
Corculum cardissa
Encyclopedia
Corculum cardissa or the heart cockle is a species
of marine bivalve
mollusc
in the family
Cardiidae. It is found in the Indo-Pacific
region. It has a symbiotic
relationship with dinoflagellate
s (zooxanthella
e), which live within its tissues.
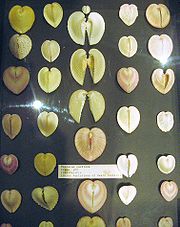
of Corculum cardissa are unequal in size and often asymmetric. Their shape is very variable but viewed from above, the outline is roughly heart shaped which gives the molluscs their common name. Viewed from the side the shape bears a resemblance to the shell of a cockle (Cerastoderma
spp.). In some specimens the posterior valve is nearly flat or has a slight hump. In others it is more rounded.
The boundary of the valves is usually flat but is sometimes somewhat sinuous
. Smaller shells tend to be elongated; larger shells are more rounded and the growth rings can be seen clearly. The shell is thin and translucent, particularly the upper side. There is an intricate mosaic pattern of more and less transparent white regions. The lower valve has a mainly white surface with a few transparent regions. The gill
s and mantle
, especially the lower siphon, are dark brown owing to the presence of microscopic algae. The outer surface of the mantle also contains granules of reddish, purple and blue pigment.
algae and muddy deposits.
 Corculum cardissa is a filter feeder
Corculum cardissa is a filter feeder
. The shell gapes slightly at the ventral end and two siphons are protruded. Water is drawn in through one and expelled through the other and plankton
and detritus
are extracted. At the same time, water passes over the gills where oxygen is absorbed.
Corculum cardissa is a hermaphrodite
. Eggs
are laid and the larva
e develop with great rapidity. Within 24 hours of fertilisation, the veliger
larvae have been observed to develop two valves and be swimming on the surface of the substrate. A day later, they had undergone metamorphosis
and had settled on the bottom as juveniles, miniature versions of the adult bivalves.
Symbiodinium. These are found in the mantle, gills and the liver. It was originally thought that the photosynthetic algae
were in the haemocoel, the fluid between the cells. It has since been found however that, in response to the presence of Symbiodinium, a tertiary series of tubules develop from the walls of the digestive system and ramify through the tissues. The algae are found in these and are separated from the blood cells in the haemolymph by a layer one cell thick. This is analogous to the tertiary tubular system found in Tridacna
and first described by Mansour in 1946, but subsequently overlooked by other researchers. The algae enter the system through the mouth. The translucent shell and the bivalve's habit of lying on the surface both encourage photosynthesis in the algae. The mollusc benefits from the metabolites produced and the alga benefits from a safe environment in which to live.
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
of marine bivalve
Bivalvia
Bivalvia is a taxonomic class of marine and freshwater molluscs. This class includes clams, oysters, mussels, scallops, and many other families of molluscs that have two hinged shells...
mollusc
Mollusca
The Mollusca , common name molluscs or mollusksSpelled mollusks in the USA, see reasons given in Rosenberg's ; for the spelling mollusc see the reasons given by , is a large phylum of invertebrate animals. There are around 85,000 recognized extant species of molluscs. Mollusca is the largest...
in the family
Family (biology)
In biological classification, family is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, genus, and species, with family fitting between order and genus. As for the other well-known ranks, there is the option of an immediately lower rank, indicated by the...
Cardiidae. It is found in the Indo-Pacific
Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a biogeographic region of the Earth's seas, comprising the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the seas connecting the two in the general area of Indonesia...
region. It has a symbiotic
Symbiosis
Symbiosis is close and often long-term interaction between different biological species. In 1877 Bennett used the word symbiosis to describe the mutualistic relationship in lichens...
relationship with dinoflagellate
Dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates are a large group of flagellate protists. Most are marine plankton, but they are common in fresh water habitats as well. Their populations are distributed depending on temperature, salinity, or depth...
s (zooxanthella
Zooxanthella
Zooxanthellae are flagellate protozoa that are golden-brown intracellular endosymbionts of various marine animals and protozoa, especially anthozoans such as the scleractinian corals and the tropical sea anemone, Aiptasia....
e), which live within its tissues.
Description
The two valvesBivalve shell
A bivalve shell is part of the body, the exoskeleton or shell, of a bivalve mollusk. In life, the shell of this class of mollusks is composed of two parts, two valves which are hinged together...
of Corculum cardissa are unequal in size and often asymmetric. Their shape is very variable but viewed from above, the outline is roughly heart shaped which gives the molluscs their common name. Viewed from the side the shape bears a resemblance to the shell of a cockle (Cerastoderma
Cerastoderma
Cerastoderma is a genus of marine bivalves, which includes the common cockle C. edule.-Species:Extant and fossil species include:* Cerastoderma edule - common cockle...
spp.). In some specimens the posterior valve is nearly flat or has a slight hump. In others it is more rounded.
The boundary of the valves is usually flat but is sometimes somewhat sinuous
Sinuous
Sinuous is a fictional snake from the third season of the animated children's television series The Animals of Farthing Wood based upon the books of the same name by author Colin Dann....
. Smaller shells tend to be elongated; larger shells are more rounded and the growth rings can be seen clearly. The shell is thin and translucent, particularly the upper side. There is an intricate mosaic pattern of more and less transparent white regions. The lower valve has a mainly white surface with a few transparent regions. The gill
Gill
A gill is a respiratory organ found in many aquatic organisms that extracts dissolved oxygen from water, afterward excreting carbon dioxide. The gills of some species such as hermit crabs have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist...
s and mantle
Mantle (mollusc)
The mantle is a significant part of the anatomy of molluscs: it is the dorsal body wall which covers the visceral mass and usually protrudes in the form of flaps well beyond the visceral mass itself.In many, but by no means all, species of molluscs, the epidermis of the mantle secretes...
, especially the lower siphon, are dark brown owing to the presence of microscopic algae. The outer surface of the mantle also contains granules of reddish, purple and blue pigment.
Habitat
Corculum cardissa is often found lying on a surface of sand among coral debris and broken shells. It usually lies horizontally in a hollow it excavates and its top is often covered with filamentousFilamentation
Filamentation is the anomalous growth of certain bacteria, such as E. coli, in which cells continue to elongate but do not divide . Bacterial filamentation is often observed as a result of bacteria responding to various stresses, including DNA damage or inhibition of replication...
algae and muddy deposits.
Biology

Filter feeder
Filter feeders are animals that feed by straining suspended matter and food particles from water, typically by passing the water over a specialized filtering structure. Some animals that use this method of feeding are clams, krill, sponges, baleen whales, and many fish and some sharks. Some birds,...
. The shell gapes slightly at the ventral end and two siphons are protruded. Water is drawn in through one and expelled through the other and plankton
Plankton
Plankton are any drifting organisms that inhabit the pelagic zone of oceans, seas, or bodies of fresh water. That is, plankton are defined by their ecological niche rather than phylogenetic or taxonomic classification...
and detritus
Detritus
Detritus is a biological term used to describe dead or waste organic material.Detritus may also refer to:* Detritus , a geological term used to describe the particles of rock produced by weathering...
are extracted. At the same time, water passes over the gills where oxygen is absorbed.
Corculum cardissa is a hermaphrodite
Hermaphrodite
In biology, a hermaphrodite is an organism that has reproductive organs normally associated with both male and female sexes.Many taxonomic groups of animals do not have separate sexes. In these groups, hermaphroditism is a normal condition, enabling a form of sexual reproduction in which both...
. Eggs
Egg (biology)
An egg is an organic vessel in which an embryo first begins to develop. In most birds, reptiles, insects, molluscs, fish, and monotremes, an egg is the zygote, resulting from fertilization of the ovum, which is expelled from the body and permitted to develop outside the body until the developing...
are laid and the larva
Larva
A larva is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle...
e develop with great rapidity. Within 24 hours of fertilisation, the veliger
Veliger
A veliger is the planktonic larva of many kinds of marine and freshwater gastropod molluscs, as well as most bivalve mollusks.- Description :...
larvae have been observed to develop two valves and be swimming on the surface of the substrate. A day later, they had undergone metamorphosis
Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops after birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation...
and had settled on the bottom as juveniles, miniature versions of the adult bivalves.
Ecology
Corculum cardissa and some other members of the family Cardiidae live in symbiosis with dinoflagellates in the genusGenus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
Symbiodinium. These are found in the mantle, gills and the liver. It was originally thought that the photosynthetic algae
Algae
Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many...
were in the haemocoel, the fluid between the cells. It has since been found however that, in response to the presence of Symbiodinium, a tertiary series of tubules develop from the walls of the digestive system and ramify through the tissues. The algae are found in these and are separated from the blood cells in the haemolymph by a layer one cell thick. This is analogous to the tertiary tubular system found in Tridacna
Tridacna
Tridacna is a genus of large and gigantic saltwater clams, marine bivalve mollusks in the subfamily Tridacninae, the giant clams. They have heavy shells, fluted with 4–6 folds. Mantle is brightly coloured. They inhabit shallow waters of coral reefs in warm seas of the Indo-Pacific region...
and first described by Mansour in 1946, but subsequently overlooked by other researchers. The algae enter the system through the mouth. The translucent shell and the bivalve's habit of lying on the surface both encourage photosynthesis in the algae. The mollusc benefits from the metabolites produced and the alga benefits from a safe environment in which to live.

