
Condensed aerosol fire suppression
Encyclopedia
Condensed aerosol fire suppression is a particle-based form of fire extinction similar to gaseous fire suppression
or dry chemical fire extinction. The aerosol employs a fire extinguishing agent consisting of very fine solid particles and gaseous matter to put out fires. The condensed aerosol microparticles and effluent gases are generated by the exothermic reaction; until discharged from the device, the particles remain in vapor state. They are cooled and "condensed" within the device and discharged as solid particles.
To the difference of gaseous suppressants, which emit only gas, and dry chemical suppression agents, which are powder-like particles of a large size (25-150 micrometres), condensed aerosols are defined by the National Fire Protection Association as releasing finely-divided solids of less than 10 micrometres in diameter. The solid particulates have a considerably smaller mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) those of dry chemical suppression agents, remain airborne significantly longer, and leave much less residue within the protected area. Whereas dry chemical systems must be directly aimed at the flame, condensed aerosols are flooding agents and therefore effective regardless of the location and height of the fire. Wet chemical systems, such as the kind generally found in foam extinguishers, must, similarly to dry chemical systems, be sprayed directionally, onto the fire. The condensed aerosol agent can be delivered by means of mechanical operation, electric operation, or combined electro-mechanical operation.
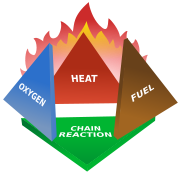 Condensed aerosol suppressants, like gaseous suppressants, use four methods to extinguish fires. They act on the four elements of the "fire tetrahedron," the disparate components that combine to create the chemical reaction underlying any fire. These four means of fire extinction are:
Condensed aerosol suppressants, like gaseous suppressants, use four methods to extinguish fires. They act on the four elements of the "fire tetrahedron," the disparate components that combine to create the chemical reaction underlying any fire. These four means of fire extinction are:
Condensed aerosols’ primary extinguishing mechanism involves the fourth element of the fire tetrahedron by means of chemical reactions with the free radicals of the flame, therefore interfering with the combustion process of the fire. Typically, condensed aerosol particulates consist of potassium carbonate
(K2CO3)) that are produced from the thermal decomposition of a solid aerosol-forming compound that includes potassium nitrate
as an oxidizer. As the aerosol particles surround and come into contact with the flame, the particulates absorb the flame heat energy breaking down and releasing large concentrations of potassium radicals (K+) (ions with an unpaired electron). The potassium radicals bond with the hydroxide (OH+), hydrogen (H+) and oxygen (O+) free radicals which sustain flame's combustion process, producing harmless by-product molecules such as potassium hydroxide
(KOH) and water (H2O).
K• + OH• = KOH
KOH + H• = K• + H2O
The potassium radicals are propagated since they are both consumed and produced by reaction with the fire radicals. Disrupting the reactions necessary to sustain the flame's combustion, the cycle continues until the combustion's chain reactions are terminated and the flame is extinguished.
As can be seen, if the flame continues to produce sufficient chemical energy, the population of potassium radicals is propagated since they are both consumed and produced by reaction with the fire radicals. This cycle continues until the combustion radical chain reactions terminates.
Condensed aerosol agents also have secondary extinguishing mechanisms implicating the other three elements of the fire tetrahedron described above. The aerosol cools the flame by engulfing it with a cloud with large concentrations of microparticles which have mass median aerodynamic diameter sizes (MMAD) as small as 1 to 2 micrometres. Though the surface area of each microparticle is extremely small, the large quantity of particles surrounding and penetrating the flame offers a sufficiently large combined surface area to absorb the flame’s heat.
On the surface of the particles, recombination of the fire radicals takes place as energy is absorbed:
O• + H• = OH•
H• + OH• = H20
Flame is the gaseous part of a fire resulting from the combustion of fuel. Aerosols particles and gases mixing with the gaseous components of the flame isolate the fire's fuel.
Attacking all the elements of the fire tetrahedron, condensed aerosol fire suppression agents are among the more effective flame-extinguishing agents. For example, some condensed aerosol fire suppressants can extinguish a Class B flammable liquid pool fire with 1/5th the amount of Halon 1301 agent or 1/10th the amount of a hydrofluorocarbon or fluoroketone based clean agent gaseous fire suppression system in terms of kilogram mass of agent per cubic meter.
Condensed aerosol devices are designed to provide a controlled discharge. The aerosol-forming compound is installed inside of the device, which is then fitted with an electric or mechanical initiator. The electric initiator is interfaced with a fire detection control unit or panel, which can be remotely operated by physical means such as by cable, hand operated with a fuse mechanism such as those used in smoke dispensing grenades, or automatic and self-triggering when outfitted with an integral heat-sensing device.
To provide total flooding fire suppression, the total quantity of aerosol required to extinguish a fire inside of fixed space must be determined. The corresponding number of aerosol devices that would collectively discharge the aerosol quantity required are then mounted, typically on the ceiling or wall. Aerosol devices equipped with electric initiators are interconnected and relayed by a fire alarm control panel. Because the aerosol devices are self-contained and function as both a storage container and as a nozzle that propels the gas, no distribution network is required to transport or distribute the fire-extinguishing agent from a remote storage location, resulting in floor space savings and transportation efficiency gains.
Local application fire suppression is typically applied by a handheld portable device tossed directly toward the fire. Unlike streaming portable fire extinguishing units, the operators are not required to place themselves at risk by approaching the fire while applying the extinguishing agent directly at the flames. The portable condensed aerosol device is typically designed to disperse aerosol in a 360° spray pattern, forming a large aerosol cloud around the vicinity of the fire. The aerosol immediately attacks the flames as its particles approach the fire and generate flame-neutralizing potassium radicals. The flames are suppressed as long as the aerosol retains sufficient density. If the aerosol fails to achieve sufficient density to extinguish the fire, it will still suppress the fire, which will retain significantly lower heat. This offers firefighters, for instance, a tool to bring down flames to a manageable heat level and reduce room temperatures while the hose team enters the burning area. As another example, First Responders can deploy condensed aerosols within an enclosed area to suppress fires while evacuating occupants to safety.
Condensed aerosol systems are suitable for special hazards applications as replacements for Halon 1301 systems and high-pressure carbon dioxide systems. Aerosol systems can also be used as alternatives to clean agent gaseous suppressants or water-mist systems.
Gaseous fire suppression
Gaseous fire suppression is a term to describe the use of inert gases and chemical agents to extinguish a fire. Also called Clean Agent Fire Suppression. These Agents are governed by the NFPA Standard for Clean Agent Fire Extinguishing Systems - NFPA 2001 in the USA, with different standards and...
or dry chemical fire extinction. The aerosol employs a fire extinguishing agent consisting of very fine solid particles and gaseous matter to put out fires. The condensed aerosol microparticles and effluent gases are generated by the exothermic reaction; until discharged from the device, the particles remain in vapor state. They are cooled and "condensed" within the device and discharged as solid particles.
To the difference of gaseous suppressants, which emit only gas, and dry chemical suppression agents, which are powder-like particles of a large size (25-150 micrometres), condensed aerosols are defined by the National Fire Protection Association as releasing finely-divided solids of less than 10 micrometres in diameter. The solid particulates have a considerably smaller mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) those of dry chemical suppression agents, remain airborne significantly longer, and leave much less residue within the protected area. Whereas dry chemical systems must be directly aimed at the flame, condensed aerosols are flooding agents and therefore effective regardless of the location and height of the fire. Wet chemical systems, such as the kind generally found in foam extinguishers, must, similarly to dry chemical systems, be sprayed directionally, onto the fire. The condensed aerosol agent can be delivered by means of mechanical operation, electric operation, or combined electro-mechanical operation.
Methods of fire extinction

- Reduction or isolation of fuel
- Reduction of heat
- Reduction or isolation of oxygen
- Inhibiting the chain reaction of the above components
Condensed aerosols’ primary extinguishing mechanism involves the fourth element of the fire tetrahedron by means of chemical reactions with the free radicals of the flame, therefore interfering with the combustion process of the fire. Typically, condensed aerosol particulates consist of potassium carbonate
Potassium carbonate
Potassium carbonate is a white salt, soluble in water , which forms a strongly alkaline solution. It can be made as the product of potassium hydroxide's absorbent reaction with carbon dioxide. It is deliquescent, often appearing a damp or wet solid...
(K2CO3)) that are produced from the thermal decomposition of a solid aerosol-forming compound that includes potassium nitrate
Potassium nitrate
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula KNO3. It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitrate ions NO3−.It occurs as a mineral niter and is a natural solid source of nitrogen. Its common names include saltpetre , from medieval Latin sal petræ: "stone salt" or possibly "Salt...
as an oxidizer. As the aerosol particles surround and come into contact with the flame, the particulates absorb the flame heat energy breaking down and releasing large concentrations of potassium radicals (K+) (ions with an unpaired electron). The potassium radicals bond with the hydroxide (OH+), hydrogen (H+) and oxygen (O+) free radicals which sustain flame's combustion process, producing harmless by-product molecules such as potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, commonly called caustic potash.Along with sodium hydroxide , this colorless solid is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications. Most applications exploit its reactivity toward acids and its corrosive...
(KOH) and water (H2O).
K• + OH• = KOH
KOH + H• = K• + H2O
The potassium radicals are propagated since they are both consumed and produced by reaction with the fire radicals. Disrupting the reactions necessary to sustain the flame's combustion, the cycle continues until the combustion's chain reactions are terminated and the flame is extinguished.
As can be seen, if the flame continues to produce sufficient chemical energy, the population of potassium radicals is propagated since they are both consumed and produced by reaction with the fire radicals. This cycle continues until the combustion radical chain reactions terminates.
Condensed aerosol agents also have secondary extinguishing mechanisms implicating the other three elements of the fire tetrahedron described above. The aerosol cools the flame by engulfing it with a cloud with large concentrations of microparticles which have mass median aerodynamic diameter sizes (MMAD) as small as 1 to 2 micrometres. Though the surface area of each microparticle is extremely small, the large quantity of particles surrounding and penetrating the flame offers a sufficiently large combined surface area to absorb the flame’s heat.
On the surface of the particles, recombination of the fire radicals takes place as energy is absorbed:
O• + H• = OH•
H• + OH• = H20
Flame is the gaseous part of a fire resulting from the combustion of fuel. Aerosols particles and gases mixing with the gaseous components of the flame isolate the fire's fuel.
Attacking all the elements of the fire tetrahedron, condensed aerosol fire suppression agents are among the more effective flame-extinguishing agents. For example, some condensed aerosol fire suppressants can extinguish a Class B flammable liquid pool fire with 1/5th the amount of Halon 1301 agent or 1/10th the amount of a hydrofluorocarbon or fluoroketone based clean agent gaseous fire suppression system in terms of kilogram mass of agent per cubic meter.
Performance
The extinguishing performance of condensed aerosol fire suppressants is dependent on the density of aerosol particulates in the immediate vicinity of the flame. As with gaseous fire suppression systems, the faster the agent can build around the flame, the more efficient the extinguishing agent will be in terminating the flame’s combustion process. The extinguishing and design densities of aerosol fire suppression agents are generally expressed in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m^3). Thus, the efficiency of aerosol extinguishing agents varies depending on a number of factors, such as the location of the aerosol relative to the flame, the proximity of other combustible flammable materials, the type of fuel involved, etc.Condensed aerosol devices are designed to provide a controlled discharge. The aerosol-forming compound is installed inside of the device, which is then fitted with an electric or mechanical initiator. The electric initiator is interfaced with a fire detection control unit or panel, which can be remotely operated by physical means such as by cable, hand operated with a fuse mechanism such as those used in smoke dispensing grenades, or automatic and self-triggering when outfitted with an integral heat-sensing device.
Uses and applications
There are two uses for applying fire extinguishing agents: as a total flooding fire protection system or as a local application fire suppression system.To provide total flooding fire suppression, the total quantity of aerosol required to extinguish a fire inside of fixed space must be determined. The corresponding number of aerosol devices that would collectively discharge the aerosol quantity required are then mounted, typically on the ceiling or wall. Aerosol devices equipped with electric initiators are interconnected and relayed by a fire alarm control panel. Because the aerosol devices are self-contained and function as both a storage container and as a nozzle that propels the gas, no distribution network is required to transport or distribute the fire-extinguishing agent from a remote storage location, resulting in floor space savings and transportation efficiency gains.
Local application fire suppression is typically applied by a handheld portable device tossed directly toward the fire. Unlike streaming portable fire extinguishing units, the operators are not required to place themselves at risk by approaching the fire while applying the extinguishing agent directly at the flames. The portable condensed aerosol device is typically designed to disperse aerosol in a 360° spray pattern, forming a large aerosol cloud around the vicinity of the fire. The aerosol immediately attacks the flames as its particles approach the fire and generate flame-neutralizing potassium radicals. The flames are suppressed as long as the aerosol retains sufficient density. If the aerosol fails to achieve sufficient density to extinguish the fire, it will still suppress the fire, which will retain significantly lower heat. This offers firefighters, for instance, a tool to bring down flames to a manageable heat level and reduce room temperatures while the hose team enters the burning area. As another example, First Responders can deploy condensed aerosols within an enclosed area to suppress fires while evacuating occupants to safety.
Condensed aerosol systems are suitable for special hazards applications as replacements for Halon 1301 systems and high-pressure carbon dioxide systems. Aerosol systems can also be used as alternatives to clean agent gaseous suppressants or water-mist systems.
Environmental issues
The United States Environmental Protection Agency has approved condensed aerosol fire suppression systems as acceptable substitutes for Halon 1301 in Total Flooding Systems.. Aerosol extinguishers are also non-ozone depleting and carry little or no global warming potential.See also
- Automatic fire suppressionAutomatic fire suppressionAutomatic fire suppression systems control and extinguish fires without human intervention.According to the National Fire Protection Association, there were 1,602,000 fires reported in the United States in 2005. There were 3,675 civilian deaths, 17,925 civilian injuries, and $9.2 billion in...
- Gaseous fire suppressionGaseous fire suppressionGaseous fire suppression is a term to describe the use of inert gases and chemical agents to extinguish a fire. Also called Clean Agent Fire Suppression. These Agents are governed by the NFPA Standard for Clean Agent Fire Extinguishing Systems - NFPA 2001 in the USA, with different standards and...
- Fire extinguisherFire extinguisherA fire extinguisher or extinguisher, flame entinguisher is an active fire protection device used to extinguish or control small fires, often in emergency situations...
- Fire protection engineeringFire protection engineeringFire Protection Engineering is the application of science and engineering principles to protect people and their environments from the destructive effects of fire and smoke....
Further reading
- Agafonov V., al. 2004. The Mechanism of Fire Suppression by Condensed Aerosols. "Proceedings of the 15th HOTC." NIST, pp 984-993.
- Dwyer, David J. 2011. Improved firefighting system Is on the way. "The Surf Rider," 14-15: 2001-01-28.
- Kibert, Charles J. 1993. Encapsulated Micron Aerosol Agents (EMMA). Halon Alternatives Technical Conference, 1993. NIST. May 11-13, 1993, pp 421-435
- Halon Alternatives for the Ship-to-Shore Connector. Spectra, 12: 2001
- Sheinson, Ronald S., al. "Suppression Effectiveness of Aerosols: The Effect of Size and Flame Type"

