the Galileo positioning system.Giove is the Italian word for "Jupiter"...
satellites for Galileo
Galileo positioning system
Galileo is a global navigation satellite system currently being built by the European Union and European Space Agency . The €20 billion project is named after the famous Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei...
. The signals of Compass-M1 are to a great extent unraveled by independent research. The orbit of Compass-M1 is nearly circular, has an altitude of 21,150 km and an inclination of 55.5 degrees.
Compass-M1 is transmitting in 3 bands: E2, E5B, and E6. In each frequency band two coherent sub-signals have been detected with a phase shift of 90 degrees (in quadrature
Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
). These signal components are further referred to as “I” and “Q”. The “I” components have shorter codes and are likely to be intended for the open service. The “Q” components have much longer codes, are more interference resistive, and are probably intended for the restricted service.
The investigation of the transmitted signals started immediately after the launch of COMPASS-M1 on April 14, 2007. Already in June engineers at CNES
CNES
The is the French government space agency . Established under President Charles de Gaulle in 1961, its headquarters are located in central Paris and it is under the supervision of the French Ministries of Defence and Research...
reported the spectrum and structure of the signals. Next month researchers from the Stanford University
Stanford University
The Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University or Stanford, is a private research university on an campus located near Palo Alto, California. It is situated in the northwestern Santa Clara Valley on the San Francisco Peninsula, approximately northwest of San...
reported complete decoding of the “I” signal scomponents. The knowledge of the codes allowed a group of engineers at Septentrio
Septentrio
Septentrio is a designer and manufacturer of high-end multi-frequency GNSS receivers. Its main target is to provide GNSS receiver boards for further system integration by Original Equipment Manufacturers...
to build the COMPASS receiver and report tracking and multipath characteristics of the “I” signals on E2 and E5B.
| Parameters | E2-I | E2-Q | E5B-I | E5B-Q | E6-I | E6-Q | GPS L1-CA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native notation | B1 | B1 | B2 | B2 | B3 | B3 | --- |
| Code modulation | BPSK(2) | BPSK(2) | BPSK(2) | BPSK(10) | BPSK(10) | BPSK (10) | BPSK (1) |
| Carrier frequency, MHz | 1561.098 | 1561.098 | 1207.14 | 1207.14 | 1268.52 | 1268.52 | 1575.42 |
| Chip rate, Mchips/sec | 2.046 | 2.046 | 2.046 | 10.230 | 10.230 | 10.230 | 1.023 |
| Code period, chips | 2046 | ?? | 2046 | ?? | 10230 | ?? | 1023 |
| Code period, msec | 1.0 | >400 | 1.0 | >160 | 1.0 | >160 | 1.0 |
| Symbols/sec | 50 | ?? | 50 | ?? | 50 | ?? | 50 |
| Navigation frames, sec | 6 | ?? | 6 | ?? | ?? | ?? | 6 |
| Navigation sub-frames, sec | 30 | ?? | 30 | ?? | ?? | ?? | 30 |
| Navigation period, min | 12.0 | ?? | 12.0 | ?? | ?? | ?? | 12.5 |
Characteristics of the “I” signals on E2 and E5B are generally similar to the civilian codes of GPS (L1-CA and L2C), but Compass signals have somewhat greater power. The notation of Compass signals used in this page follows the naming of the frequency bands and agrees with the notation used in the American literature on the subject, but the notation used by the Chinese seems to be different and is quoted in the first row of the table.
Compass launches
| Mission | Date | Name | Launch center | Launch vehicle | Bus Satellite bus A satellite bus or spacecraft bus is the general model on which multiple-production satellite spacecraft are often based. The bus is the infrastructure of a spacecraft, usually providing locations for the payload .They are most commonly used for geosynchronous satellites, particularly... |
Orbit |
| 07-32 | 2007.04.13 | Compass-M1 | Xichang Xichang Satellite Launch Center The Xichang Satellite Launch Center also known as Base 27 , is a People’s Republic of China space vehicle launch facility approximately 64 km northwest of Xichang City, Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture in Sichuan Province.... |
CZ-3C Long March 3C The Long March 3C , also known as the Chang Zheng 3C, CZ-3C and LM-3C, is a Chinese orbital carrier rocket. It is launched from Launch Complex 2 at the Xichang Satellite Launch Centre. A 3-stage rocket with two strapon liquid rocket boosters, it is a member of the Long March 3 rocket family, and... |
DFH-3 | MEO Medium Earth Orbit Medium Earth orbit , sometimes called intermediate circular orbit , is the region of space around the Earth above low Earth orbit and below geostationary orbit .... ~21,500 km |
| 07-37 | 2009.04.14 | Compass-G2 | Xichang | CZ-3C | DFH-3 | GEO Geostationary orbit A geostationary orbit is a geosynchronous orbit directly above the Earth's equator , with a period equal to the Earth's rotational period and an orbital eccentricity of approximately zero. An object in a geostationary orbit appears motionless, at a fixed position in the sky, to ground observers... drifting |
| 07-38 | 2010.01.16 | Compass-G1 Compass-G1 Compass-G1, also known as Beidou-2 G1 is a Chinese navigation satellite which will become part of the Compass navigation system. It was launched in January 2010, and became the third Compass satellite to be launched after Compass-M1 and Compass-G2.... |
Xichang | CZ-3C | DFH-3 | GEO 144.5°E |
| 07-39 | 2010.06.02 | Compass-G3 | Xichang | CZ-3C | DFH-3 | GEO 84.0°E |
| 07-40 | 2010.07.31 | Compass-IGSO1 Compass-IGSO1 Compass-IGSO1, also known as Beidou-2 IGSO1 is a Chinese navigation satellite which will become part of the Compass navigation system. It was launched in July 2010, and became the fifth Compass satellite to be launched after Compass-M1, G2, G1, and G3.... |
Xichang | CZ-3A Long March 3A The Long March 3A , also known as the Chang Zheng 3A, CZ-3A and LM-3A, is a Chinese orbital carrier rocket. It is a 3-stage rocket, and is usually used to place communications satellites and Beidou navigation satellites into geosynchronous transfer orbits.It has formed the basis of the Long March... |
DFH-3 | HEO ~36,000 km |
| 07-43 | 2010.10.31 | Compass-G4 | Xichang | CZ-3C Long March 3C The Long March 3C , also known as the Chang Zheng 3C, CZ-3C and LM-3C, is a Chinese orbital carrier rocket. It is launched from Launch Complex 2 at the Xichang Satellite Launch Centre. A 3-stage rocket with two strapon liquid rocket boosters, it is a member of the Long March 3 rocket family, and... |
DFH-3 | GEO 160.0°E |
| 07-45 | 2010.12.17 | Compass-IGSO2 | Xichang | CZ-3A | DFH-3 | HEO ~36,000 km |
| 07-46 | 2011.04.10 | Compass-IGSO3 | Xichang | CZ-3A | DFH-3 | HEO ~36,000 km |
| 07-49 | 2011.07.27 | Compass-IGSO-4 | Xichang | CZ-3A | DFH-3 | HEO ~36,000 km |

