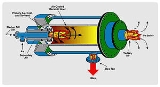
Cyclone furnace
Overview
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
combustor
Combustor
A combustor is a component or area of a gas turbine, ramjet, or scramjet engine where combustion takes place. It is also known as a burner, combustion chamber or flame holder. In a gas turbine engine, the combustor or combustion chamber is fed high pressure air by the compression system. The...
commonly used in large industrial boilers.
Developed in the early 1942 by Babcock & Wilcox
Babcock and Wilcox
The Babcock & Wilcox Company is a U.S.-based company that provides design, engineering, manufacturing, construction and facilities management services to nuclear, renewable, fossil power, industrial and government customers worldwide. B&W's boilers supply more than 300,000 megawatts of installed...
to take advantage of coal grades not suitable for pulverized coal combustion
Pulverized coal-fired boiler
A pulverized coal-fired boiler is an industrial or utility boiler that generates thermal energy by burning pulverized coal that is blown into the firebox....
, cyclone furnaces feed coal in a spiral manner into a combustion chamber for maximum combustion efficiency.
During coal combustion in a furnace, volatile
Volatility (chemistry)
In chemistry and physics, volatility is the tendency of a substance to vaporize. Volatility is directly related to a substance's vapor pressure. At a given temperature, a substance with higher vapor pressure vaporizes more readily than a substance with a lower vapor pressure.The term is primarily...
components burn without much difficulty. Fuel carbon “char” particles (heavier, less volatile coal constituents) require much higher temperatures and a continuing supply of oxygen.
Unanswered Questions

