
Critical assumption planning
Encyclopedia
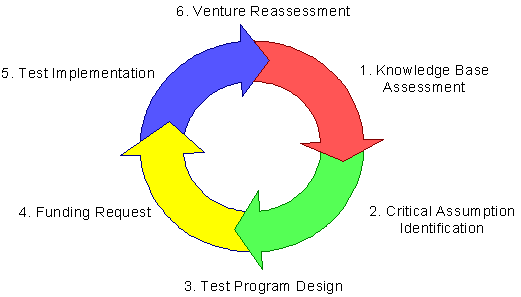
Critical assumption planning is a service mark of D. Dunham & Co and was described in Journal of Business Venturing by Sykes in 1995. Critical Assumption Planning (CAP) helps managers and entrepreneurs maximize business development learning at least cost. The continuous process consists of six steps: Knowledge Base Assessment, Critical Assumption Planning, Test Program Design, Funding Request, Test Implementation and Venture Reassessment.
CAP involves six steps, combined in a "Learning Loop". Once all six steps are completed, a milestone is reached and the loop starts over again. The loop is constantly repeated as the business is developing.
to check are the definition of the business concept and an assessment of the competition.
In order to determine the criticality of the assumptions, they need to be quantified; it is then possible to put the financial results in a spreadsheet
and link them together. These financial impacts will change for the various assumptions.
CAP measures the criticality of an assumption as a change in the net present value
of a venture (NPV). To determine criticality each assumption is assigned a range of uncertainty: base case, best and worst case. Then, assumption for assumption, while keeping the other assumptions at base case
, the NPV changes for each assumption in the worst and best case scenarios are checked.
The NPV analysis proves the company with information about the criticality of an assumption. Two signals strongly indicate a critical assumption: a big difference in NPV between the best and worst-case scenarios, or a huge loss of NPV in the worst-case scenario
other times a working prototype needs to be developed. The order in which the assumptions are tested is critical in terms of the money spent on testing. One
of the major focuses of the CAP method is to maximize the learning per unit expenditure on testing.
In order to determine the best testing option the test Effectiveness ratio (e)
is calculated for one or more assumptions based on the estimated Costs (C), Time spend on testing (T) and the estimated reduction (R) between the NPV values of the assumptions (P as a percentage of the NPV range). Using these parameters, the effectiveness ratio (e) is calculated:
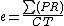
Once the best testing option is chosen from the different test effectiveness values, the organisation can finish the planning of the test.
Australian CAP Case Study
Overview
CAP is built on the foundation of the work of Block (1989) who showed that assumptions can stand in the way of perceiving current business realities. The identification and assessment of assumptions solves this problem and forms the foundation for managing new business ventures.CAP involves six steps, combined in a "Learning Loop". Once all six steps are completed, a milestone is reached and the loop starts over again. The loop is constantly repeated as the business is developing.

Knowledge-base assessment
This step takes "a comprehensive analysis of what is known and unknown about the competition, market and technology" (Sykes 1995). In this step the entrepreneur oversees his plans and the first assumptions are exposed. Important parts of the business planBusiness plan
A business plan is a formal statement of a set of business goals, the reasons why they are believed attainable, and the plan for reaching those goals. It may also contain background information about the organization or team attempting to reach those goals....
to check are the definition of the business concept and an assessment of the competition.
Critical assumption identification
During this step the assumptions are identified and there is a determination of criticality. The hardest part of CAP is to identify the assumptions that are not written down.In order to determine the criticality of the assumptions, they need to be quantified; it is then possible to put the financial results in a spreadsheet
Spreadsheet
A spreadsheet is a computer application that simulates a paper accounting worksheet. It displays multiple cells usually in a two-dimensional matrix or grid consisting of rows and columns. Each cell contains alphanumeric text, numeric values or formulas...
and link them together. These financial impacts will change for the various assumptions.
CAP measures the criticality of an assumption as a change in the net present value
Net present value
In finance, the net present value or net present worth of a time series of cash flows, both incoming and outgoing, is defined as the sum of the present values of the individual cash flows of the same entity...
of a venture (NPV). To determine criticality each assumption is assigned a range of uncertainty: base case, best and worst case. Then, assumption for assumption, while keeping the other assumptions at base case
Ceteris paribus
or is a Latin phrase, literally translated as "with other things the same," or "all other things being equal or held constant." It is an example of an ablative absolute and is commonly rendered in English as "all other things being equal." A prediction, or a statement about causal or logical...
, the NPV changes for each assumption in the worst and best case scenarios are checked.
The NPV analysis proves the company with information about the criticality of an assumption. Two signals strongly indicate a critical assumption: a big difference in NPV between the best and worst-case scenarios, or a huge loss of NPV in the worst-case scenario
Test program design
The assumptions need to be tested. Sometimes good market research is enough,other times a working prototype needs to be developed. The order in which the assumptions are tested is critical in terms of the money spent on testing. One
of the major focuses of the CAP method is to maximize the learning per unit expenditure on testing.
In order to determine the best testing option the test Effectiveness ratio (e)
is calculated for one or more assumptions based on the estimated Costs (C), Time spend on testing (T) and the estimated reduction (R) between the NPV values of the assumptions (P as a percentage of the NPV range). Using these parameters, the effectiveness ratio (e) is calculated:
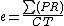
Once the best testing option is chosen from the different test effectiveness values, the organisation can finish the planning of the test.
Funding request
When the test program design is ready and the costs are clear, resources have to be allocated to the test program. In most companies or start-ups clearance from senior managers or venture capitalists is needed to conduct the tests.Venture Reassessment
When the results of one or more tests are known, it might be that resources need to be re-allocated and business plans have to be updated.See also
- Assumption-based planning
Australian CAP Case Study

