
Cromwell tank
Encyclopedia
Tank, Cruiser, Mk VIII, Cromwell (A27M),The designation as the eighth Cruiser tank design, its name given for ease of reference and its General Staff specification number respectively and the related Centaur tank, were one of the most successful series of cruiser tank
s fielded by Britain
in the Second World War. The Cromwell tank, named after the English Civil War
leader Oliver Cromwell
, was the first tank in the British arsenal to combine a dual-purpose gun, high speed from the powerful and reliable Meteor
engine, and reasonable armour
, all in one balanced package. Its design formed the basis of the Comet tank
.
The Cromwell first saw action in the Battle of Normandy
in June 1944. The tank equipped the armoured reconnaissance regiments, of the Royal Armoured Corps
, within the 7th, 11th, and Guards Armoured Divisions. While the armour regiments of the latter two divisions were equipped with M4 Shermans, the armour regiments of the 7th Armour was fully equipped with Cromwell tanks.
, which although not yet in service would become obsolete in time. In late 1940, the General Staff
set out the specifications for the new tank, and designs were submitted in early 1941. The tank would be fitted with the QF 6 pounder
gun with the expectation that it would enter service in 1942.
Due to the typical rushed production and lack of components, the A24 Cavalier
, then known as "Cromwell I", built by Nuffield had far too many problems to see active combat service. One of the key problems was that its Nuffield-built
Liberty engine was simply not up to the task. It had been ordered as it was based on tried equipment and therefore should have entered service with minimal delay.
Leyland and Birmingham Railway Carriage & Wagon
had been involved in the development and had offered similar designs to Nuffield.
A second specification for a better tank was the General Staff A27. The tank would be fitted with the QF 6 pounder gun with the expectation that it would enter service in 1942. Once it became clear there would be delays, a programme was set in place to fit the 6 pounder to the Crusader to get some 6 pounder tanks in service.
At the same time, a new engine was designed to be a tank powerplant. The Meteor engine was based on the powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin
engine used in aircraft such as the Spitfire
. Rolls-Royce, Leyland and BRC&W produced a prototype by January 1942 based on the Crusader but using the Meteor. With nearly 600 hp it proved to be exceptionally mobile when trialled. Leyland were lined up to produce the Meteor but withdrew in mid-1941 as they had doubts about being able to provide sufficient cooling. Rolls-Royce
, the makers of the Merlin, were already fully committed to manufacturing the Merlin and could not spare the facilities for the Meteor, and so manufacture was passed to the Rover Car Company
.
The General staff issued new specifications to cover the tanks. The BRC&W design using the Meteor was A27M (or "Cromwell III") and Leyland's version of it to take the Liberty was A27L ("Cromwell II"). Nuffields A24 with the Liberty was the Cromwell II. The naming was reworked in November 1942 with the A27L as Centaur, A27M as Cromwell and A24 as Cavalier.
Production began in November 1942. It would take considerable time for Rover to make ready production lines for the Meteor, and it was not until a few months later, in January 1943, that sufficient Meteor engines were available and the A27M Cromwell began production. The Centaur production design allowed for the later conversion to the Meteor engine and many Centaurs would be converted to Cromwells before use.
and English Electric
Some variants were produced with 14 inches (355.6 mm) tracks, later 15.5-inch tracks were used.
The suspension was of the Christie type
with long helical springs (in tension) angled back to keep the hull sides low. Of the five roadwheels each side, four had shock absorbers. The tracks were driven by sprocketed wheels at the rear and tension adjusted at the front idler; this being standard British practice. The side of the hull was made up of two spaced plates, the suspension units between them, and the outer plate having cutouts for the movement of the roadwheel axles. The gearbox had five forward and one reverse gears. The first gear was for "confined spaces, on steep inclines or...sharp turns"
The Meteor engine delivered 540 hp at 2,250 rpm. This was the maximum rpm which was limited by governors built into the magnetos. Fuel consumption on "pool" petrol (67 octane) was between 0.5 and 1.5 miles per gallon depending on terrain.
The driver was sat on the right in the front of the hull, separated from the hull gunner by a bulkhead. The driver had two periscopes and a visor in the hull front. The visor could be opened fully or a small "gate" in it opened; in the latter case a thick glass block protected the driver.
A bulkhead with access holes separated the driver and hull gunner from the fighting compartment. A further bulkhead separated the fighting compartment from the engine and transmission bay. The engine compartment drew cooling air in through the top of each side and the roof and exhausted it to the rear. To allow fording through up to 4 ft (1.2 m) deep water a flap could be moved over to cover the lowermost air outlet. Air for the engine could be drawn from the fighting compartment or the exterior; it was then passed through oil bath cleaners.
The Cromwell still had revisions to make before service, most notably changing from the QF 6-pounder
(57 mm) to the ROQF 75 mm
gun, which was an adaptation of the 6 pounder design to fire the ammunition of the US M3 75 mm gun, which gave it a better HE round to use in infantry support. This meant the 75 would use the same mounting as the 6 pounder however it was not until June 1944 that Cromwell first saw action during Operation Overlord
, the Allied
invasion of Normandy. It had a mixed reception by crews. It was faster and had a lower profile than the Sherman tank and thicker frontal armor; 3 inches (76mm) versus the 2 inches (51mm) of the Sherman. On later Cromwells this was increased incrementally, first to 3 1/4 inches (82mm), then finally to 4 inches (102mm). The 75 mm gun, though able to fire a useful HE shell, was not as effective against armour as the 6 pdr or the Ordnance QF 17 pounder gun though it was more powerful than the original 75 mm gun mounted on the Sherman. A derivative of Cromwell was begun to take the 17 pounder, this fell behind and in practice the majority of the 17 pounder gun armed tanks to see service in the war were Firefly variant of the Sherman
.
There was a 7.92 mm Besa machine gun
mounted coaxially to the main armament operated by the gunner. A second was "gimbal" mounted in the front of the hull. The mounting gave 45 degress of coverage to the front (it had 25 degrees of vertical movement as well) and sighting was by a No. 35 telescope which was connected through a linkage to the mounting.
In the top of the turret was mounted a 2 inch "bombthrower" angled to fire forward. Thirty smoke grenade
s were carried for it.
 The Centaur was chiefly used for training; only those in specialist roles saw action. The Close Support version of the Centaur with a 95 mm howitzer replacing the 75mm saw service in small numbers as part of the Royal Marine Armoured Support Group on D-Day
The Centaur was chiefly used for training; only those in specialist roles saw action. The Close Support version of the Centaur with a 95 mm howitzer replacing the 75mm saw service in small numbers as part of the Royal Marine Armoured Support Group on D-Day
, and a number were used as the basis for combat engineering vehicles such as an armoured bulldozer.
The Sherman remained the most common tank in British and Commonwealth armoured units. Cromwells were used to fully equip only one division, the 7th Armoured Division. The Cromwell was also used as the main tank in the armoured reconnaissance regiments of British armoured divisions, in North West Europe, because of its great speed. The Cromwell in turn was succeeded by small numbers of the Comet tank
. Although the Comet was similar to the Cromwell, and shared some components, it was a much better tank with the 77 mm gun (a version of the 17 pounder)
In general the Cromwell was found to be very reliable with remarkable speed and manoevrability though it required more maintenance than the Sherman.
The Cromwell was given a modification to the exhaust to direct the fumes so that they were not drawn into the fighting compartment - a problem found when tanks were drawn up together preparing for the advance.
In Northern Europe, the Cromwell was used by Allied units of the 1st Polish Armoured Division and Czech Armoured Brigade.
After the war, the Cromwell remained in British service. It saw service in the Korean War
with 7 RTR and 8th King's Royal Irish Hussars
It was also used by Finland
(Charioteer version).
and the engine was governed to give a top speed of 32 mph (51.5 km/h), which was still fast for its time. Thanks to its Christie parentage the Cromwell was very agile on the battlefield. The dual purpose 75 mm main gun fired the same ammunition as the US 75 mm gun and therefore it had around the same HE and armour-piercing capabilities as the 75 mm equipped Sherman tank. The armour on the Cromwell ranged from 8 mm up to 76 mm thick overall. However, on all-welded vehicles built by BRCW Co. Ltd
, the weight saved by the welding allowed for the fitting of appliqué armour plates on the nose, vertical drivers' plate and turret front, increasing the maximum thickness to 102 mm. In period photos, these vehicles are identified by their War Department numbers carrying the suffix W, i.e. T121710W. This armour compared well with that of the Sherman although the Cromwell did not share the Sherman’s sloped glacis plate. The Cromwell crews in North-West Europe succeeded in outflanking the heavier and more sluggish German tanks with superior speed, manoeuvrability and reliability. However, the Cromwell was still not a match for the best German armour and British tank design would go through another stage, the Comet tank
, before going ahead in the tank development race with the Centurion tank
.
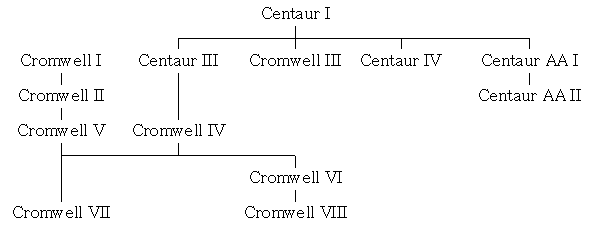
The modifications and developments of the Cromwell were classified under "Type" and "Mark". A single Mark could cover up to four Types and a Type up to six Marks making classification complex.
The Types ran from A (the earliest Cavaliers, Centaurs and Cromwells) to F (a late model Cromwell with driver's side escape hatch).
Centaur I: First draft. Armed with the Royal Ordnance QF 6 pounder
(57 mm) gun (with 64 rounds of ammunition). It was used only for training. 1,059 produced.
Porpoise was also used by the M7 Priest 105 mm howitzers.
Centaur II: Mark I with wider tracks and no hull machine gun. Experimental only.
Centaur III: Centaur armed with the 75 mm ROQF Mk V
gun. In 1943, most Centaur I's were converted to III's, but a few remained as such. 233 produced.
Centaur IV: Centaur armed with a 95 mm howitzer (with 51 rounds of ammunition). This is the only version of the Centaur known to have seen combat, in service with the Royal Marines
Armoured Support Group
. The vehicles were fitted with wading gear to get them ashore. Trunking waterproofed the engine inlets and covers were fitted to the guns. 114 produced.
Centaur, AA Mk I: Used a Crusader III, Anti-Aircraft Mk II turret fitted with twin 20 mm Polsten guns
. Were originally deployed in Normandy, but withdrawn as unnecessary due to Allied air superiority. 95 were produced.
Centaur, AA Mk II: Used a Crusader III, AA Mk III turret with twin 20 mm Polsten AA guns
.
Cromwell I: Exactly the same as the Centaur I, but using the Meteor engine. Only 357 produced due to the switch from the 6 pounder (57 mm) to the 75 mm gun.
 Cromwell II: Increased track width and removal of the hull machine gun to increase stowage. None produced.
Cromwell II: Increased track width and removal of the hull machine gun to increase stowage. None produced.
Cromwell III: Centaur I upgraded with Meteor V12 engine. Only ~ 200 produced due to scarcity of Centaur I's.
Cromwell IV: Centaur I or III upgraded with Meteor engine, or built as such. The most numerous variant with over 1,935 units produced.
Cromwell IVw: Meteor engine, and all welded hull.
Cromwell Vw: Cromwell built from the start with the 75 mm gun and a welded instead of riveted hull.
Cromwell VI: Cromwell armed with 95 mm howitzer. 341 produced.
Cromwell VII: Cromwell IV and V upgraded with additional armour (101 mm to front), wider (15.5 inch) tracks, and additional gearbox. These were introduced very late in the war and did not see much in the way of combat. ~ 1,500 produced.
Cromwell VIIw: Cromwell Vw reworked to Cromwell VII standard, or built as new to that standard
Cromwell VIII: Cromwell VI reworked with same upgrades as VII.
 Tank, Cruiser, Challenger (A30)
Tank, Cruiser, Challenger (A30)
:The design combined lengthened Cromwell chassis and the 17-pounder
gun in a new turret.
SP 17pdr, A30 (Avenger): A version of the Challenger using a lighter open-topped turret.
Centaur Dozer: A Centaur with the turret removed and given a simple dozer blade operated by a winch. Since the winch passed over the top of the hull it was not possible to retain the turret. One of Hobart's Funnies
. 250 produced. (version pictured uses hydraulic controls)
Centaur Observation Post (OP): A Centaur with a dummy main gun, and extra radio telecommunications.
Centaur Kangaroo: A Centaur with turret removed to make space for passengers. (Few produced)
Centaur Armoured Recovery Vehicle
(ARV): A Centaur with turret removed, and replaced with winch
fitted instead, and an optional A-frame
.
Cromwell Command
Cromwell Observation Post
Cromwell Control
Excelsior tank: experimental design with elements of Infantry tank
as a possible replacement for Churchill tank
FV 4101 Charioteer: Cromwell hull with a QF 20 pounder gun
in a tall turret, designed in the 1950s. 200 produced.
and one owned by the Cobbaton Combat Collection in the United Kingdom, are in running condition.
Other examples include:
There are two surviving Centaur IV CS in Normandy, at Benouville near Pegasus Bridge
and at La Brèche d’Hermanville
Cruiser tank
The cruiser tank was a British tank concept of the inter-war period. This concept was the driving force behind several tank designs which saw action during the Second World War....
s fielded by Britain
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
in the Second World War. The Cromwell tank, named after the English Civil War
English Civil War
The English Civil War was a series of armed conflicts and political machinations between Parliamentarians and Royalists...
leader Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell was an English military and political leader who overthrew the English monarchy and temporarily turned England into a republican Commonwealth, and served as Lord Protector of England, Scotland, and Ireland....
, was the first tank in the British arsenal to combine a dual-purpose gun, high speed from the powerful and reliable Meteor
Rolls-Royce Meteor
The Rolls-Royce Meteor was a British tank engine of the Second World War.It was developed from the Rolls-Royce Merlin aero-engine by W. A. Robotham and his chassis design and development division at Belper, as they were not involved in aero-engine work...
engine, and reasonable armour
Vehicle armour
Military vehicles are commonly armoured to withstand the impact of shrapnel, bullets, missiles, or shells, protecting the personnel inside from enemy fire. Such vehicles include tanks, aircraft, and ships....
, all in one balanced package. Its design formed the basis of the Comet tank
Comet tank
The Tank, Cruiser, Comet I was a British cruiser tank that first saw use near the end of World War II. It was designed to provide greater anti-tank capability to Cromwell tank squadrons. It was armed with a 77mm HV, a derivative of the 17 pounder, with the result it was one of the few British...
.
The Cromwell first saw action in the Battle of Normandy
Battle of Normandy
The Invasion of Normandy was the invasion and establishment of Allied forces in Normandy, France, during Operation Overlord in World War II. It was the largest amphibious operation in history...
in June 1944. The tank equipped the armoured reconnaissance regiments, of the Royal Armoured Corps
Royal Armoured Corps
The Royal Armoured Corps is currently a collection of ten regular regiments, mostly converted from old horse cavalry regiments, and four Yeomanry regiments of the Territorial Army...
, within the 7th, 11th, and Guards Armoured Divisions. While the armour regiments of the latter two divisions were equipped with M4 Shermans, the armour regiments of the 7th Armour was fully equipped with Cromwell tanks.
Development
The Cromwell and the related Centaur were the product of further development of British cruiser tanks, and they were designed as the replacement for the Crusader tankCrusader tank
The Tank, Cruiser, Mk VI or A15 Crusader was one of the primary British cruiser tanks of the early part Second World War and perhaps the most important British tank of the North African Campaign...
, which although not yet in service would become obsolete in time. In late 1940, the General Staff
General Staff
A military staff, often referred to as General Staff, Army Staff, Navy Staff or Air Staff within the individual services, is a group of officers and enlisted personnel that provides a bi-directional flow of information between a commanding officer and subordinate military units...
set out the specifications for the new tank, and designs were submitted in early 1941. The tank would be fitted with the QF 6 pounder
Ordnance QF 6 pounder
The Ordnance Quick-Firing 6-pounder 7 cwt, or just 6 pounder, was a British 57 mm gun, their primary anti-tank gun during the middle of World War II, as well as the main armament for a number of armoured fighting vehicles...
gun with the expectation that it would enter service in 1942.
Due to the typical rushed production and lack of components, the A24 Cavalier
Cavalier tank
The Tank, Cruiser, Mk VII Cavalier was an unsuccessful design of British cruiser tank during World War II. It suffered from an underpowered engine, and problems because of the rush to design and build it.- Development :...
, then known as "Cromwell I", built by Nuffield had far too many problems to see active combat service. One of the key problems was that its Nuffield-built
Nuffield Organisation
The Nuffield Organisation was a vehicle manufacturing company in the United Kingdom. Named after its founder, William Morris, 1st Viscount Nuffield, it was formed in 1938 as the merger of Nuffield's Morris Motor Company , another of Nuffield's companies the MG Car Company and Riley.Morris Motors...
Liberty engine was simply not up to the task. It had been ordered as it was based on tried equipment and therefore should have entered service with minimal delay.
Leyland and Birmingham Railway Carriage & Wagon
Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company
The Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company was a railway locomotive and carriage builder, founded in Birmingham, England and, for most of its existence, located at nearby Smethwick, with the factory was divided by the boundary between the two places...
had been involved in the development and had offered similar designs to Nuffield.
A second specification for a better tank was the General Staff A27. The tank would be fitted with the QF 6 pounder gun with the expectation that it would enter service in 1942. Once it became clear there would be delays, a programme was set in place to fit the 6 pounder to the Crusader to get some 6 pounder tanks in service.
At the same time, a new engine was designed to be a tank powerplant. The Meteor engine was based on the powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin
Rolls-Royce Merlin
The Rolls-Royce Merlin is a British liquid-cooled, V-12, piston aero engine, of 27-litre capacity. Rolls-Royce Limited designed and built the engine which was initially known as the PV-12: the PV-12 became known as the Merlin following the company convention of naming its piston aero engines after...
engine used in aircraft such as the Spitfire
Supermarine Spitfire
The Supermarine Spitfire is a British single-seat fighter aircraft that was used by the Royal Air Force and many other Allied countries throughout the Second World War. The Spitfire continued to be used as a front line fighter and in secondary roles into the 1950s...
. Rolls-Royce, Leyland and BRC&W produced a prototype by January 1942 based on the Crusader but using the Meteor. With nearly 600 hp it proved to be exceptionally mobile when trialled. Leyland were lined up to produce the Meteor but withdrew in mid-1941 as they had doubts about being able to provide sufficient cooling. Rolls-Royce
Rolls-Royce Limited
Rolls-Royce Limited was a renowned British car and, from 1914 on, aero-engine manufacturing company founded by Charles Stewart Rolls and Henry Royce on 15 March 1906 as the result of a partnership formed in 1904....
, the makers of the Merlin, were already fully committed to manufacturing the Merlin and could not spare the facilities for the Meteor, and so manufacture was passed to the Rover Car Company
Rover (car)
The Rover Company is a former British car manufacturing company founded as Starley & Sutton Co. of Coventry in 1878. After developing the template for the modern bicycle with its Rover Safety Bicycle of 1885, the company moved into the automotive industry...
.
The General staff issued new specifications to cover the tanks. The BRC&W design using the Meteor was A27M (or "Cromwell III") and Leyland's version of it to take the Liberty was A27L ("Cromwell II"). Nuffields A24 with the Liberty was the Cromwell II. The naming was reworked in November 1942 with the A27L as Centaur, A27M as Cromwell and A24 as Cavalier.
Production began in November 1942. It would take considerable time for Rover to make ready production lines for the Meteor, and it was not until a few months later, in January 1943, that sufficient Meteor engines were available and the A27M Cromwell began production. The Centaur production design allowed for the later conversion to the Meteor engine and many Centaurs would be converted to Cromwells before use.
Design
The frame was of rivetted construction though welding was used later. The armour plate was then bolted to the frame; large bosses on the outside of the plate were used on the turret. Several British firms besides Leyland contributed to production of the Cromwell and Centaur including LMS Railway, Morris Motors, Metro-Cammell, Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon CompanyBirmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company
The Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company was a railway locomotive and carriage builder, founded in Birmingham, England and, for most of its existence, located at nearby Smethwick, with the factory was divided by the boundary between the two places...
and English Electric
English Electric
English Electric was a British industrial manufacturer. Founded in 1918, it initially specialised in industrial electric motors and transformers...
Some variants were produced with 14 inches (355.6 mm) tracks, later 15.5-inch tracks were used.
The suspension was of the Christie type
Christie suspension
The Christie suspension is a suspension system developed by American engineer Walter Christie for his tank designs. It allowed considerably longer movement than conventional leaf spring systems then in common use, which allowed his tanks to have considerably greater cross-country speed and a lower...
with long helical springs (in tension) angled back to keep the hull sides low. Of the five roadwheels each side, four had shock absorbers. The tracks were driven by sprocketed wheels at the rear and tension adjusted at the front idler; this being standard British practice. The side of the hull was made up of two spaced plates, the suspension units between them, and the outer plate having cutouts for the movement of the roadwheel axles. The gearbox had five forward and one reverse gears. The first gear was for "confined spaces, on steep inclines or...sharp turns"
The Meteor engine delivered 540 hp at 2,250 rpm. This was the maximum rpm which was limited by governors built into the magnetos. Fuel consumption on "pool" petrol (67 octane) was between 0.5 and 1.5 miles per gallon depending on terrain.
The driver was sat on the right in the front of the hull, separated from the hull gunner by a bulkhead. The driver had two periscopes and a visor in the hull front. The visor could be opened fully or a small "gate" in it opened; in the latter case a thick glass block protected the driver.
A bulkhead with access holes separated the driver and hull gunner from the fighting compartment. A further bulkhead separated the fighting compartment from the engine and transmission bay. The engine compartment drew cooling air in through the top of each side and the roof and exhausted it to the rear. To allow fording through up to 4 ft (1.2 m) deep water a flap could be moved over to cover the lowermost air outlet. Air for the engine could be drawn from the fighting compartment or the exterior; it was then passed through oil bath cleaners.
The Cromwell still had revisions to make before service, most notably changing from the QF 6-pounder
Ordnance QF 6 pounder
The Ordnance Quick-Firing 6-pounder 7 cwt, or just 6 pounder, was a British 57 mm gun, their primary anti-tank gun during the middle of World War II, as well as the main armament for a number of armoured fighting vehicles...
(57 mm) to the ROQF 75 mm
Ordnance QF 75 mm
The Ordnance QF 75 mm, abbreviated to OQF 75 mm, was a British tank-gun of the Second World War. It was used instead of the Ordnance QF 6 pounder , an anti-tank gun, to give better performance against infantry targets in a similar fashion to the 75 mm gun fitted to the American...
gun, which was an adaptation of the 6 pounder design to fire the ammunition of the US M3 75 mm gun, which gave it a better HE round to use in infantry support. This meant the 75 would use the same mounting as the 6 pounder however it was not until June 1944 that Cromwell first saw action during Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the code name for the Battle of Normandy, the operation that launched the invasion of German-occupied western Europe during World War II by Allied forces. The operation commenced on 6 June 1944 with the Normandy landings...
, the Allied
Allies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
invasion of Normandy. It had a mixed reception by crews. It was faster and had a lower profile than the Sherman tank and thicker frontal armor; 3 inches (76mm) versus the 2 inches (51mm) of the Sherman. On later Cromwells this was increased incrementally, first to 3 1/4 inches (82mm), then finally to 4 inches (102mm). The 75 mm gun, though able to fire a useful HE shell, was not as effective against armour as the 6 pdr or the Ordnance QF 17 pounder gun though it was more powerful than the original 75 mm gun mounted on the Sherman. A derivative of Cromwell was begun to take the 17 pounder, this fell behind and in practice the majority of the 17 pounder gun armed tanks to see service in the war were Firefly variant of the Sherman
Sherman Firefly
The Sherman Firefly was a World War II British variant of the American Sherman tank, fitted with the powerful British 17 pounder anti-tank gun as its main weapon...
.
There was a 7.92 mm Besa machine gun
Besa machine gun
The Besa Machine Gun was a British version of the Czechoslovak ZB-53 air-cooled, belt-fed machine-gun, which in the Czechoslovak army was marked as the TK vz. 37...
mounted coaxially to the main armament operated by the gunner. A second was "gimbal" mounted in the front of the hull. The mounting gave 45 degress of coverage to the front (it had 25 degrees of vertical movement as well) and sighting was by a No. 35 telescope which was connected through a linkage to the mounting.
In the top of the turret was mounted a 2 inch "bombthrower" angled to fire forward. Thirty smoke grenade
Smoke grenade
Smoke grenades are canister-type grenades used as ground-to-ground or ground-to-air signaling devices, target or landing zone marking devices, or as screening devices for unit movements. Smoke grenades are normally considered non-lethal, although incorrect use may cause death...
s were carried for it.
Production
Total A27 production consisted of 4,016 tanks; 950 of which were Centaurs and 3,066 Cromwells. In addition, 375 Centaur hulls were built to be fitted with an anti-aircraft gun turret; only 95 of these were completed.Combat service

D-Day
D-Day is a term often used in military parlance to denote the day on which a combat attack or operation is to be initiated. "D-Day" often represents a variable, designating the day upon which some significant event will occur or has occurred; see Military designation of days and hours for similar...
, and a number were used as the basis for combat engineering vehicles such as an armoured bulldozer.
The Sherman remained the most common tank in British and Commonwealth armoured units. Cromwells were used to fully equip only one division, the 7th Armoured Division. The Cromwell was also used as the main tank in the armoured reconnaissance regiments of British armoured divisions, in North West Europe, because of its great speed. The Cromwell in turn was succeeded by small numbers of the Comet tank
Comet tank
The Tank, Cruiser, Comet I was a British cruiser tank that first saw use near the end of World War II. It was designed to provide greater anti-tank capability to Cromwell tank squadrons. It was armed with a 77mm HV, a derivative of the 17 pounder, with the result it was one of the few British...
. Although the Comet was similar to the Cromwell, and shared some components, it was a much better tank with the 77 mm gun (a version of the 17 pounder)
In general the Cromwell was found to be very reliable with remarkable speed and manoevrability though it required more maintenance than the Sherman.
The Cromwell was given a modification to the exhaust to direct the fumes so that they were not drawn into the fighting compartment - a problem found when tanks were drawn up together preparing for the advance.
In Northern Europe, the Cromwell was used by Allied units of the 1st Polish Armoured Division and Czech Armoured Brigade.
After the war, the Cromwell remained in British service. It saw service in the Korean War
Korean War
The Korean War was a conventional war between South Korea, supported by the United Nations, and North Korea, supported by the People's Republic of China , with military material aid from the Soviet Union...
with 7 RTR and 8th King's Royal Irish Hussars
8th King's Royal Irish Hussars
The 8th King's Royal Irish Hussars was a cavalry regiment in the British Army, first raised in 1693. It saw service for three centuries, before being amalgamated into The Queen's Royal Irish Hussars in 1958....
It was also used by Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
(Charioteer version).
Performance
The Cromwell was the fastest British tank to serve in the Second World War , with a top (ungoverned) speed of 40 mph (64.4 km/h). However this speed proved too much for even the Christie suspensionChristie suspension
The Christie suspension is a suspension system developed by American engineer Walter Christie for his tank designs. It allowed considerably longer movement than conventional leaf spring systems then in common use, which allowed his tanks to have considerably greater cross-country speed and a lower...
and the engine was governed to give a top speed of 32 mph (51.5 km/h), which was still fast for its time. Thanks to its Christie parentage the Cromwell was very agile on the battlefield. The dual purpose 75 mm main gun fired the same ammunition as the US 75 mm gun and therefore it had around the same HE and armour-piercing capabilities as the 75 mm equipped Sherman tank. The armour on the Cromwell ranged from 8 mm up to 76 mm thick overall. However, on all-welded vehicles built by BRCW Co. Ltd
Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company
The Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company was a railway locomotive and carriage builder, founded in Birmingham, England and, for most of its existence, located at nearby Smethwick, with the factory was divided by the boundary between the two places...
, the weight saved by the welding allowed for the fitting of appliqué armour plates on the nose, vertical drivers' plate and turret front, increasing the maximum thickness to 102 mm. In period photos, these vehicles are identified by their War Department numbers carrying the suffix W, i.e. T121710W. This armour compared well with that of the Sherman although the Cromwell did not share the Sherman’s sloped glacis plate. The Cromwell crews in North-West Europe succeeded in outflanking the heavier and more sluggish German tanks with superior speed, manoeuvrability and reliability. However, the Cromwell was still not a match for the best German armour and British tank design would go through another stage, the Comet tank
Comet tank
The Tank, Cruiser, Comet I was a British cruiser tank that first saw use near the end of World War II. It was designed to provide greater anti-tank capability to Cromwell tank squadrons. It was armed with a 77mm HV, a derivative of the 17 pounder, with the result it was one of the few British...
, before going ahead in the tank development race with the Centurion tank
Centurion tank
The Centurion, introduced in 1945, was the primary British main battle tank of the post-World War II period. It was a successful tank design, with upgrades, for many decades...
.
Variants

The modifications and developments of the Cromwell were classified under "Type" and "Mark". A single Mark could cover up to four Types and a Type up to six Marks making classification complex.
The Types ran from A (the earliest Cavaliers, Centaurs and Cromwells) to F (a late model Cromwell with driver's side escape hatch).
Centaur I: First draft. Armed with the Royal Ordnance QF 6 pounder
Ordnance QF 6 pounder
The Ordnance Quick-Firing 6-pounder 7 cwt, or just 6 pounder, was a British 57 mm gun, their primary anti-tank gun during the middle of World War II, as well as the main armament for a number of armoured fighting vehicles...
(57 mm) gun (with 64 rounds of ammunition). It was used only for training. 1,059 produced.
Porpoise was also used by the M7 Priest 105 mm howitzers.
Centaur II: Mark I with wider tracks and no hull machine gun. Experimental only.
Centaur III: Centaur armed with the 75 mm ROQF Mk V
Ordnance QF 75 mm
The Ordnance QF 75 mm, abbreviated to OQF 75 mm, was a British tank-gun of the Second World War. It was used instead of the Ordnance QF 6 pounder , an anti-tank gun, to give better performance against infantry targets in a similar fashion to the 75 mm gun fitted to the American...
gun. In 1943, most Centaur I's were converted to III's, but a few remained as such. 233 produced.
Centaur IV: Centaur armed with a 95 mm howitzer (with 51 rounds of ammunition). This is the only version of the Centaur known to have seen combat, in service with the Royal Marines
Royal Marines
The Corps of Her Majesty's Royal Marines, commonly just referred to as the Royal Marines , are the marine corps and amphibious infantry of the United Kingdom and, along with the Royal Navy and Royal Fleet Auxiliary, form the Naval Service...
Armoured Support Group
Royal Marines Armoured Support Group
The current Royal Marines Armoured Support Group is an element of the Royal Marines which operates the Viking BvS 10, All Terrain Vehicle. It is the successor to the Royal Marines Armoured Support Company, and is in effect on permanent loan from operational command of 3 Commando Brigade to the...
. The vehicles were fitted with wading gear to get them ashore. Trunking waterproofed the engine inlets and covers were fitted to the guns. 114 produced.
Centaur, AA Mk I: Used a Crusader III, Anti-Aircraft Mk II turret fitted with twin 20 mm Polsten guns
Polsten
The Polsten was a low cost Polish development of the 20 mm Oerlikon gun. The Polsten was designed to be simpler and much cheaper to build than the Oerlikon without reducing effectiveness.-Development:...
. Were originally deployed in Normandy, but withdrawn as unnecessary due to Allied air superiority. 95 were produced.
Centaur, AA Mk II: Used a Crusader III, AA Mk III turret with twin 20 mm Polsten AA guns
Polsten
The Polsten was a low cost Polish development of the 20 mm Oerlikon gun. The Polsten was designed to be simpler and much cheaper to build than the Oerlikon without reducing effectiveness.-Development:...
.
Cromwell I: Exactly the same as the Centaur I, but using the Meteor engine. Only 357 produced due to the switch from the 6 pounder (57 mm) to the 75 mm gun.

Cromwell III: Centaur I upgraded with Meteor V12 engine. Only ~ 200 produced due to scarcity of Centaur I's.
Cromwell IV: Centaur I or III upgraded with Meteor engine, or built as such. The most numerous variant with over 1,935 units produced.
Cromwell IVw: Meteor engine, and all welded hull.
Cromwell Vw: Cromwell built from the start with the 75 mm gun and a welded instead of riveted hull.
Cromwell VI: Cromwell armed with 95 mm howitzer. 341 produced.
Cromwell VII: Cromwell IV and V upgraded with additional armour (101 mm to front), wider (15.5 inch) tracks, and additional gearbox. These were introduced very late in the war and did not see much in the way of combat. ~ 1,500 produced.
Cromwell VIIw: Cromwell Vw reworked to Cromwell VII standard, or built as new to that standard
Cromwell VIII: Cromwell VI reworked with same upgrades as VII.
Vehicles based on chassis

Cruiser Mk VIII Challenger
The Tank, Cruiser, Challenger was a British tank of World War II. It mounted the 17 Pounder gun on the Cromwell chassis to add heavier anti-tank firepower to the cruiser tank units....
:The design combined lengthened Cromwell chassis and the 17-pounder
Ordnance QF 17 pounder
The Ordnance Quick-Firing 17 pounder was a 76.2 mm gun developed by the United Kingdom during World War II. It was used as an anti-tank gun on its own carriage, as well as equipping a number of British tanks. It was the most effective Allied anti-tank gun of the war...
gun in a new turret.
SP 17pdr, A30 (Avenger): A version of the Challenger using a lighter open-topped turret.
Centaur Dozer: A Centaur with the turret removed and given a simple dozer blade operated by a winch. Since the winch passed over the top of the hull it was not possible to retain the turret. One of Hobart's Funnies
Hobart's Funnies
Hobart's Funnies were a number of unusually modified tanks operated during World War II by the United Kingdom's 79th Armoured Division or by specialists from the Royal Engineers. They were designed in light of problems that more standard tanks experienced during the Dieppe Raid, so that the new...
. 250 produced. (version pictured uses hydraulic controls)
Centaur Observation Post (OP): A Centaur with a dummy main gun, and extra radio telecommunications.
Centaur Kangaroo: A Centaur with turret removed to make space for passengers. (Few produced)
Centaur Armoured Recovery Vehicle
Armoured recovery vehicle
An armoured recovery vehicle is a type of armoured fighting vehicle used to repair battle- or mine-damaged as well as broken-down armoured vehicles during combat, or to tow them out of the danger zone for more extensive repairs...
(ARV): A Centaur with turret removed, and replaced with winch
Winch
A winch is a mechanical device that is used to pull in or let out or otherwise adjust the "tension" of a rope or wire rope . In its simplest form it consists of a spool and attached hand crank. In larger forms, winches stand at the heart of machines as diverse as tow trucks, steam shovels and...
fitted instead, and an optional A-frame
A-Frame
An A-frame is a basic structure designed to bear a load in a lightweight economical manner. The simplest form of an A-frame is two similarly sized beams, arranged in a 45-degree or greater angle, attached at the top...
.
Cromwell Command
- The main gun was removed and it carried one No. 19 (Low Power) and one No. 19 (High Power) Wireless sets. These were used by brigade and divisional headquarters.
Cromwell Observation Post
- Cromwell IV, Cromwell VI, or Cromwell VIII fitted with extra radio equipment; 2 x No. 19 and 2 x No. 38 (portable) radios. The main gun was retained.
Cromwell Control
- Two No. 19 Low Power radio. Main armament kept. Used by regimental headquarters
Excelsior tank: experimental design with elements of Infantry tank
Infantry tank
The infantry tank was a concept developed by the British and French in the years leading up to World War II. Infantry tanks were tanks designed to support the infantry in the attack. To achieve this they were generally heavily armoured compared to the cruiser tanks, to allow them to operate in...
as a possible replacement for Churchill tank
Churchill tank
The Tank, Infantry, Mk IV was a heavy British infantry tank used in the Second World War, best known for its heavy armour, large longitudinal chassis with all-around tracks with multiple bogies, and its use as the basis of many specialist vehicles. It was one of the heaviest Allied tanks of the war...
FV 4101 Charioteer: Cromwell hull with a QF 20 pounder gun
Ordnance QF 20 pounder
The Ordnance QF 20 pounder was a British 84 mm tank gun introduced in 1948 and used in the Centurion tank and the Charioteer tank destroyer...
in a tall turret, designed in the 1950s. 200 produced.
Surviving vehicles
Around 40 Centaur and Cromwell tanks survive, ranging from scrapyard wrecks to fully restored museum vehicles. At least two, one owned by the Czech Republic Army Technical Museum at LešanyLešany (Prostějov District)
Lešany is a village and municipality in Prostějov District in the Olomouc Region of the Czech Republic.The municipality covers an area of , and has a population of 383 ....
and one owned by the Cobbaton Combat Collection in the United Kingdom, are in running condition.
Other examples include:
- Bovington Tank MuseumBovington Tank MuseumThe Tank Museum is a collection of armoured fighting vehicles in the United Kingdom that traces the history of the tank. With almost 300 vehicles on exhibition from 26 countries it is the second-largest collection of tanks and armoured fighting vehicles in the world.The Musée des Blindés in France...
, DorsetDorsetDorset , is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The county town is Dorchester which is situated in the south. The Hampshire towns of Bournemouth and Christchurch joined the county with the reorganisation of local government in 1974...
, England. Well preserved Cromwell IV displayed in interior location accessible to public on payment of entry fee to museum. - Thetford ForestThetford ForestThetford Forest is the largest lowland pine forest in Britain, Thetford Forest Park is located in a region straddling the north of Suffolk and the south of Norfolk in England...
, NorfolkNorfolkNorfolk is a low-lying county in the East of England. It has borders with Lincolnshire to the west, Cambridgeshire to the west and southwest and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the North Sea coast and to the north-west the county is bordered by The Wash. The county...
, England. Cromwell IV in outside location freely accessible to public. This tank is located on the A1065 two miles north of MundfordMundfordMundford is a village and civil parish in the English county of Norfolk. It is situated at the intersection of two major routes, the A134 Colchester to King's Lynn road and the A1065 Mildenhall to Fakenham road, about north west of Thetford...
. Between January and May 1944 the area was occupied by armoured regiments of the 7th Armoured Division (Desert Rats) prior to their embarking for Normandy. The tank forms part of a 1998 memorial to the Division. It is in good display condition having been refurbished and painted as a replica of the tank Little Audrey of 1st Royal Tank Regiment1st Royal Tank RegimentThe 1st Royal Tank Regiment is an armoured regiment of the British Army. It is part of the Royal Tank Regiment, itself part of the Royal Armoured Corps. It was originally formed as 1st Battalion, Royal Tank Corps in 1934....
. - The Royal Australian Armoured Corps Army Tank Museum, Puckapunyal, Victoria. Cromwell MkI shipped to AustraliaAustraliaAustralia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
to assist with the up gunning of the Australian Cruiser tanksSentinel tankThe Sentinel tank was a cruiser tank designed in Australia in World War II in response to the war in Europe, and to the threat of Japan expanding the war to the Pacific or even a feared Japanese invasion of Australia. It was the first tank to be built with a hull cast as a single piece, and the...
but did not arrive before that programme had been terminated. Repainted with the markings it arrived in Australia with, it is now under cover on display at the museum. - The Israeli Armored Corps Museum in LatrunLatrunLatrun is a strategic hilltop in the Ayalon Valley in Israel overlooking the road to Jerusalem. It is located 25 kilometers west of Jerusalem and 14 kilometers southeast of Ramla.-Etymology:...
. Cromwell IV tank, that was used by the IDFIsrael Defense ForcesThe Israel Defense Forces , commonly known in Israel by the Hebrew acronym Tzahal , are the military forces of the State of Israel. They consist of the ground forces, air force and navy. It is the sole military wing of the Israeli security forces, and has no civilian jurisdiction within Israel...
in War of Independence (1948–1949). - The Liberty Park in OverloonOverloonOverloon, mun. Boxmeer, is a village in the Netherlands in the province of North Brabant. It is best known as the site of the National Museum of War and Resistance of the Netherlands, and for a World War II battle that occurred around the village in September and October 1944.As a result most of...
, The Netherlands. Cromwell IV tank, that remained on the battlefield after Operation Aintree during the Battle for Overloon in October 1944 in which the 11th Armoured Division was involved. This tank is on display in the museum, accessible to the public on payment of entry fee to museum. - The Tank Museum Museum, Greek Army Armored Training Center , Avlona, near Athens, Greece. Centaur I (A27L) tank. The Greek Army received 52 Centaur I tanks from the British in 1946.
- Centaur tanks have been discovered in a good state of preservation in the SolentSolentThe Solent is a strait separating the Isle of Wight from the mainland of England.The Solent is a major shipping route for passengers, freight and military vessels. It is an important recreational area for water sports, particularly yachting, hosting the Cowes Week sailing event annually...
, but are unlikely to be recovered.
There are two surviving Centaur IV CS in Normandy, at Benouville near Pegasus Bridge
Pegasus Bridge
Pegasus Bridge is a bascule bridge , built in 1934, that crossed the Caen Canal, between Caen and Ouistreham, in Normandy, France....
and at La Brèche d’Hermanville
Hermanville-sur-Mer
Hermanville-sur-Mer is a commune in the Calvados department in the Basse-Normandie region in northwestern France.-Population:-Sights:* 13th century church* Commonwealth war cemetery* Old village center...
External links
- OnWar specifications: Cromwell I, Cromwell IV

