
Congenital rubella syndrome
Encyclopedia
Congenital rubella syndrome (CRS) can occur in a developing fetus of a pregnant woman who has contracted rubella
during her first trimester. If infection occurs 0–28 days before conception, there is a 43% chance the infant will be affected. If the infection occurs 0–12 weeks after conception, there is a 51% chance the infant will be affected. If the infection occurs 13–26 weeks after conception there is a 23% chance the infant will be affected by the disease. Infants are not generally affected if rubella is contracted during the third trimester, or 26–40 weeks after conception. Problems rarely occur when rubella is contracted by the mother after 20 weeks of gestation
and continues to disseminate the virus after birth.
It was discovered in 1941 by Australian Norman McAllister Gregg
.
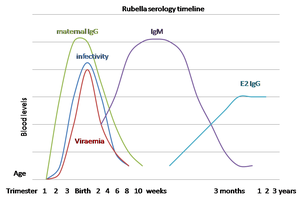 The classic triad for congenital rubella syndrome is:
The classic triad for congenital rubella syndrome is:
Other manifestations of CRS may include:
Children who have been exposed to rubella in the womb should also be watched closely as they age for any indication of the following:
Rubella
Rubella, commonly known as German measles, is a disease caused by the rubella virus. The name "rubella" is derived from the Latin, meaning little red. Rubella is also known as German measles because the disease was first described by German physicians in the mid-eighteenth century. This disease is...
during her first trimester. If infection occurs 0–28 days before conception, there is a 43% chance the infant will be affected. If the infection occurs 0–12 weeks after conception, there is a 51% chance the infant will be affected. If the infection occurs 13–26 weeks after conception there is a 23% chance the infant will be affected by the disease. Infants are not generally affected if rubella is contracted during the third trimester, or 26–40 weeks after conception. Problems rarely occur when rubella is contracted by the mother after 20 weeks of gestation
Gestation
Gestation is the carrying of an embryo or fetus inside a female viviparous animal. Mammals during pregnancy can have one or more gestations at the same time ....
and continues to disseminate the virus after birth.
It was discovered in 1941 by Australian Norman McAllister Gregg
Norman Gregg
Sir Norman McAlister Gregg, MC was an Australian ophthalmologist, who discovered that rubella suffered by a pregnant woman could cause birth defects in her child .-Early life and education:...
.
Presentation

- Sensorineural deafnessSensorineural hearing lossSensorineural hearing loss is a type of hearing loss in which the root cause lies in the vestibulocochlear nerve , the inner ear, or central processing centers of the brain....
(58% of patients) - Eye abnormalities—especially retinopathyRetinopathyRetinopathy is a general term that refers to some form of non-inflammatory damage to the retina of the eye. Frequently, retinopathy is an ocular manifestation of systemic disease.-Pathophysiology:Causes of retinopathy are varied:...
, cataractCataractA cataract is a clouding that develops in the crystalline lens of the eye or in its envelope, varying in degree from slight to complete opacity and obstructing the passage of light...
and microphthalmiaMicrophthalmiaMicrophthalmia also referred to as microphthalmos, nanophthalmia or nanophthalmos, is a developmental disorder of the eye that literally means small eye...
(43% of patients) - Congenital heart disease—especially patent ductus arteriosusPatent ductus arteriosusPatent ductus arteriosus is a congenital disorder in the heart wherein a neonate's ductus arteriosus fails to close after birth. Early symptoms are uncommon, but in the first year of life include increased work of breathing and poor weight gain...
(50% of patients)
Other manifestations of CRS may include:
- SpleenSpleenThe spleen is an organ found in virtually all vertebrate animals with important roles in regard to red blood cells and the immune system. In humans, it is located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood in case of hemorrhagic shock...
, liverLiverThe liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
or bone marrowBone marrowBone marrow is the flexible tissue found in the interior of bones. In humans, bone marrow in large bones produces new blood cells. On average, bone marrow constitutes 4% of the total body mass of humans; in adults weighing 65 kg , bone marrow accounts for approximately 2.6 kg...
problems (some of which may disappear shortly after birth) - Mental retardationMental retardationMental retardation is a generalized disorder appearing before adulthood, characterized by significantly impaired cognitive functioning and deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors...
- Small head size (microcephalyMicrocephalyMicrocephaly is a neurodevelopmental disorder in which the circumference of the head is more than two standard deviations smaller than average for the person's age and sex. Microcephaly may be congenital or it may develop in the first few years of life...
) - Eye defects
- Low birth weight
- Thrombocytopenic purpuraThrombocytopenic purpuraThrombocytopenic purpura are purpura associated with a reduction in circulating blood platelets which can result from a variety of causes.- Types :...
(presents as a characteristic blueberry muffin rashBlueberry muffin babyBlueberry muffin baby is a term used to describe the characteristic distributed purpura due to extramedullary hematopoiesis found in infants.It was originally considered characteristic of rubella, but is now considered to be potentially associated with many other conditions, such as cytomegalovirus...
) - HepatomegalyHepatomegalyHepatomegaly is the condition of having an enlarged liver. It is a nonspecific medical sign having many causes, which can broadly be broken down into infection, direct toxicity, hepatic tumours, or metabolic disorder. Often, hepatomegaly will present as an abdominal mass...
- Micrognathia
Children who have been exposed to rubella in the womb should also be watched closely as they age for any indication of the following:
- Developmental delay
- Autism spectrum disordersAutism spectrumThe term "autism spectrum" is often used to describe disorders that are currently classified as pervasive developmental disorders. Pervasive developmental disorders include autism, Asperger syndrome, Childhood disintegrative disorder, Rett syndrome and Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise...
- SchizophreniaSchizophreniaSchizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social...
- Growth retardation
- Learning disabilitiesLearning disabilityLearning disability is a classification including several disorders in which a person has difficulty learning in a typical manner, usually caused by an unknown factor or factors...
- Diabetes
- GlaucomaGlaucomaGlaucoma is an eye disorder in which the optic nerve suffers damage, permanently damaging vision in the affected eye and progressing to complete blindness if untreated. It is often, but not always, associated with increased pressure of the fluid in the eye...

