
Continental Portugal
Encyclopedia
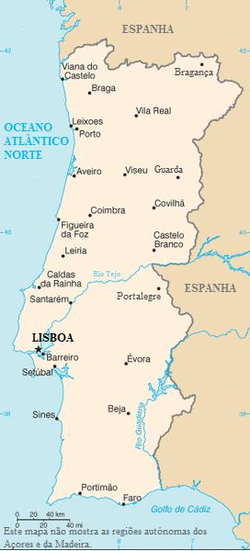
Mainland
Mainland is a name given to a large landmass in a region , or to the largest of a group of islands in an archipelago. Sometimes its residents are called "Mainlanders"...
Portuguese
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
territory, located on Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
's Iberian Peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
.
The designation is sometimes used to differentiate the continental
Continental Europe
Continental Europe, also referred to as mainland Europe or simply the Continent, is the continent of Europe, explicitly excluding European islands....
territory of Portugal (also known as The Continent - O Continente) from the insular territory of Portugal. The latter is composed by the Madeira
Madeira
Madeira is a Portuguese archipelago that lies between and , just under 400 km north of Tenerife, Canary Islands, in the north Atlantic Ocean and an outermost region of the European Union...
and Azores
Azores
The Archipelago of the Azores is composed of nine volcanic islands situated in the middle of the North Atlantic Ocean, and is located about west from Lisbon and about east from the east coast of North America. The islands, and their economic exclusion zone, form the Autonomous Region of the...
archipelagos in the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
. It is also a NUTS I
Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics
The Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics or Nomenclature of Units for Territorial Statistics is a geocode standard for referencing the subdivisions of countries for statistical purposes...
division (see administrative divisions of Portugal: NUTS for details). While in modern Portugal the difference between continental and total territory is not significant (in terms of area), it mattered during the existence of the Portuguese Empire
Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire , also known as the Portuguese Overseas Empire or the Portuguese Colonial Empire , was the first global empire in history...
, when this terminology was used.
The Azores and Madeira archipelagos are also commonly referred to as The Autonomous Regions
Autonomous regions of Portugal
The two Autonomous Regions of Portugal are the Azores and Madeira...
(As Regiões Autónomas), Insular Portugal (Portugal Insular) or simply The Islands (As Ilhas).
Mainland Portugal has 89,015 km² or 96.6% of the national territory of 92,145 km² and 10,041,813 inhabitants or 95.1% of the total population of 10,555,853.
See also
- PortugalPortugalPortugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
- Mainland Portugal
- Regions of Portugal
- Autonomous regions of PortugalAutonomous regions of PortugalThe two Autonomous Regions of Portugal are the Azores and Madeira...
- AzoresAzoresThe Archipelago of the Azores is composed of nine volcanic islands situated in the middle of the North Atlantic Ocean, and is located about west from Lisbon and about east from the east coast of North America. The islands, and their economic exclusion zone, form the Autonomous Region of the...
- MadeiraMadeiraMadeira is a Portuguese archipelago that lies between and , just under 400 km north of Tenerife, Canary Islands, in the north Atlantic Ocean and an outermost region of the European Union...
- Azores
- Portugal's Exclusive Economic ZonePortugal's Exclusive Economic ZonePortugal has the 3rd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of the EU and the 20th largest EEZ in the world, at 1,727,408 km2.-Portugal's Exclusive Economic Zone:*Continental Portugal 327,667 km2*Azores Islands 953,633 km2...

