
Computer module
Encyclopedia
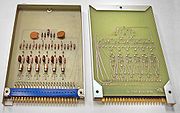
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
. An example might be an inverter
Inverter (logic gate)
In digital logic, an inverter or NOT gate is a logic gate which implements logical negation. The truth table is shown on the right.This represents perfect switching behavior, which is the defining assumption in Digital electronics. In practice, actual devices have electrical characteristics that...
or flip-flop
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic...
, which would require two or more transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
s and a small number of additional supporting devices. Modules would be inserted into a chassis and then wired together to produce a larger logic unit, like an adder.
Modules were the basic building block of most early computer designs, until they started being replaced by integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
s in the 1960s, which were essentially an entire module packaged onto a single computer chip. Modules with discrete components continued to be used in specialist roles into the 1970s, notably high-speed designs like the CDC 8600
CDC 8600
The CDC 8600 was the last of Seymour Cray's supercomputer designs while working for the Control Data Corporation. The "natural successor" to the CDC 6600 and CDC 7600, the 8600 was intended to be about 10 times as fast as the 7600, already the fastest computer on the market.Development started in...
, but advances in chip design led to the disappearance of the discrete-component module in the 1970s.

