
Cortex (botany)
Encyclopedia
Botany
Botany, plant science, or plant biology is a branch of biology that involves the scientific study of plant life. Traditionally, botany also included the study of fungi, algae and viruses...
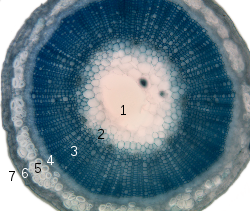
, the cortex is the outer layer of the stem
Plant stem
A stem is one of two main structural axes of a vascular plant. The stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes, the nodes hold buds which grow into one or more leaves, inflorescence , conifer cones, roots, other stems etc. The internodes distance one node from another...
or root
Root
In vascular plants, the root is the organ of a plant that typically lies below the surface of the soil. This is not always the case, however, since a root can also be aerial or aerating . Furthermore, a stem normally occurring below ground is not exceptional either...
of a plant, bounded on the outside by the epidermis
Epidermis (botany)
The epidermis is a single-layered group of cells that covers plants' leaves, flowers, roots and stems. It forms a boundary between the plant and the external environment. The epidermis serves several functions, it protects against water loss, regulates gas exchange, secretes metabolic compounds,...
and on the inside by the endodermis
Endodermis
The endodermis is the central, innermost layer of cortex in some land plants. It is made of compact living cells surrounded by an outer ring of endodermal cells that are impregnated with hydrophobic substances to restrict apoplastic flow of water to the inside...
. It is composed mostly of undifferentiated cells, usually large thin-walled parenchyma
Parenchyma
Parenchyma is a term used to describe a bulk of a substance. It is used in different ways in animals and in plants.The term is New Latin, f. Greek παρέγχυμα - parenkhuma, "visceral flesh", f. παρεγχεῖν - parenkhein, "to pour in" f. para-, "beside" + en-, "in" + khein, "to pour"...
cells of the ground tissue
Ground tissue
The types of ground tissue found in plants develop from ground tissue meristem and consists of three simple tissues:* Parenchyma...
system. The outer cortical cells often acquire irregularly thickened cell walls, and are called collenchyma cells. Some of the outer cortical cells may contain chloroplast
Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that conduct photosynthesis. Chloroplasts capture light energy to conserve free energy in the form of ATP and reduce NADP to NADPH through a complex set of processes called photosynthesis.Chloroplasts are green...
s. It is responsible for the transportation of materials into the central cylinder of the root through diffusion and may also be used for food storage in the form of starch.

