
Curie constant
Encyclopedia
The Curie constant is a material-dependent property that relates a material's magnetic susceptibility
to its temperature.
Curie's constant in SI units is

where is the permeability constant,
is the permeability constant,  is the number of magnetic atoms (or molecules) per unit volume,
is the number of magnetic atoms (or molecules) per unit volume, 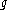 is the Landé g-factor
is the Landé g-factor
,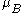 (9.27400915e-24 J/T or A·m2) is the Bohr magneton,
(9.27400915e-24 J/T or A·m2) is the Bohr magneton,  is the angular momentum
is the angular momentum
quantum number and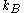 is Boltzmann's constant. For a two level system with magnetic moment
is Boltzmann's constant. For a two level system with magnetic moment  , the formula reduces to
, the formula reduces to
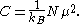
The constant is used in Curie's Law
, which states that for a fixed value of a magnetic field, the magnetization of a material is (approximately) inversely proportional to temperature.
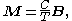
This equation was first derived by Pierre Curie
(Marie Curie's husband).
Because of the relationship between magnetic susceptibility
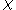 , magnetization
, magnetization 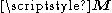 and applied magnetic field
and applied magnetic field 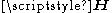 :
:

this shows that for a paramagnetic system of non-interacting magnetic moments, magnetization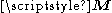 is inversely related to temperature
is inversely related to temperature 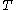 (see Curie's Law
(see Curie's Law
).
Magnetic susceptibility
In electromagnetism, the magnetic susceptibility \chi_m is a dimensionless proportionality constant that indicates the degree of magnetization of a material in response to an applied magnetic field...
to its temperature.
Curie's constant in SI units is

where
 is the permeability constant,
is the permeability constant,  is the number of magnetic atoms (or molecules) per unit volume,
is the number of magnetic atoms (or molecules) per unit volume, 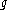 is the Landé g-factor
is the Landé g-factorLandé g-factor
In physics, the Landé g-factor is a particular example of a g-factor, namely for an electron with both spin and orbital angular momenta. It is named after Alfred Landé, who first described it in 1921....
,
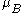 (9.27400915e-24 J/T or A·m2) is the Bohr magneton,
(9.27400915e-24 J/T or A·m2) is the Bohr magneton,  is the angular momentum
is the angular momentumAngular momentum
In physics, angular momentum, moment of momentum, or rotational momentum is a conserved vector quantity that can be used to describe the overall state of a physical system...
quantum number and
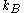 is Boltzmann's constant. For a two level system with magnetic moment
is Boltzmann's constant. For a two level system with magnetic moment  , the formula reduces to
, the formula reduces to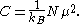
The constant is used in Curie's Law
Curie's law
In a paramagnetic material the magnetization of the material is directly proportional to an applied magnetic field. However, if the material is heated, this proportionality is reduced: for a fixed value of the field, the magnetization is inversely proportional to temperature...
, which states that for a fixed value of a magnetic field, the magnetization of a material is (approximately) inversely proportional to temperature.
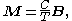
This equation was first derived by Pierre Curie
Pierre Curie
Pierre Curie was a French physicist, a pioneer in crystallography, magnetism, piezoelectricity and radioactivity, and Nobel laureate. He was the son of Dr. Eugène Curie and Sophie-Claire Depouilly Curie ...
(Marie Curie's husband).
Because of the relationship between magnetic susceptibility
Magnetic susceptibility
In electromagnetism, the magnetic susceptibility \chi_m is a dimensionless proportionality constant that indicates the degree of magnetization of a material in response to an applied magnetic field...
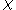 , magnetization
, magnetization 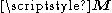 and applied magnetic field
and applied magnetic field 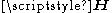 :
:
this shows that for a paramagnetic system of non-interacting magnetic moments, magnetization
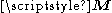 is inversely related to temperature
is inversely related to temperature 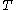 (see Curie's Law
(see Curie's LawCurie's law
In a paramagnetic material the magnetization of the material is directly proportional to an applied magnetic field. However, if the material is heated, this proportionality is reduced: for a fixed value of the field, the magnetization is inversely proportional to temperature...
).

