
Cyclododecahexaene
Encyclopedia
Cyclododecahexaene or [12]annulene (C12H12) is a member of a series of annulene
s with some interest in organic chemistry
with regard to the study of aromaticity
These compounds are in general unstable due to their antiaromaticity
and built-up of steric strain. On the other hand the di-anion with 14 electrons is a Hückel aromat
and more stable.
According to in silico
experiments the tri-trans isomer is expected to be the most stable, followed by the 1,7-ditrans and the all cis-isomers (+1 kcal/mol) and by the 1,5-ditrans isomer (+5 kcal/mol).
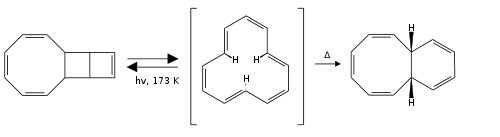
The first [12]annulene with sym-tri-trans configuration was synthesized in 1970 from a tricyclic precursor by photolysis at low temperatures. On heating the compound rearranges to a bicyclic [6,4,0] isomer. Reducing the compound at low temperatures allowed analysis of the dianion by proton NMR
with the inner protons resonating at - 4.5 ppm relative to TMS, evidence of an aromatic diamagnetic ring current.
 In one study the 1,7-ditrans isomer is generated at low temperatures in THF
In one study the 1,7-ditrans isomer is generated at low temperatures in THF
by dehydrohalogenation
of a hexabromocyclododecane with potassium tert-butoxide
. Reduction of this compound at low temperature with caesium
metal leads first to the radical anion and then to the dianion. The chemical shift
for the internal protons in this compound is with +0.2 ppm much more modest than in the tri-trans isomer.
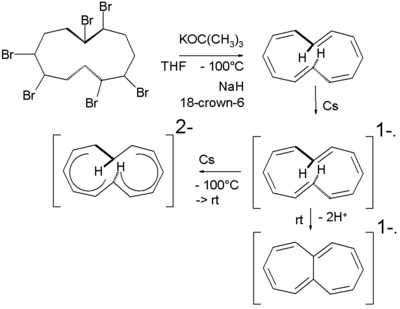 Heating the radical ion solution to room temperature
Heating the radical ion solution to room temperature
leads to loss of one equivalent of hydrogen and formation of the heptalene
radical anion.
Annulene
Annulenes are completely conjugated monocyclic hydrocarbons. They have the general formula CnHn or CnHn+1...
s with some interest in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
with regard to the study of aromaticity
Aromaticity
In organic chemistry, Aromaticity is a chemical property in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibit a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August...
These compounds are in general unstable due to their antiaromaticity
Antiaromaticity
Antiaromatic molecules are cyclic systems containing alternating single and double bonds, where the pi electron energy of antiaromatic compounds is higher than that of its open-chain counterpart. Therefore antiaromatic compounds are unstable and highly reactive; often antiaromatic compounds...
and built-up of steric strain. On the other hand the di-anion with 14 electrons is a Hückel aromat
Hückel's rule
In organic chemistry, Hückel's rule estimates whether a planar ring molecule will have aromatic properties. The quantum mechanical basis for its formulation was first worked out by physical chemist Erich Hückel in 1931...
and more stable.
According to in silico
In silico
In silico is an expression used to mean "performed on computer or via computer simulation." The phrase was coined in 1989 as an analogy to the Latin phrases in vivo and in vitro which are commonly used in biology and refer to experiments done in living organisms and outside of living organisms,...
experiments the tri-trans isomer is expected to be the most stable, followed by the 1,7-ditrans and the all cis-isomers (+1 kcal/mol) and by the 1,5-ditrans isomer (+5 kcal/mol).
The first [12]annulene with sym-tri-trans configuration was synthesized in 1970 from a tricyclic precursor by photolysis at low temperatures. On heating the compound rearranges to a bicyclic [6,4,0] isomer. Reducing the compound at low temperatures allowed analysis of the dianion by proton NMR
Proton NMR
Proton NMR is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance in NMR spectroscopy with respect to hydrogen-1 nuclei within the molecules of a substance, in order to determine the structure of its molecules. In samples where natural hydrogen is used, practically all of the hydrogen consists of the...
with the inner protons resonating at - 4.5 ppm relative to TMS, evidence of an aromatic diamagnetic ring current.

Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity at standard temperature and pressure. This heterocyclic compound has the chemical formula 4O. As one of the most polar ethers with a wide liquid range, it is a useful solvent. Its main use, however, is as a precursor...
by dehydrohalogenation
Dehydrohalogenation
Dehydrohalogenation is an organic reaction from which an alkene is obtained from an alkyl halide . It is also called a β-Elimination reaction and is a type of elimination reaction....
of a hexabromocyclododecane with potassium tert-butoxide
Potassium tert-butoxide
Potassium tert-butoxide is the chemical compound with the formula 3COK. This colourless solid is a strong base useful in organic synthesis. It exists as a tetrameric cubane-like cluster...
. Reduction of this compound at low temperature with caesium
Caesium
Caesium or cesium is the chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-gold alkali metal with a melting point of 28 °C , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at room temperature...
metal leads first to the radical anion and then to the dianion. The chemical shift
Chemical shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of a nucleus relative to a standard. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule...
for the internal protons in this compound is with +0.2 ppm much more modest than in the tri-trans isomer.

Room temperature
-Comfort levels:The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers has listings for suggested temperatures and air flow rates in different types of buildings and different environmental circumstances. For example, a single office in a building has an occupancy ratio per...
leads to loss of one equivalent of hydrogen and formation of the heptalene
Heptalene
Heptalene is a polycyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C12H10, composed of two fused cycloheptatriene rings....
radical anion.

