
Cophasing
Encyclopedia
In astronomy, the term cophasing or phasing describes the process of controlling the individual segments in a segmented mirror
or a telescope so that the segments form a larger composite mirroring surface. Cophasing implies precise, active control of three degrees of freedom
of each individual segment mirror: translation along the optical axis
(piston) and rotation about two axes perpendicular to the optical axis (tip-tilt).
Each segment of the segmented telescope
is a solid body having 6 degrees of freedom exposed to the gravitation force
, wind blowing, and other mechanical forces. If the position of each segment is not controlled the resolution
of the whole telescope will be the same as if telescope had the diameter equal to the size of one segment. To achieve a resolution commensurable with that of a monolithic telescope of the same diameter the segmented surface must be controlled with a precision better than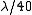 surface rms.
surface rms.
Projects for future extremely large telescope
s (ELTs) generally depend on the use of a segmented primary mirror. While the basic technologies required for segmented telescopes have been demonstrated for the 10m Keck telescope or GTC telescope
, ELTs of diameters form 50 to 100 m represent a qualitative change with respect to wave front control related to segmentation in comparison with the current 10 meters technology.
Segmented mirror
A segmented mirror is an array of smaller mirrors designed to act as segments of a single large curved mirror. The segments can be either spherical or asymmetric . They are used as objectives for large reflecting telescopes...
or a telescope so that the segments form a larger composite mirroring surface. Cophasing implies precise, active control of three degrees of freedom
Degrees of freedom
Degrees of freedom can mean:* Degrees of freedom , independent displacements and/or rotations that specify the orientation of the body or system...
of each individual segment mirror: translation along the optical axis
Optical axis
An optical axis is a line along which there is some degree of rotational symmetry in an optical system such as a camera lens or microscope.The optical axis is an imaginary line that defines the path along which light propagates through the system...
(piston) and rotation about two axes perpendicular to the optical axis (tip-tilt).
Each segment of the segmented telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
is a solid body having 6 degrees of freedom exposed to the gravitation force
Newton's law of universal gravitation
Newton's law of universal gravitation states that every point mass in the universe attracts every other point mass with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them...
, wind blowing, and other mechanical forces. If the position of each segment is not controlled the resolution
Optical resolution
Optical resolution describes the ability of an imaging system to resolve detail in the object that is being imaged.An imaging system may have many individual components including a lens and recording and display components...
of the whole telescope will be the same as if telescope had the diameter equal to the size of one segment. To achieve a resolution commensurable with that of a monolithic telescope of the same diameter the segmented surface must be controlled with a precision better than
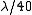 surface rms.
surface rms.Projects for future extremely large telescope
Extremely large telescope
An extremely large telescope is an astronomical observatory featuring a telescope with an aperture of more than 20 m diameter when discussing reflecting telescopes of optical wavelengths including ultraviolet , visible, and near infrared wavelengths. Among many planned capabilities, ELTs are...
s (ELTs) generally depend on the use of a segmented primary mirror. While the basic technologies required for segmented telescopes have been demonstrated for the 10m Keck telescope or GTC telescope
Gran Telescopio Canarias
The Gran Telescopio Canarias , also known as GranTeCan or GTC, is a reflecting telescope undertaking commissioning observations at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on the island of La Palma, in the Canary Islands of Spain, as of July 2009.Construction of the telescope, sited on a volcanic...
, ELTs of diameters form 50 to 100 m represent a qualitative change with respect to wave front control related to segmentation in comparison with the current 10 meters technology.

